 W
WThe European Union is a geo-political entity covering a large portion of the European continent. It is founded upon numerous treaties and has undergone expansions and secessions that have taken it from 6 member states to 27, a majority of the states in Europe.
 W
WThe period saw the first moves towards European unity as the first bodies began to be established in the aftermath of the Second World War. In 1951 the first community, the European Coal and Steel Community was established and moves on new communities quickly began. Early attempts at military and political unity failed, eventually leading to the Treaties of Rome in 1957.
 W
WThe history of the European Communities between 1958 and 1972 saw the early development of the European Communities. The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) had just been joined by the European Atomic Energy Community (Euratom) and the European Economic Community (EEC), the latter of which soon became the most important. In 1967 the EEC's institutions took over the other two with the EEC's Commission holding its first terms under Hallstein and Rey.
 W
WBetween 1973 and 1993 the European Communities saw the first enlargement of the Communities and increasing integration under the Delors Commission leading to the creation of the European Union in 1993.
 W
WThe 1973 enlargement of the European Communities was the first enlargement of the European Communities (EC), now the European Union (EU). Denmark, Ireland and the United Kingdom (UK) acceded to the EC on 1 January 1973. Gibraltar and Greenland also joined the EC as part of the United Kingdom and Denmark respectively, but the Danish Faroe Islands, the other British Overseas Territories and the Crown dependencies of the United Kingdom did not join the EC.
 W
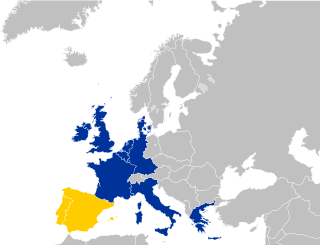
WSpain and Portugal acceded to the European Communities, now the European Union, in 1986. This was the third enlargement of the Communities, following on from the 1973 and 1981 enlargements. Their accessions are considered to be a part of the broader Mediterranean enlargement of the European Union.
 W
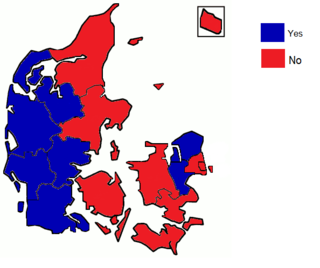
WA referendum on the Maastricht Treaty was held in Denmark on 2 June 1992. It was rejected by 50.7% of voters with a turnout of 83.1%. The rejection was a blow to the process of European integration, although the process continued. The result of the referendum, along with the "petit oui" in the French Maastricht referendum signaled the end of the "permissive consensus" on European integration which had existed in most of continental Europe until then. This was expressed by Pascal Lamy, chef de cabinet for Jacques Delors, the president of the European Commission, who remarked that, “Europe was built in a St. Simonian [i.e., technocratic] way from the beginning, this was Monnet’s approach: The people weren’t ready to agree to integration, so you had to get on without telling them too much about what was happening. Now St. Simonianism is finished. It can’t work when you have to face democratic opinion.” From this point forward issues relating to European integration were subject to much greater scrutiny across much of Europe, and overt euroscepticism gained prominence. Only France, Denmark and Ireland held referendums on Maastricht ratification.
 W
WThe history of the European Union between 1993 and 2004 was the period between its creation and the 2004 enlargement. The European Union was created at the dawn of the post–Cold War era and saw a series of successive treaties laying the ground for the euro, foreign policy and future enlargement. Three new member states joined the previous twelve in this period and the European Economic Area extended the reach of the EU's markets to three more.
 W
WA second referendum on the Maastricht Treaty was held in Denmark on 18 May 1993. After rejecting the treaty in a referendum the previous year, this time it was approved by 56.7% of voters with an 86.5% turnout.
 W
WThe 1995 enlargement of the European Union saw Austria, Finland, and Sweden accede to the European Union (EU). This was the EU's fourth enlargement and came into effect on 1 January of that year. All these states were previous members of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) and had traditionally been less interested in joining the EU than other European countries. Norway had negotiated to join alongside the other three but following the signing of the treaty, membership was turned down by the Norwegian electorate in the 1994 national referendum. Switzerland also applied for membership on 26 May 1992, but withdrew it after a negative referendum result on 6 December 1992.
 W
WA referendum on the Amsterdam Treaty was held in Denmark on 28 May 1998. It was approved by 55.1% of voters with a turnout of 76.2%. The treaty subsequently came into effect on 1 May 1999.
 W
WThe history of the European Union since 2004 is the current timeline of the European union. It is a period of significant upheaval and reform following the 2004 enlargement of the European Union. The EU has taken on ten new members, eight of which were initially much poorer than the EU average, and took in a further two in 2007 with many more on the way. It created the euro a few years before and had to expand this, and the Schengen Area to its new members. However this was overshadowed by the late-2000s recession and damaging disputes over the European Constitution and its successor, the Treaty of Lisbon. Throughout this period, the European People's Party has been the largest group in the European Parliament and provides every President of the European Commission.
 W
WThe largest expansion of the European Union (EU), in terms of territory, number of states, and population took place on 1 May 2004.
 W
WOn 1 January 2007, Bulgaria and Romania became member states of the European Union (EU) in the fifth wave of EU enlargement.
 W
WKonrad Hermann Joseph Adenauer was a German statesman who served as the first Chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany from 1949 to 1963. From 1946 to 1966, he was the first leader of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), a Christian democratic party he co-founded, that under his leadership became one of the most influential parties in the country.
 W
WThe Benelux memorandum of 1955 was a document drafted by the three Benelux countries on 18 May 1955 as a means to reviving European integration on the basis of a general common market.
 W
WCount René Boël (1899-1990) was a Belgian industrialist and Director of the Usine Gustave Boël. He was married with Yvonne Solvay (1896-1930), granddaughter of Ernest Solvay. They have two sons Yves Boël and Pol Boël and one daughter Antoinette Boël (1925-1982).
 W
WThe Hague Congress or the Congress of Europe, considered by many as the first federal moment of the European history, was held in The Hague from 7–11 May 1948 with 750 delegates participating from around Europe as well as observers from Canada and the United States of America.
 W
WRichard Nikolaus Eijiro, Count of Coudenhove-Kalergi was an Austrian-Japanese politician, philosopher and Count of Coudenhove-Kalergi. A pioneer of European integration, he served as the founding president of the Paneuropean Union for 49 years. His parents were Heinrich von Coudenhove-Kalergi, an Austro-Hungarian diplomat, and Mitsuko Aoyama, the daughter of an oil merchant, antiques-dealer and major landowner in Tokyo. His childhood name in Japan was Aoyama Eijiro. He became a Czechoslovak citizen in 1919 and then took French nationality from 1939 until his death.
 W
WThe Crocodile Club was an informal group of members of the European Parliament (MEP) that favoured greater European integration, to the extent of a European federation, and greater powers to the European Parliament.
 W
WJean-Paul de Dadelsen, was a French schoolmaster, officer, journalist, broadcaster and poet. He was an early supporter of a European Common Market and adviser to Jean Monnet.
 W
WWilliam Joseph "Wild Bill" Donovan was an American soldier, lawyer, intelligence officer and diplomat, best known for serving as the head of the Office of Strategic Services (OSS), the precursor to the Central Intelligence Agency, during World War II. He is regarded as the founding father of the CIA, and a statue of him stands in the lobby of the CIA headquarters building in Langley, Virginia.
 W
WEurafrica, refers to the German idea of strategic partnership between Africa and Europe. In the decades before World War II, German supporters of European integration advocated a merger of African colonies as a first step towards a federal Europe. As a genuine political project, it played a crucial role in the early development of the European Union but was largely forgotten afterwards. In the context of a renewed EU Strategy for Africa, and controversies about a Euromediterranean Partnership, the term has gone through a revival of sorts in recent years.
 W
WThe euro came into existence on 1 January 1999, although it had been a goal of the European Union (EU) and its predecessors since the 1960s. After tough negotiations, particularly due to opposition from the United Kingdom, the Maastricht Treaty entered into force in 1993 with the goal of creating an economic and monetary union by 1999 for all EU states except the UK and Denmark.
 W
WThe europa was a token coinage created in 1928 by Joseph Archer, a politician and industrialist from the Nièvre region in France. The currency was promoted by Philibert Besson, the elected deputy for the Haute-Loire who, along with Archer, was an influential figure in the European federalist movement. The coins were minted in the name of a hypothetical "Federated States of Europe". Unlike contemporary currencies based on the gold standard, the europa was intended to derive its notional value from its value in labour.
 W
WThe European Communities (EC), sometimes referred to as the European Community, were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community, and the European Economic Community (EEC); the last of which was renamed the European Community (EC) in 1993 by the Maastricht Treaty, which formed the European Union.
 W
WThe European Convention was the 1999 convention which drafted the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union. The convention was called in 1999 by the Cologne European Council to consolidate rights for EU citizens and enshrine them at EU level.
 W
WThe European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization that aimed to bring about economic integration among its member states. It was created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957. Upon the formation of the European Union in 1993, the EEC was incorporated into the EU and renamed the European Community (EC). In 2009, the EC formally ceased to exist and its institutions were directly absorbed by the EU. This made the Union the formal successor institution of the Community.
 W
WEurosclerosis is a term coined by German economist Herbert Giersch in the 1970s, to describe a pattern of economic stagnation in Europe that may have resulted from government over-regulation and overly generous social benefits policies. The term alludes to the medical term sclerosis, and is a rhyme of the archaic term neurosclerosis.
 W
WThe Fouchet Plan was an unsuccessful plan written by Christian Fouchet, France's ambassador to Denmark, and proposed by French President Charles de Gaulle in 1961 as part of de Gaulle's grand design for Europe at the time. The plan included a three-power directorate, consisting of France, Britain and the United States. The idea was to form a new 'Union of States', an intergovernmental alternative to the European Communities that had been created a few years prior. De Gaulle feared a loss of French national influence in the Communities, which were becoming increasingly supranational so the plan was an attempt to keep the balance of power in France's favor. The success of the European Communities and the lack of enthusiasm of other states for the idea stopped the implementation of the Fouchet Plan.
 W
WThe founding fathers of the European Union are 11 men officially recognised as major contributors to European unity and the development of what is now the European Union. All but one were from the Inner Six of the European Union.
 W
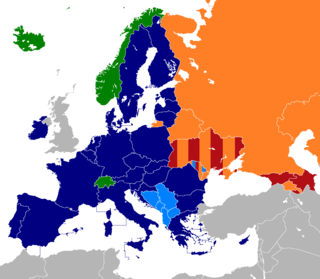
WAt present, there are four multi-lateral free trade areas in Europe, and one former free trade area in recent history. Note that there are also a number of bilateral free trade agreements between states and between trade blocks; and that some states participate in more than one free trade area.
 W
WArsène Heitz was a German-French draughtsman, born in Strasbourg, who worked at the Council of Europe. He is the co-author of the Flag of Europe.
 W
WThe United Kingdom was a member state of the European Union (EU) and of its predecessor the European Communities (EC) - principally the European Economic Community (EEC) from 1 January 1973 until 31 January 2020. Since the foundation of the EEC, the UK had been an important neighbour and then leading member state, until Brexit ended 47 years of membership. During the UK’s time as a member state two referendums were held on the issue of its membership, with the first being held on 5 June 1975, resulting in a vote to stay in the EC, and the second, held on 23 June 2016, which resulted in the vote to leave the EU.
 W
WThe Inner Six, or simply "the Six", were the six founding member states of the European Communities. They were in contrast to the outer seven who formed the European Free Trade Association rather than engage in supranational European integration. Five of the Outer Seven later joined the European Communities.
 W
WThe Intergovernmental Conference on the Common Market and Euratom was held in Brussels and started on 26 June 1956 with a session in the Grand Salon of the Belgian Foreign Ministry. The negotiations went on at the Château of Val-Duchesse in Auderghem (Brussels) and would continue until March 1957. The conference was held to draft the Treaties establishing the European Economic Community (EEC) and the European Atomic Energy Community. The conference built on the results of the Spaak Report of the Spaak Committee and the decision taken at the Venice Conference to prepare the plan for the establishment of a common market and the establishment of a European Community for the peaceful use of atomic energy.
 W
WThe Jean Monnet Foundation for Europe is an organisation which supports initiatives dedicated to the construction of European unity. The foundation is inspired by the thinking, methods and actions of Jean Monnet.
 W
WTheodore de Korwin Szymanowski ; Polish: Teodor Dyzma Makary Korwin Szymanowski pronounced [tɛɔdɔr, dɨzmaˌ makarɨ 'kɔrvin ʂɨmaˈnɔfskʲi]); born in Cygów, Poland on 4 July 1846, died in Kiev, on 20 September 1901) was a Polish nobleman and impoverished landowner, an economic and political theorist writing in French. He was the author in 1885 of a strikingly original economic blueprint for a proto Unified Europe and for the abolition of African slavery. He was also a Polish poet.
 W
WPaul Michel Gabriel, Baron Lévy was a Belgian journalist and professor. He was born in Brussels and was a Holocaust survivor. He worked for many years as Director of Information at the Council of Europe, helping to create the Flag of Europe in the 1950s in collaboration with Arsène Heitz.
 W
WThe London and Paris Conferences were two related conferences held in London and Paris during September–October 1954 to determine the status of West Germany. The talks concluded with the signing of the Paris Agreements, which granted West Germany full sovereignty, ended the occupation, and allowed its admittance to NATO. Furthermore, both West Germany and Italy joined the Brussels Treaty on 23 October 1954. The Agreements went into force on 5 May 1955. The participating powers included France, the United Kingdom, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, West Germany, Italy, Canada, the United States, and remaining NATO members.
 W
WThe Luxembourg Compromise was an agreement reached in January 1966 to resolve the "empty chair crisis" which had caused a stalemate within European Economic Community.
 W
WMarcel Alfons Gilbert van Meerhaeghe was a Belgian economist, professor, publicist and columnist.
 W
WThe Messina Conference of 1955 was a meeting of the six member states of the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC). The conference assessed the progress of the ECSC and, deciding that it was working well, proposed further European integration. This initiative led to the creation in 1957 of the European Economic Community and Euratom.
 W
WJean Omer Marie Gabriel Monnet was a French entrepreneur, diplomat, financier, administrator, and political visionary. An influential supporter of European unity, he is considered as one of the founding fathers of the European Union.
 W
WThe Noordwijk Conference was held in Noordwijk, near The Hague, on 6 September 1955 to evaluate the progress made by the Spaak Committee set up by the Messina Conference. The conference was attended by the Foreign Ministers of the six Member States of the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC). Chairman of the conference was Johan Willem Beyen, then Netherlands Minister for Foreign Affairs.
 W
WThe Ohlin Report was a report drafted by a group of experts of the International Labour Organization led by Bertil Ohlin in 1956. Together with the Spaak Report it provided the basis for the Treaty of Rome on the common market in 1957 and the creation of the European Economic Community in 1958.
 W
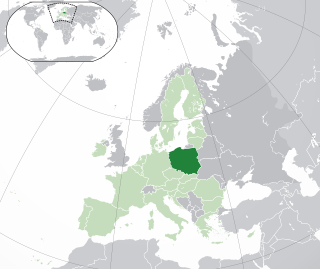
WPoland has been a member state of the European Union since 1 May 2004, with the Treaty of Accession 2003 signed on 16 April 2003 in Athens as the legal basis for Poland's accession to the EU. The actual process of integrating Poland into the EU began with Poland's application for membership in Athens on 8 April 1994, and then the confirmation of the application by all member states in Essen from 9–10 December 1994. Poland's integration into the European Union is a dynamic and continuously ongoing process.
 W
WJózef Hieronim Retinger was a Polish scholar, international political activist with access to some of the leading power brokers of the 20th century, a publicist and writer.
 W
WJean-Baptiste Nicolas Robert Schuman was a Luxembourg-born French statesman. Schuman was a Christian Democrat political thinker and activist. Twice Prime Minister of France, a reformist Minister of Finance and a Foreign Minister, he was instrumental in building postwar European and trans-Atlantic institutions and was one of the founders of the European Union, the Council of Europe and NATO. The 1964–1965 academic year at the College of Europe was named in his honour.
 W
WThe Solemn Declaration on European Union was signed by the then 10 heads of state and government on Sunday 19 June 1983, at the Stuttgart European Council held in Stuttgart.
 W
WThe Spaak Committee was an Intergovernmental Committee set up by the Foreign Ministers of the six Member States of the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) as a result of the Messina Conference of 1955. The Spaak Committee started its work on 9 July 1955 and ended on 20 April 1956, when the Heads of Delegation of the six Member States of the ECSC approved the Spaak report. The committee worked on two main topics, one was the creation of a general common market and the other one was the establishment of a European Community for the peaceful use of atomic energy.
 W
WThe Spaak Report or Brussels Report on the General Common Market is the report drafted by the Spaak Committee in 1956. The Intergovernmental Committee, headed by Paul-Henri Spaak, presented its definitive report on 21 April 1956 to the six governments of the member states of the European Coal and Steel Community.
 W
WPaul-Henri Charles Spaak was an influential Belgian Socialist politician, diplomat and statesman. Along with Robert Schuman, Alcide De Gasperi and Konrad Adenauer he was a leader in the formation of the institutions that evolved into the European Union.
 W
WBetween 1993 and 2009, the European Union (EU) legally comprised three pillars. This structure was introduced with the Treaty of Maastricht on 1 November 1993, and was eventually abandoned on 1 December 2009 upon the entry into force of the Treaty of Lisbon, when the EU obtained a consolidated legal personality.The European Communities pillar handled economic, social and environmental policies. It comprised the European Community (EC), the European Coal and Steel Community, and the European Atomic Energy Community (EURATOM). The Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP) pillar took care of foreign policy and military matters. Police and Judicial Co-operation in Criminal Matters (PJCCM) brought together co-operation in the fight against crime. This pillar was originally named Justice and Home Affairs (JHA)
 W
WThis is a timeline of European Union history and its previous development.
 W
WThe European Political Community (EPC) was proposed in 1952 as a combination of the existing European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) and the proposed European Defence Community (EDC). A draft EPC treaty, as drawn up by the ECSC assembly, would have seen a directly elected assembly, a senate appointed by national parliaments and a supranational executive accountable to the parliament.
 W
WTREVI was an intergovernmental network, or forum, of national officials from ministries of justice and the interior outside the European Community framework, proposed during the European Council meeting in Rome, 1–2 December 1975. It was formalized in Luxembourg on 29 June 1976 at a meeting of the European Council's Interior Ministers. It ceased to exist when it was integrated into the so-called Justice and Home Affairs (JHA) pillar of the European Union (EU) upon the entry into force of the Treaty of Maastricht in 1993.
 W
WThe Venice Conference was held in Venice on 29 and 30 May 1956. The Foreign Ministers of the six Member States of the European Coal and Steel Community met at the Cini Foundation on the Venetian island of San Giorgio Maggiore to discuss the Spaak Report of the Spaak Committee. At the conference the Foreign Ministers explained the views of the ECSC governments on the proposals in the Spaak Report. As a result of the conference they decided to organize the Intergovernmental Conference on the Common Market and Euratom in order to prepare for establishment of a common market and a European Community for the peaceful use of nuclear power.
 W
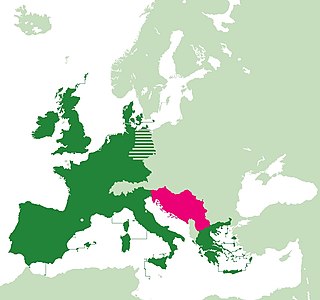
WFrom the establishment of the European Economic Community in 1957 until the breakup of Yugoslavia in the early 1990s, thus during the Cold War period, the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was the first socialist state to develop relations with the organisation. Notwithstanding occasional and informal proposals coming from both sides, Yugoslavia never became a full member state of the EEC.