 W
WThe Battle of Agua Carta, or the Battle of Lindo Lugar, was an engagement between the National Guard of Nicaragua and the rebels of Augusto César Sandino in 1932. It was fought near Mount Kilambe at the Agua Carta, a river in Sandino territory, as part of the American occupation of Nicaragua and a long lasting civil war.
 W
WThe Autonomous Regional Council of the South Caribbean Coast, abbreviated as the CRACCS, is the devolved legislature of the South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region (RACCS). It has the power to legislate on a wide variety of economic, social, and cultural issues not reserved to the central government.
 W
WThe Battle of Achuapa, or the Achuapa massacre, took place on December 31, 1930 during the American occupation of Nicaragua of 1926–1933.
 W
WThe Battle of Coyotepe Hill was a significant engagement during the United States occupation of Nicaragua from August through November 1912 during the insurrection staged by Minister of War General Luis Mena against the government of President Adolfo Díaz.
 W
WThe Battle of El Bramadero, or the Battle of Bromaderos, took place between the 27 and 28 February 1928 during the American occupation of Nicaragua of 1926–1933 and the Sandino Rebellion. The battle began on the twenty-seventh when a convoy of thirty-six Marines, one American naval pharmacist's mate, twenty Nicaraguan "muleros," two Nicaraguan "'Jefe' muleros," and 99 mules led by First Lieutenant Edward F. O'Day moving along the Yalí–Condega trail was ambushed by a force of Sandinista rebels led by Miguel Angel Ortez.
 W
WThe Battle of El Sauce, or the Battle of Punta de Rieles or Punta Rieles, took place on the 26 December 1932 during the American occupation of Nicaragua of 1926–1933. It was the last major battle of the Sandino Rebellion of 1927–1933. The incident has its origins in Nicaraguan President José María Moncada's plan to commemorate the completion of the León-El Sauce railway on the 28 December 1932.
 W
WThe Battle of Masaya took place on 19 September 1912, during the American occupation of Nicaragua of 1912—1925 and the Nicaraguan civil war of 1912.
 W
WThe Battle of San Fernando took place on July 25, 1927 during the American occupation of Nicaragua of 1926–1933. Shortly after the Battle of Ocotal, an expedition of seventy-eight American Marines and thirty-seven Nicaraguan Provisional Guardsmen led by Major Oliver Floyd were sent hunting for rebel leader Augusto César Sandino. One of their destinations was the town of San Fernando, where Sandino had about forty men waiting for the Marines and their Nicaraguan allies. He placed a sentry outside the village to alert his men of the Marines and Provisional Guard's arrival, but the watchman abandoned his post to be alone with an Indian girl in a nearby shack. The Marines and Nicaraguan government troops marched into San Fernando at 3:00, finding it largely deserted. While galloping across the town's "open, grassy plaza" in order to question an old man, Captain Victor F. Bleasdale and Marine Private Rafael Toro received fire from the waiting Sandinistas, with Toro being mortally wounded. Eventually, the Sandinistas were driven back, leaving eleven of their dead behind. Fighting was over by 3:45. In addition to Marine and Sandinista losses, one woman was wounded in the legs by fire from an automatic weapon.
 W
WThe Battle of Santa Clara took place on 27 July 1927, during the American occupation of Nicaragua of 1926–1933. After being ambushed by Sandinista forces at the Battle of San Fernando, Major Oliver Floyd's expedition of American Marines and Nicaraguan Provisional Guardsmen continued its advance into enemy-held territory in northern Nicaragua.
 W
WThe Filibuster War or Walker affair was a military conflict between filibustering multinational troops stationed in Nicaragua and a coalition of Central American armies. An American, William Walker, briefly invaded Nicaragua in 1855 with a small army. He seized control of the country by 1856, but was ousted the following year.
 W
WThe Captaincy General of Guatemala, also known as the Kingdom of Guatemala, was an administrative division of the Spanish Empire, under the viceroyalty of New Spain in Central America, including the present-day nations of Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador, and Guatemala, and the Mexican state of Chiapas. The governor-captain general was also president of the Royal Audiencia of Guatemala, the superior court.
 W
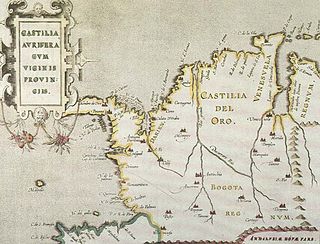
WCastilla de Oro or del Oro was the name given by the Spanish settlers at the beginning of the 16th century to the Central American territories from the Gulf of Urabá, near today's Colombian-Panamanian border, to the Belén River. Beyond that river, the region was known as Veragua, and was disputed by the Spanish crown along with the Columbus family. The name "Castilla de Oro" was made official in May 1513 by King Ferdinand II of Aragon, then regent of the Crown of Castile.
 W
WThe Greater Republic of Central America, later the United States of Central America, originally planned to be known as the Republic of Central America, was a short-lived political union between El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua, lasting from 1896 to 1898. It was an attempt to revive the failed Federal Republic of Central America that existed earlier in the century.
 W
WFernando Chamorro Alfaro was a General and member of the governing junta of Nicaragua (1860–1863).
 W
WThe Contras were the various U.S.-backed and funded right-wing rebel groups that were active from 1979 to the early 1990s in opposition to the Marxist Sandinista Junta of National Reconstruction Government in Nicaragua. Among the separate contra groups, the Nicaraguan Democratic Force (FDN) emerged as the largest by far. In 1987, virtually all contra organizations were united, at least nominally, into the Nicaraguan Resistance.
 W
WThe Duchy of Veragua was a Spanish hereditary domain created in 1537 in the reign of King Charles I in a small section of the territory of Veragua. The first Duke of Veragua was Admiral Luis Colón y Toledo, grandson and heir of Christopher Columbus. Holders of this title also lay claim to the title Admiral of the Ocean Sea. The establishment of the duchy was the resolution of a longstanding dispute between the Spanish Crown and the heirs of Columbus, who had claimed a greater area. Luis Colón was also made Marquess of Jamaica.
 W
WThe Federal Republic of Central America, also called the United Provinces of Central America in its first year of creation, is a defunct sovereign state in Central America that consisted of the territories of the former Captaincy General of Guatemala of New Spain. It existed from 1823 to 1841, as a republican democracy.
 W
WThe First Central American Civil War was a civil political and military conflict within the Federal Republic of Central America which lasted from 1826 until 1829. The civil war was fought between Liberal and Conservative lines with Francisco Morazán leading the Liberals and Manuel José Arce, a former Liberal, leading the Conservatives.
Gil González Dávila or Gil González de Ávila was a Spanish Conquistador and the first European to arrive in present-day Nicaragua.
 W
WCharles Frederick Henningsen was a writer, mercenary, filibuster, and munitions expert. He participated in civil wars and independence movements in Spain, Nicaragua, Hungary, and the United States.
 W
WFrancisco Hernández de Córdoba is usually reputed as the founder of Nicaragua, and in fact he founded two important Nicaraguan cities, Granada and León. The currency of Nicaragua is named the córdoba in his memory.
 W
WThe Institute of History of Nicaragua and Central America is a research institute that is connected to the Central American University in Nicaragua.
 W
WThe Jaguar Smile is Salman Rushdie's first full-length non-fiction book, which he wrote in 1987 after visiting Nicaragua. The book is subtitled A Nicaraguan Journey and relates his travel experiences, the people he met as well as views on the political situation then facing the country. The book was written during a break the author took from writing his controversial novel, The Satanic Verses.
 W
WThe Battle of La Flor was fought in May 1928 between the United States Marines, their Nicaraguan National Guardsmen allies, and a force of Sandinista rebels. It occurred at a hill north of the La Flor coffee plantation and ended with a rebel victory when the Americans and Nicaraguan National Guard troops were forced to withdraw.
 W
WThe Battle of La Paz Centro took place on May 16, 1927 during the American occupation of Nicaragua of 1926–1933. It took place after the end of Nicaraguan civil war of 1926–1927 and prior to the Sandino Rebellion of 1927–1933.
 W
WThe Second Battle of Las Cruces, or the New Year's Day Battle, was a major engagement during the American occupation of Nicaragua. It was fought on 1 January 1928, during an expedition to destroy a Sandinista fortress. A column of United States Marines and Nicaraguan National Guardsmen were attacked by a superior force of rebels entrenched on Las Cruises Hill and, after a long battle, the Americans and Nicaraguans routed the Sandinistas and captured their positions.
 W
WA Caudillo is part of the larger Iberian tradition of authoritarian leaders, with roots in the Iberian past, particularly in the Reconquista. A number of military leaders who were part of the Spanish American struggle for independence took on political roles in during the establishment of new sovereign nation-states. The establishment of military strong men as the head of new national governments did not generally come via elections, but many did have strong popular support. Caudillos often have a personalist connection with their popular followers, combining charisma and machismo ("manliness"), access to political and economic power. They often desire to legitimize their rule. Many caudillos brought order to their areas of control, but also resorted to violence with their armed supporters to achieve it. The early nineteenth century has been considered the "Age of Caudillos," but authoritarian regimes existed in the twentieth century as well, with caudillismo casting a long shadow.
 W
WLos Placeres is an archeological site located between the “Waspán” and “Tabacalera Nicaragüense” neighborhoods at kilometer 4½ of the “Carretera Norte”, in Managua, en Nicaragua. The site extends to the coast of Lake Managua. A large part of the area that delimits the site is being impacted by a new urban settlement known as Barrio Hugo Chávez, which divides the site, where its new settlers have disturbed the ground for installation of pipes for drinking water, toilet and housing, this activity has caused a serious incidental findings and impacts to the prehispanic archaeological site.
 W
WMesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in North America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. Within this region pre-Columbian societies flourished for more than 1000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Mesoamerica was the site of two of the most profound historical transformations in world history: primary urban generation, and the formation of New World cultures out of the long encounters among Indigenous, European, African and Asian cultures.
 W
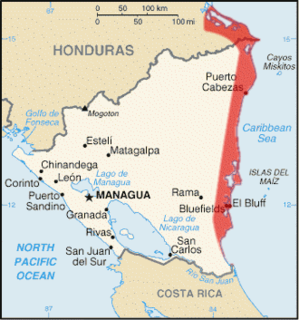
WThe Mosquito Coast, also known as the Miskito Coast and the Miskito Kingdom, historically included the kingdom's fluctuating area along the eastern coast of present-day Nicaragua and Honduras. It formed part of the Western Caribbean Zone. It was named after the local Miskito Amerindians and was long dominated by British interests. The Mosquito Coast was incorporated into Nicaragua in 1894; however, in 1960, the northern part was granted to Honduras by the International Court of Justice.
 W
WThe National Congress of Nicaragua was the legislature of Nicaragua before the Nicaraguan Revolution of 1979.
 W
WNicaragua Betrayed, published by Western Islands in 1980, is the memoir of former President of Nicaragua Anastasio Somoza Debayle, who had been toppled the previous year by the Sandinista insurgency. At the time of the book's publication, Somoza was living in Asunción, Paraguay, as a personal guest of President Alfredo Stroessner.
 W
WThe 1972 Nicaragua earthquake occurred at 12:29:44 a.m. local time on December 23 near Managua, the capital of Nicaragua. It had a moment magnitude of 6.3 and a maximum MSK intensity of IX (Destructive). The epicenter was 28 kilometers northeast of the city centre and a depth of about 10 kilometers. The earthquake caused widespread casualties among Managua's residents: 4,000–11,000 were killed, 20,000 were injured and over 300,000 were left homeless.
 W
WThe Republic of Nicaragua v. The United States of America (1986) was a case where the International Court of Justice (ICJ) held that the U.S. had violated international law by supporting the Contras in their rebellion against the Sandinistas and by mining Nicaragua's harbors. The case was decided in favor of Nicaragua and against the United States with the awarding of reparations to Nicaragua.
 W
WThe Nicaraguan Revolution encompassed the rising opposition to the Somoza dictatorship in the 1960s and 1970s, the violent campaign led by the Sandinista National Liberation Front (FSLN) to oust the dictatorship in 1978–79, the subsequent efforts of the FSLN to govern Nicaragua from 1979 to 1990, and the Contra War, which was waged between the FSLN-led government of Nicaragua and the United States-backed Contras from 1981–1990. The revolution marked a significant period in the history of Nicaragua and revealed the country as one of the major proxy war battlegrounds of the Cold War, attracting much international attention.
 W
WThe Battle of Ocotal occurred in July 1927, during the American occupation of Nicaragua. A large force of rebels loyal to Augusto César Sandino attacked the garrison of Ocotal, which was held by a small group of US Marines and Nicaraguan National Guards. Ultimately the rebels were defeated with heavy losses, while the Americans and their Nicaraguan allies suffered very light casualties.
 W
WONUCA and ONUSAL were two United Nations peacekeeping missions deployed in Central America during the late 1980s and early 1990s.
 W
WBetween 1665 and 1857, Caribbean pirates and filibusters operated in Lake Nicaragua and the surrounding shores. The Spanish city of Granada, located on the lake, was an important trading centre for much of its early history so it was a prime target for pirates such as Henry Morgan and freebooters like William Walker.
 W
WThe Rama are an indigenous people living on the eastern coast of Nicaragua. Since the start of European colonization, the Rama population has declined as a result of disease, conflict, and loss of territory. In recent years, however, the Rama population has increased to around 2,000 individuals. A majority of the population lives on the island of Rama Cay, which is located in the Bluefields Lagoon. Additional small Rama communities are dispersed on the mainland from Bluefields to Greytown. The Rama are one of three main indigenous groups on Nicaragua’s Caribbean coast.
 W
WThe San Juan Expedition took place between March and November 1780 during the American War of Independence when a British force under the command of John Polson and Captain Horatio Nelson landed on the coast of the present-day Nicaragua, with the aim of sailing up the San Juan River to capture the strategically crucial towns of Granada and León, located on the northwestern shore of Lake Nicaragua.
 W
WThe Somoza family was an autocratic family dictatorship in Nicaragua that lasted forty-three years, from 1936 to 1979. They were closely allied with the United States.
 W
WThe Battle of Telpaneca was an engagement fought during the United States occupation of Nicaragua in 1927.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 653, adopted unanimously on 20 April 1990, after recalling resolutions 644 (1989) and 650 (1990), the Council endorsed a report by the Secretary-General and authorised new additions to the mandate of the United Nations Observer Group in Central America.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 675, adopted unanimously on 5 November 1990, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989) and 644 (1989), the Council endorsed a report by the Secretary-General and decided to extend the mandate of the United Nations Observer Group in Central America for a further six months until 7 May 1991.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 719, adopted unanimously on 6 November 1991, after recalling resolutions 637 (1989), 644 (1989), 675 (1990) and 691 (1991), the Council endorsed a report by the Secretary-General and decided to extend the mandate of the United Nations Observer Group in Central America for a further five months and twenty-three days until 30 April 1992.
 W
WUnited Nations Security Council resolution 730, adopted unanimously on 16 January 1992, after recalling resolutions 719 (1991) and 729 (1992) the Council approved a report by the Secretary-General from 14 January, and decided to terminate the mandate of the United Nations Observer Group in Central America (ONUCA) with effect from 17 January 1992.
 W
WThe Viceroyalty of New Granada was the name given on 27 May 1717, to the jurisdiction of the Spanish Empire in northern South America, corresponding to modern Colombia, Ecuador, and Venezuela. Created in 1717 by king Felipe V, inside of a new territorial control policy, it was suspended in 1723 due to financial problems and was restored in 1739 until the independence movement suspended it again in 1810. The territory corresponding to Panama was incorporated later in 1739, and the provinces of Venezuela were separated from the Viceroyalty and assigned to the Captaincy General of Venezuela in 1777. In addition to these core areas, the territory of the Viceroyalty of New Granada included Guyana, southwestern Suriname, parts of northwestern Brazil, and northern Peru.
 W
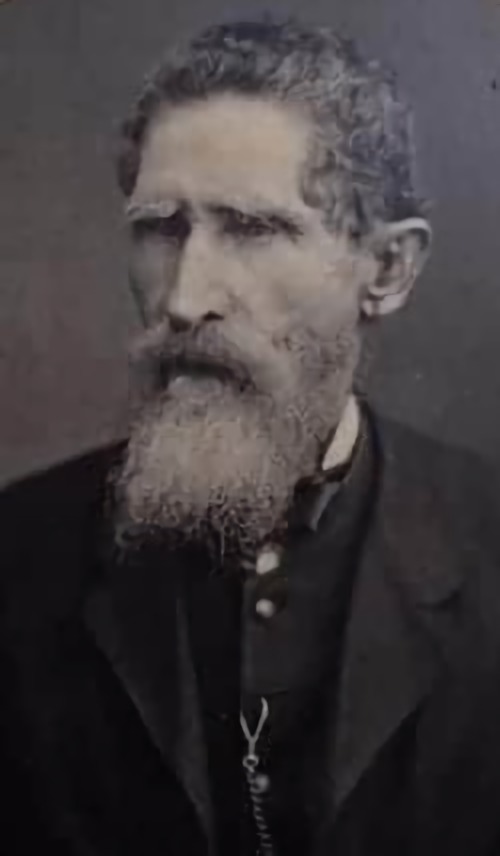
WFlorencio Xatruch was a general who led the Honduran expeditionary force against William Walker in Nicaragua in 1856.