 W
WThe Abbasid Caliphate was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib, from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Sasanian capital city of Ctesiphon. The Abbasid period was marked by reliance on Persian bureaucrats for governing the territories as well as an increasing inclusion of non-Arab Muslims in the ummah. Persian customs were broadly adopted by the ruling elite, and they began patronage of artists and scholars. Baghdad became a center of science, culture, philosophy and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam.
 W
WThe Alchon Huns, also known as the Alchono, Alxon, Alkhon, Alkhan, Alakhana and Walxon, were a nomadic people who established states in Central Asia and South Asia during the 4th and 6th centuries CE. They were first mentioned as being located in Paropamisus, and later expanded south-east, into the Punjab and central India, as far as Eran and Kausambi. The Alchon invasion of the Indian subcontinent eradicated the Kidarite Huns who had preceded them by about a century, and contributed to the fall of the Gupta Empire, in a sense bringing an end to Classical India.
 W
WThe First Republic of Armenia, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Armenia, was the first modern Armenian state since the loss of Armenian statehood in the Middle Ages.
 W
WThe timeline of the Assyrian Empire
 W
WThe Central Powers, also Central Empires, was one of the two main coalitions that fought World War I (1914–18). It consisted of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire and Bulgaria; hence it is also known as the Quadruple Alliance.
 W
WThe Emirate of Diriyah, also transliterated as the Emirate of Dir'iyah, and known as the First Saudi State, was established in the year 1744 when Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab and Prince Muhammad bin Saud formed an alliance to found a socio-religious reform movement to unify the many states of the Arabian Peninsula. In 1744, both Muhammed bin Abd Al Wahhab and Muhammad bin Saud took an oath to achieve their goal.
 W
WEast Pakistan was the eastern provincial wing of Pakistan between 1947 and 1971, covering the territory of the modern country Bangladesh. Its land borders were with India and Burma, with a coastline on the Bay of Bengal. East Pakistanis were popularly known as "Pakistani Bengalis"; to distinguish this region from the India's state West Bengal, East Pakistan was known as "Pakistani Bengal".
 W
WThe Fatimid Caliphate, an Ismaili Shia caliphate of the 10th to the 12th centuries AD, spanned a large area of North Africa, from the Red Sea in the east to the Atlantic Ocean in the west. The Fatimid dynasty, of Arab origin, ruled territories across the Mediterranean coast of Africa and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height the caliphate included - in addition to Egypt - varying areas of the Maghreb, Sudan, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hijaz.
 W
WFree Dadra and Nagar Haveli was a de-facto state that existed in the Indian Sub-continent between 1954 and 1961. It was declared by pro-India forces that had gained control of the region from Portugal in 1954 and ceased to exist after being formally annexed by India on 11 August 1961 as the Union Territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli.
 W
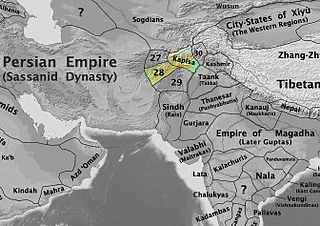
WGuzgan is the name of a historical region and early medieval principality in what is now northern Afghanistan.
 W
WThe Sultanate of Jambi was a region ruled by a sultan in northern Sumatra. The Dutch conquered the sultanate and killed the sultan in 1904. The sultanate has since been restored in recent years. The original sultanate was centered in the modern-day province of Jambi in Indonesia.
 W
WThe Kazakh Khanate, was a successor of the Golden Horde existing from the 15th to 19th century, located roughly on the territory of the present-day Republic of Kazakhstan. From 16th to 17th century, the khanate ruled and expanded its territories to eastern Cumania, to most of Uzbekistan, Karakalpakstan and the Syr Darya river with military confrontation as far as Astrakhan and Khorasan Province, which are now in Russia and Iran, respectively. The Kazakhs invaded the Khanate of Bukhara and occupied several Uzbek cities such Bukhara, Samarkand. The Khanate also engaged in slavery and raids in its neighboring countries of Russia and Central Asia, and was later weakened by a series of Oirat and Dzungar invasions. These resulted in a decline and further disintegration into three Jüz-es, which gradually lost their sovereignty and were incorporated to the expanding Russian Empire. Its establishment marked the beginning of Kazakh statehood whose 550th anniversary was celebrated in 2015.
 W
WKhwarazm, or Chorasmia, is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the east by the Kyzylkum desert, on the south by the Karakum desert, and on the west by the Ustyurt Plateau. It was the center of the Iranian Khwarazmian civilization, and a series of kingdoms such as the Khwarazmian dynasty and the Afrighid dynasty, whose capitals were Kath, Gurganj and – from the 16th century on – Khiva. Today Khwarazm belongs partly to Uzbekistan and partly to Turkmenistan.
 W
WThe Second Kingdom of Kakheti was a late medieval/early modern monarchy in eastern Georgia, centered at the province of Kakheti, with its capital first at Gremi and then at Telavi. It emerged in the process of a tripartite division of the Kingdom of Georgia in 1465 and existed, with several brief intermissions, until 1762 when Kakheti and the neighboring Georgian kingdom of Kartli were merged through a dynastic succession under the Kakhetian branch of the Bagrationi dynasty. Through most of its turbulent history, Kakheti was tributary to the Persians, whose efforts to keep the reluctant Georgian kingdom within its sphere of influence resulted in a series of military conflicts and deportations.
 W
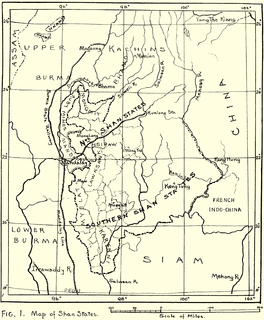
WThe Kingdom of Pong or Pong Kingdom was an ethnically Tai state that controlled several smaller states along the frontier of what is now Myanmar and Assam.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Rob was a small kingdom in Central Asia, in southern Bactria. It corresponds to the modern Rui in the Province of Samangan, modern Afghanistan. Numerous documents in the Bactrian language in the Bactrian script have been found from the archives of the Kingdom of Rob.
 W
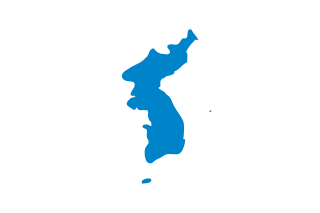
WKorea is a region in East Asia. Since 1945 it has been divided into two sovereign states: North Korea and South Korea. Korea consists of the mainland Korea, Jeju Island, and several minor islands near the peninsula. It is bordered by China to the northwest and Russia to the northeast. It is separated from Japan to the east by the Korea Strait and the Sea of Japan.
 W
WLâm Ấp was a Cham kingdom located in central Vietnam that existed from around 192 CE to 629 CE in what is today central Vietnam. and was one of the earliest recorded Champa kingdoms. The ruins of its capital, the ancient city of Kandapurpura is now located in Long Tho Hill, 3 kilometers to the west of the city of Huế.
 W
WMong Mao, Möngmao or Mao kingdom was an ethnically Dai state that controlled several smaller Tai states or chieftainships along the frontier of what is now Myanmar, China, the states of Northeast India of Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh, principally set in the Dehong region of Yunnan with a capital near the modern-day border town of Ruili. The name of the main river in this region is the Nam Mao, also known as the Shweli River.
 W
WThe Nezak Huns were one of the four groups of Huna people in the area of the Hindu Kush. The Nezak kings, with their characteristic gold bull's-head crown, ruled from Ghazni and Kapisa. While their history is obscured, the Nezak's left significant coinage documenting their polity's prosperity. They are called Nezak because of the inscriptions on their coins, which often bear the mention "Nezak Shah". They were the last of the four major "Hunic" states known collectively as Xionites or "Hunas", their predecessors being, in chronological order, the Kidarites, the Hephthalites, and the Alchon.
 W
WThe Parthian Empire, also known as the Arsacid Empire, was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquering the region of Parthia in Iran's northeast, then a satrapy (province) under Andragoras, in rebellion against the Seleucid Empire. Mithridates I (r. c. 171–132 BC) greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce.
 W
WPratapgarh was a medieval kingdom in the north-east of the Indian subcontinent. Composed of the present-day Indian district of Karimganj as well as parts of Tripura State and Sylhet, Bangladesh, the kingdom was ruled by a line of Muslim monarchs over a mixed population of Hindu and Islamic adherents. It was bordered by the larger kingdoms of Kachar, Tripura and Bengal.
 W
WThe Provisional Military Dictatorship of Mughan was a British-controlled anti-communist short-lived state founded in the Lankaran region on August 1, 1918. The Mughan government did not support independence of Azerbaijan and it was led by white Russian colonel T. P. Sukhorukov who acted under the protection of the British occupation of Baku. Mughan declared to be an autonomous part of "single and indivisible Russia." On December 1918, it was reorganized as Mughan Territorial Administration. On April 25, 1919, a violent protest organized by Talysh workers of pro-Bolshevik orientation exploded in Lankaran and deposed the Mughan Territorial Administration. On May 15, the Extraordinary Congress of the "Councils of Workers' and Peasants' Deputies" of Lankaran district proclaimed the Mughan Soviet Republic.
 W
WThe People's Committee of North Korea was a provisional government governing the northern portion of the Korean Peninsula from 1947 until 1948.
 W
WThe Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, Northern Africa, and Western Asia ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a principate with Italy as metropole of the provinces and the city of Rome as sole capital. After the military crisis, the empire was ruled by multiple emperors who shared rule over the Western Roman Empire and over the Eastern Roman Empire. Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until 476 AD, when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople, following the capture of Ravenna by the barbarians of Odoacer and the subsequent deposition of Romulus Augustulus. The fall of the Western Roman Empire to Germanic kings, along with the hellenization of the Eastern Roman Empire into the Byzantine Empire, conventionally marks the end of Ancient Rome and the beginning of the Middle Ages.
 W
WThe Russian Empire was a historical empire that extended across Eurasia and North America from 1721, following the end of the Great Northern War, until the Republic was proclaimed by the Provisional Government that took power after the February Revolution of 1917. The third-largest empire in history, at its greatest extent stretching over three continents, Europe, Asia, and North America, the Russian Empire was surpassed in size only by the British and Mongol empires, leaving the empire lasting 196 years. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighboring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Persia and the Ottoman Empire. It played a major role in 1812–1814 in defeating Napoleon's ambitions to control Europe and expanded to the west and south, becoming one of the most powerful European empires of all time.
 W
WThe Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, previously known as the Russian Soviet Republic and the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic as well as being unofficially known as Soviet Russia, Russian Federation or simply Russia, was an independent socialist state from 1917 to 1922, and afterwards the largest and most populous of the Soviet socialist republics of the Soviet Union (USSR) from 1922 to 1991, until becoming a sovereign part of the Soviet Union with priority of Russian laws over Union-level legislation in 1990 and 1991, the last two years of the existence of the USSR. The Russian Republic was composed of sixteen smaller constituent units of autonomous republics, five autonomous oblasts, ten autonomous okrugs, six krais and forty oblasts. Russians formed the largest ethnic group. The capital of the Russian SFSR was Moscow and the other major urban centers included Leningrad, Novosibirsk, Sverdlovsk, Gorky and Kuybishev.
 W
WThe Samtskhe-Saatabago or Samtskhe Atabegate, also called the Principality of Samtskhe, was a Georgian feudal principality in Zemo Kartli, ruled by an atabeg (tutor) of Georgia for nearly three and a half centuries, between 1268 and 1625. Its territory consisted of the modern-day Samtskhe-Javakheti region and the historical region of Tao-Klarjeti.
 W
WThe Sikh Empire was a state originating in the Indian subcontinent, formed under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh, who established a secular empire based in the Punjab. The empire existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849 and was forged on the foundations of the Khalsa from a collection of autonomous Sikh misls. At its peak in the 19th century, the Empire extended from the Khyber Pass in the west to western Tibet in the east, and from Mithankot in the south to Kashmir in the north. Religiously diverse, with an estimated population of 3.5 million in 1831, it was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to be annexed by the British Empire.
 W
WSikkim is a state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to India's Siliguri Corridor near Bangladesh. Sikkim is the least populous and second smallest among the Indian states. A part of the Eastern Himalaya, Sikkim is notable for its biodiversity, including alpine and subtropical climates, as well as being a host to Kangchenjunga, the highest peak in India and third highest on Earth. Sikkim's capital and largest city is Gangtok. Almost 35% of the state is covered by the Khangchendzonga National Park – a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Sikkim, earlier known as Dremoshong, was a hereditary monarchy from 1642 to 16 May 1975 in the Eastern Himalayas. It was ruled by Chogyals of the Namgyal dynasty.
 W
WThe polity of Tibet between the collapse of the Qing dynasty in 1912 and the annexation by the People's Republic of China in 1951 was a de facto independent state.
 W
WThe Turkestan Autonomy, or Kokand Autonomy, was an unrecognized state in Central Asia that existed at the beginning of the Russian Civil War. It was formed on 27 November 1917 and existed until 22 February 1918. It was a secular republic, headed by a president.
 W
WThe United Arab Republic was a sovereign state in the Middle East from 1958 to 1971. It was initially a political union between Egypt and Syria from 1958 until Syria seceded from the union after the 1961 Syrian coup d'état — leaving a rump state. Egypt continued to be known officially as the United Arab Republic until 1971.
 W
WZakarid Armenia, was an Armenian principality between 1201 and 1360, ruled by the Zakarid-Mkhargrzeli dynasty. The city of Ani was the capital of the princedom. The Zakarids were vassals to the Bagrationi dynasty in Georgia, but frequently acted independently and at times titled themselves as kings. In 1236, they became vassals to the Mongol Empire. Their descendants continued to hold Ani until the 1330s, when they lost it to a succession of Turkish dynasties, including the Kara Koyunlu, who made Ani their capital.
 W
WThe Republic of Zamboanga was a short-lived revolutionary government, founded by General Vicente Alvarez with his Zamboangueño Revolutionary Forces after the Spanish government in Zamboanga, Philippines officially surrendered and turned over Real Fuerza de Nuestra Señora La Virgen del Pilar de Zaragoza to Gen. Vicente Álvarez in May 1899. On 28 May 1899, Gen. Vicente Álvarez proclaimed independence and became the first and last genuinely elected president of the republic.