 W
WAbdullah's entry into Transjordan on 21 November 1920 marked the beginning of the second period of Hashemite rule in the Transjordan region following a brief interregnum period. Abdullah, the second son of Sharif Hussein, arrived from Hejaz by train in Ma'an in southern Transjordan on 21 November 1920 to redeem the Kingdom his brother had lost. Transjordan then was in disarray and widely considered to be ungovernable with its dysfunctional local governments.
 W
WThe Madaba Map, also known as the Madaba Mosaic Map, is part of a floor mosaic in the early Byzantine church of Saint George in Madaba, Jordan. The Madaba Map is of the Middle East, and part of it contains the oldest surviving original cartographic depiction of the Holy Land and especially Jerusalem. It dates to the 6th century AD.
 W
WThe Mutasarrifate of Jerusalem, also known as the Sanjak of Jerusalem, was an Ottoman district with special administrative status established in 1872. The district encompassed Jerusalem as well as Bethlehem, Hebron, Jaffa, Gaza and Beersheba. During the late Ottoman period, the Mutasarrifate of Jerusalem, together with the Sanjak of Nablus and Sanjak of Akka (Acre), formed the region that was commonly referred to as "Palestine". It was the 7th most heavily populated region of the Ottoman Empire's 36 provinces.
 W
WThe Occupation of Ma'an was the post-World War I occupation of the Sanjak of Ma'an, which straddled the regions of Syria and Arabia, by members of the Hashemite family, who came to power in various regions of the Near East and Arabia; they were King Hussein in the Kingdom of Hejaz, Emir Faisal representing the Arab government in Damascus and Abdullah, who was to become Emir of Transjordan. The region includes the governorates of Ma'an and Aqaba, today in Jordan, as well as the area which was to become a large part of the Israeli Southern District, including the city of Eilat.
 W
WPalaestina Salutaris or Palaestina Tertia was a Byzantine province, which covered the area of the Negev, Sinai and south-west of Transjordan, south of the Dead Sea. The province, a part of the Diocese of the East, was split from Arabia Petraea during the reforms of Diocletian in c.300 CE, and existed until the Muslim Arab conquests of the 7th century.
 W
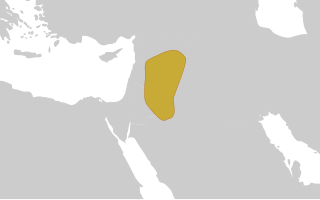
WThe Salīḥids, also known simply as Salīḥ or by their royal house, the Zokomids were the dominant Arab foederati of the Byzantine Empire in the 5th century. They succeeded the Tanukhids, who were dominant in the 4th century, and were in turn defeated and replaced by the Ghassanids in the early 6th century.
 W
WThe region of Syria, known in modern literature as Greater Syria, "Syria-Palestine", or the Levant, is an area east of the Mediterranean Sea. The region has been controlled by numerous different peoples, including ancient Egyptians, Canaanites, Israelites, Assyria, Babylonia, the Achaemenid Empire, the ancient Macedonians, the Roman Empire, the Byzantine Empire, the Rashidun Caliphate, the Umayyad Caliphate, the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimid Caliphate, the Crusaders, the Ayyubid dynasty, the Mamluk Sultanate, the Ottoman Empire, the United Kingdom and the French Third Republic.