 W
WThe Late Bronze Age collapse was a transition period in the Near East, Anatolia, the Aegean region, North Africa, the Caucasus, the Balkans and the Eastern Mediterranean from the Late Bronze Age to the Early Iron Age, a transition which historians believe was violent, sudden, and culturally disruptive. The palace economy of the Aegean region and Anatolia that characterized the Late Bronze Age disintegrated, transforming into the small isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages.
 W
WAlashiya, also spelled Alasiya, also known as the Kingdom of Alashiya, was a state which existed in the Middle and Late Bronze Ages, and was situated somewhere in the Eastern Mediterranean. It was a major source of goods, especially copper, for ancient Egypt and other states in the Ancient Near East. It is referred to in a number of the surviving texts and is now thought to be the ancient name of Cyprus, or an area of Cyprus. This was confirmed by the scientific analysis performed in the Tel Aviv University of the clay tablets which were sent from Alashiya to other rulers.
 W
WAmmurapi was the last Bronze Age ruler and king of the ancient Syrian city of Ugarit. Ammurapi was a contemporary of the Hittite King Suppiluliuma II. He wrote a preserved vivid letter RS 18.147 in response to a plea for assistance from the king of Alashiya.
 W
WThe Battle of Djahy was a major land battle between the forces of pharaoh Ramesses III and the Sea Peoples who intended to invade and conquer Egypt. The conflict occurred somewhere on the Egyptian Empire's easternmost frontier in Djahy or modern-day southern Lebanon, in the eighth year of pharaoh Ramesses III or about c. 1178 BC.
 W
WThe biblical Battle of Mount Tabor takes place during the time of the Judges between the forces of King Jabin of Canaan who ruled from Hazor, and the Israelite army led by Barak and Deborah. It is recorded in the Book of Judges, chapters 4 and 5.
 W
WThe Battle of the Delta was a sea battle between Egypt and the Sea Peoples, circa 1175 BCE when the Egyptian pharaoh Ramesses III repulsed a major sea invasion. The conflict occurred somewhere at the shores of the eastern Nile Delta and partly on the borders of the Egyptian Empire in Syria, although their precise locations are unknown. This major conflict is recorded on the temple walls of the mortuary temple of pharaoh Ramesses III at Medinet Habu.
 W
WDeir Alla is the site of an ancient Near Eastern town in Balqa Governorate, Jordan, thought to be the biblical Pethor.
 W
WThe Dorian invasion is a concept devised by historians of Ancient Greece to explain the replacement of pre-classical dialects and traditions in southern Greece by the ones that prevailed in Classical Greece. The latter were named Dorian by the ancient Greek writers, after the Dorians, the historical population that spoke them.
 W
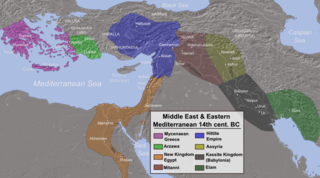
WElam was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of modern-day Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of southern Iraq. The modern name Elam stems from the Sumerian transliteration elam(a), along with the later Akkadian elamtu, and the Elamite haltamti. Elamite states were among the leading political forces of the Ancient Near East. In classical literature, Elam was also known as Susiana, a name derived from its capital Susa.
 W
WEnkomi is a village near Famagusta in Cyprus. It is the site of an important Bronze Age city, possibly the capital of Alasiya. Enkomi is under the de facto control of Northern Cyprus.
 W
WThe Greek Dark Ages is the period of Greek history from the end of the Mycenaean palatial civilization around 1100 BC to the beginning of Archaic age around 750 BC.
 W
WHattusa was the capital of the Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey, within the great loop of the Kızılırmak River.
 W
WThe Hekla 3 eruption (H-3) circa 1000 BC is considered the most severe eruption of Hekla during the Holocene. It threw about 7.3 km3 of volcanic rock into the atmosphere, placing its Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) at 5. This would have cooled temperatures in the Northern Hemisphere for several years afterwards.
 W
WIklaina is a historic village in the municipal unit of Pylos, Messenia, Greece. It is situated in low hills, approximately 10 km to the northeast of the town of Pylos. Important archaeological remains of the Late Bronze Age period have been brought to light through excavations and surface survey by the Athens Archaeological Society and the University of Missouri–St. Louis under the direction of Professor Michael Cosmopoulos. The finds include an early Mycenaean palace, giant terrace walls, murals, an advanced drainage system, and a clay tablet from between 1450 and 1350 B.C. featuring an early example of Linear B writing. Other periods represented are the Late Classical and the Byzantine.
 W
WThe Luwians were a group of Anatolian peoples who lived in central, western, and southern Anatolia, in present-day Turkey, in the Bronze Age and the Iron Age. They spoke the Luwian language, an Indo-European language of the Anatolian sub-family, which was written in cuneiform imported from Mesopotamia, and a unique native hieroglyphic script, which was sometimes used by the linguistically related Hittites also.
 W
WThe Merneptah Stele – also known as the Israel Stele or the Victory Stele of Merneptah – is an inscription by the ancient Egyptian Pharaoh Merneptah discovered by Flinders Petrie in 1896 at Thebes, and now housed in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo.
 W
WThe Middle Assyrian Empire is the period in the history of Assyria between the fall of the Old Assyrian Empire in the 14th century BC and the establishment of the Neo-Assyrian Empire in the 10th century BC.
 W
WMiletus was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Caria. Its ruins are located near the modern village of Balat in Aydın Province, Turkey. Before the Persian invasion in the middle of the 6th century BC, Miletus was considered among the greatest and wealthiest of Greek cities.
 W
WMycenae is an archaeological site near Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about 120 kilometres south-west of Athens; 11 kilometres north of Argos; and 48 kilometres south of Corinth. The site is 19 kilometres inland from the Saronic Gulf and built upon a hill rising 900 feet above sea level.
 W
WNebuchadnezzar I or Nebuchadrezzar I, r. c. 1125–1104 BC, was the fourth king of the Second Dynasty of Isin and Fourth Dynasty of Babylon. He ruled for 22 years according to the Babylonian King List C, and was the most prominent monarch of this dynasty. He is best known for his victory over Elam and the recovery of the cultic idol of Marduk.
 W
WNichoria is a site in Messenia, on a ridgetop near modern Rizomylos, at the northwestern corner of the Messenian Gulf. From the Middle to Late Bronze Age it cultivated olive and terebinth for export. During the Helladic period it was part of the Mycenaean civilisation.
 W
WThe Palace of Nestor was an important centre in Mycenaean times, and described in Homer's Odyssey and Iliad as Nestor's kingdom of "sandy Pylos".
 W
WPyla-Kokkinokremos was a Late Bronze Age settlement on Cyprus, abandoned after a brief occupation.
 W
WPylos, historically also known as Navarino, is a town and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. It was the capital of the former Pylia Province. It is the main harbour on the Bay of Navarino. Nearby villages include Gialova, Pyla, Elaiofyto, Schinolakka, and Palaionero. The town of Pylos has 2,345 inhabitants, the municipal unit of Pylos 5,287 (2011). The municipal unit has an area of 143.911 km2.
 W
WUsermaatre Meryamun Ramesses III was the second Pharaoh of the Twentieth Dynasty in Ancient Egypt. He is thought to have reigned from 1186 to 1155 BC and is considered to be the last great monarch of the New Kingdom to wield any substantial authority over Egypt. His long reign saw the decline of Egyptian political and economic power, linked to a series of invasions and internal economic problems that also plagued pharaohs before him. He has also been described as "warrior Pharaoh" due to his strong military strategies. He led the way by defeating the invaders known as "the Sea Peoples", who had caused destruction in other civilizations and empires. He was able to save Egypt from collapsing at the time when many other empires fell during the Late Bronze Age; however, the damage of the invasions took a toll on Egypt.
 W
WThe Sea Peoples are a purported seafaring confederation that attacked ancient Egypt and other regions of the East Mediterranean prior to and during the Late Bronze Age collapse. Following the creation of the concept in the nineteenth century, it became one of the most famous chapters of Egyptian history, given its connection with, in the words of Wilhelm Max Müller: "the most important questions of ethnography and the primitive history of classic nations". Their origins undocumented, the various Sea Peoples have been proposed to have originated from places that include western Asia Minor, the Aegean, the Mediterranean islands and Southern Europe. Although the archaeological inscriptions do not include reference to a migration, the Sea Peoples are conjectured to have sailed around the eastern Mediterranean and invaded Anatolia, Syria, Phoenicia, Canaan, Cyprus and Egypt toward the end of the Bronze Age.
 W
WŠutruk-Nakhunte was king of Elam from about 1184 to 1155 BC, and the second king of the Shutrukid Dynasty.
 W
WSuppiluliuma II, the son of Tudḫaliya IV, was the last known king of the New Kingdom of the Hittite Empire, ruling c. 1207–1178 BC, contemporary with Tukulti-Ninurta I of the Middle Assyrian Empire.
 W
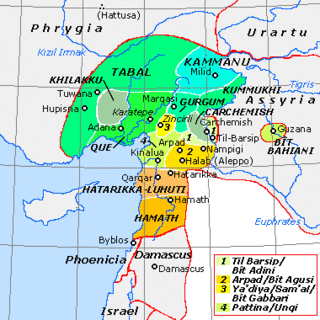
WThe states that are called Syro-Hittite, or Luwian-Aramean, were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern parts of modern Syria, known in ancient times as lands of Hatti and Aram. They arose following the collapse of the Hittite New Kingdom in the 12th century BCE, and lasted until they were subdued by the Assyrian Empire in the 8th century BCE. They are grouped together by scholars, on the basis of several cultural criteria, that are recognized as similar and mutually shared between both societies, northern (Luwian) and southern (Aramean). Cultural exchange between those societies is seen as a specific regional phenomena, particularly in light of significant linguistic distinctions between two main regional languages, with Luwian belonging to Anatolian group of Indo-European languages, and Aramean belonging to Western Semitic group of Semitic languages. Several questions that are related to regional grouping of Luwian and Aramean states are viewed differently among scholars, including some views that are critical towards such grouping in general.
 W
WThe Third Intermediate Period of ancient Egypt began with the death of Pharaoh Ramesses XI in 1070 BC, which ended the New Kingdom, and was eventually followed by the Late Period. Various points are offered as the beginning for the latter era, though it is most often regarded as dating from the foundation of the Twenty-Sixth Dynasty by Psamtik I in 664 BC, following the departure of the Nubian Kushite rulers of the Twenty-fifth Dynasty by the Assyrians under King Assurbanipal. The concept of a "Third Intermediate Period" was coined in 1978 by British Egyptologist Kenneth Kitchen.
 W
WTiglath-Pileser I was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian period. According to Georges Roux, Tiglath-Pileser was "one of the two or three great Assyrian monarchs since the days of Shamshi-Adad I". He was known for his "wide-ranging military campaigns, his enthusiasm for building projects, and his interest in cuneiform tablet collections". Under him, Assyria became the leading power of the Ancient Near East, a position the kingdom largely maintained for the next five hundred years. He expanded Assyrian control into Anatolia and Syria, and to the shores of the Mediterranean Sea. From his surviving inscriptions, he seems to have carefully cultivated a fear of himself in his subjects and in his enemies alike.
 W
WIn Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and has been narrated through many works of Greek literature, most notably Homer's Iliad. The core of the Iliad describes a period of four days and two nights in the tenth year of the decade-long siege of Troy; the Odyssey describes the journey home of Odysseus, one of the war's heroes. Other parts of the war are described in a cycle of epic poems, which have survived through fragments. Episodes from the war provided material for Greek tragedy and other works of Greek literature, and for Roman poets including Virgil and Ovid.
 W
WTroy was a city in the northwest of Asia Minor, southwest of the Çanakkale Strait, south of the mouth of the Dardanelles and northwest of Mount Ida. The location in the present day is the hill of Hisarlik and its immediate vicinity. In modern scholarly nomenclature, the Ridge of Troy borders the Plain of Troy, flat agricultural land, which conducts the lower Scamander River to the strait. Troy was the setting of the Trojan War described in the Greek Epic Cycle, in particular in the Iliad, one of the two epic poems attributed to Homer. Metrical evidence from the Iliad and the Odyssey suggests that the name Ἴλιον (Ilion) formerly began with a digamma: Ϝίλιον (Wilion); this is also supported by the Hittite name for what is thought to be the same city, Wilusa. According to archaeologist Manfred Korfmann, Troy's location near the Aegean Sea, as well as the Sea of Marmara and the Black Sea, made it a hub for military activities and trade, and the chief site of a culture that Korfmann calls the "Maritime Troja Culture", which extended over the region between these seas.
 W
WThe Twentieth Dynasty of Egypt is the third and last dynasty of the Ancient Egyptian New Kingdom period, lasting from 1189 BC to 1077 BC. The 19th and 20th Dynasties furthermore together constitute an era known as the Ramesside period.
 W
WTwosret was the last known ruler and the final Pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt.
 W
WUgarit was an ancient port city in northern Syria, in the outskirts of modern Latakia, discovered by accident in 1928 together with the Ugaritic texts. Its ruins are often called Ras Shamra after the headland where they lie.
 W
WZababa-šuma-iddina was the 35th and penultimate king of the Kassite or 3rd dynasty of Babylon, who reigned for just one year, ca. 1158 BC. He was without apparent ties to the royal family and there is uncertainty concerning the circumstances of his coming to power.