 W
WThe history of the Jews in Spain stretches back to Biblical times according to Jewish history. Spanish Jews once constituted one of the largest and most prosperous Jewish communities in the world. Spain was the unquestioned leader of world Jewry: scientific and philological study of the Hebrew Bible began, secular poetry was written in Hebrew for the first time, and for the only time between Biblical times and the origins of the modern state of Israel, a Jew commanded a Jewish army. This period ended definitively with the anti-Jewish riots of 1391 and the Alhambra Decree of 1492, as a result of which the majority of Jews in Spain converted to Catholicism and those who continued to practice Judaism were forced into exile, although many thousands returned in the years following the expulsion.
 W
WThe Alba Bible is a 1430 illuminated manuscript translation of the Old Testament made directly from Hebrew into Mediaeval Castilian. The translation was carried out under the direction of Moses Arragel, rabbi of the Jewish community of Maqueda in the Spanish province of Toledo, at the behest of Don Luis de Guzmán, Grand Master of the military-religious Order of Calatrava.
 W
WAlcalá de Guadaíra is a town located approximately 17 km southeast of Seville, Spain; in recent years the expansion of Seville has meant that Alcalá has become a suburb of that city. Alcalá used to be known as Alcalá de los Panaderos because it provided most of Seville's bread. The town is located on the banks of the Guadaíra River, and watermills built during the Moorish period of Spain can still be found in the area.
 W
WAlcalá de Henares is a Spanish city in the Community of Madrid. Straddling the Henares River, it is located 35 kilometres to the northeast of the centre of Madrid. As of 2018, it has a population of 193,751, making it the region's third-most populated municipality.
 W
WAlcañiz is a town and municipality of Teruel province in the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain. The town is located on the banks of the river Guadalope. Alcañiz is the unofficial capital of the Lower Aragon historical region. It lies some 113 km from Teruel, the provincial capital, and 92 km from Zaragoza, the capital of Aragon.
 W
WThe Alhambra Decree was an edict issued on 31 March 1492, by the joint Catholic Monarchs of Spain ordering the expulsion of practicing Jews from the Crowns of Castile and Aragon and its territories and possessions by 31 July of that year. The primary purpose was to eliminate their influence on Spain's large converso population and ensure they did not revert to Judaism. Over half of Spain's Jews had converted as a result of the religious persecution and pogroms which occurred in 1391. Due to continuing attacks, around 50,000 more had converted by 1415. A further number of those remaining chose to convert to avoid expulsion. As a result of the Alhambra decree and persecution in prior years, over 200,000 Jews converted to Catholicism and between 40,000 and 100,000 were expelled, an unknown number returning to Spain in the years following the expulsion.:17
 W
WAn auto-da-fé was the ritual of public penance carried out between the 15th and 19th centuries of condemned heretics and apostates imposed by the Spanish, Portuguese, or Mexican Inquisition as punishment and enforced by civil authorities. Its most extreme form was death by burning.
 W
WLope de Barrientos (1382–1469), sometimes called Obispo Barrientos, was a powerful clergyman and statesman of the Crown of Castile during the 15th century, although his prominence and the influence he wielded during his lifetime is not a subject of common study in Spanish history.
 W
WSusana Ben Susón, nicknamed La Susona, was a young Jewish convert from Seville and features in a legend. She was the daughter of don Diego Susón a Jewish convert.
 W
WA converso, "convert", was a Jew who converted to Catholicism in Spain or Portugal, particularly during the 14th and 15th centuries, or one of his or her descendants.
 W
WIn the Iberian peninsula, the crown rabbi was a secular, administrative post occupied by a member of the Jewish community for the benefit of the governing state, and existed in the kingdoms of Castile, Aragon, Navarre and Portugal as far back as the 13th century, and is referred to as crown rabbi by historians in English, as well as by court rabbi and other terms.
 W
WCrypto-Judaism is the secret adherence to Judaism while publicly professing to be of another faith; practitioners are referred to as "crypto-Jews".
 W
WThe Disputation of Tortosa was one of the famous ordered disputations between Christians and Jews of the Middle Ages, held in the years 1413–1414 in the city of Tortosa, Catalonia, Crown of Aragon. According to the Jewish Encyclopedia it was not a free and authentic debate, but was an attempt by Christians to force conversion on the Jews.
 W
WThe Ferrara Bible was a 1553 publication of the Ladino version of the Tanakh used by Sephardi Jews. It was paid for and made by Yom-Tob ben Levi Athias and Abraham ben Salomon Usque, and was dedicated to Ercole II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara. Ercole's wife Renée of France was a Protestant, daughter of Louis XII of France.
 W
WGibraltar is a British Overseas Territory located at the southern tip of the Iberian Peninsula. It has an area of 6.7 km2 (2.6 sq mi) and is bordered to the north by Spain. The landscape is dominated by the Rock of Gibraltar at the foot of which is a densely populated town area, home to over 32,000 people, primarily Gibraltarians.
 W
WIsrael and Spain have maintained diplomatic ties since 1986. Israel has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Tel Aviv, an honorary consulate in Haifa and a General Consulate in Jerusalem, which is regarded as diplomatic missions to the city of Jerusalem, Gaza and the territories of the West Bank. In additions to both countries being member states of the United Nations, both countries are members of the Union for the Mediterranean. The two countries are also involved with various programmes and agreements through the European Union, of which Spain is a member, and its relations with Israel.
 W
WMarranos were Spanish and Portuguese Jews living in the Iberian Peninsula who converted or were forced to convert to Christianity during the Middle Ages, yet continued to practice Judaism in secret.
 W
WAlso known as The pogroms of 1391, the Massacre of 1391 was a display of antisemitism and violence against Jews in Spain. It was one of the Middle Ages' largest attacks on the Jews, who were ultimately given the choice of converting or leaving Spain in 1492. While the Jews in the Iberian Peninsula at this time were generally disliked, violence against the Jews was common even until the 1400s. However, 1391 marked a peak in the violence against the Jews.
 W
WThe Black Death persecutions and massacres were a series of violent attacks on Jewish communities falsely blamed for outbreaks of the Black Death in Europe from 1348 to 1351.
 W
WFrom about 1590 on, there had been a Portuguese Jewish community in Hamburg, whose qehilla existed until its compulsory merger with the Ashkenazi congregation in July 1939. The first Sephardic settlers were Portuguese Marranos, who had fled their country under Philip II and Philip III, at first concealing their religion in their new place of residence. Many of them had emigrated from Spain in the belief that they had found refuge in Portugal.
 W
WThe Reconquista was a period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula of about 780 years between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711, the expansion of the Christian kingdoms throughout Hispania, and the fall of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada in 1492.
 W
WSagunto Castle is a fortress overlooking the town of Sagunto, near Valencia in Spain. The site's history extends back over two thousand years and includes Iberian, Roman and medieval remains. During the Islamic period, the castle was known as Murbĩtar and Morvedre. The castle was declared a National Monument in 1931.
 W
WSephardic law and customs are the practice of Judaism by the Sephardim, the descendants of the historic Jewish community of the Iberian Peninsula. Some definitions of "Sephardic" also include Mizrahi Jews, many of whom follow the same traditions of worship but have different ethno-cultural traditions. Sephardi Rite is not a denomination or movement like Orthodox, Reform, and other Ashkenazi Rite worship traditions. Sephardim thus comprise a community with distinct cultural, juridical and philosophical traditions.
 W
WShem Tob's Hebrew Gospel of Matthew is the oldest extant Hebrew version of the Gospel of Matthew. It was included in the 14th-century work Eben Boḥan by the Spanish Jewish Rabbi Shem-Tov ben Isaac ben Shaprut. George Howard has argued that Shem Tov's Matthew comes from a much earlier Hebrew text that was later translated into Greek and other languages. A characteristic feature of this Hebrew gospel is the appearance in 20 places of השם, in the abbreviated form ה״, where the Gospel of Matthew has Κύριος.
 W
WSos del Rey Católico is a historic town and municipality in the Cinco Villas comarca, province of Zaragoza, in Aragon, Spain.
 W
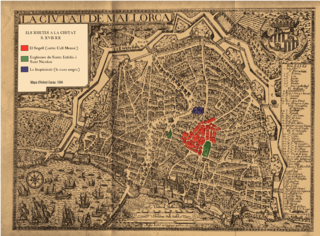
WThe Xuetes are a social group on the Spanish island of Majorca, in the Mediterranean Sea, who are descendants of Majorcan Jews that either were conversos or were Crypto-Jews, forced to keep their religion hidden. They practiced strict endogamy by marrying only within their own group. Many of their descendants observe a syncretist form of Christian worship known as Xueta Christianity.