 W
WMongol Armenia or Ilkhanid Armenia refers to the period in which both Armenia and the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia became tributary and vassal to the Mongol Empire in the 1230s. Armenia and Cilicia remained under Mongol influence until around 1335.
 W
WThe Mongol conquests of the 13th century resulted in widespread destruction that has been widely noted in scholarly literature. The Mongol army conquered hundreds of cities and villages and also killed millions of men, women and children. It has been estimated that approximately 11% of the world's population was killed either during or immediately after the Turco-Mongol invasions. If the calculations are accurate, the events would be the deadliest acts of mass killings in human history.
 W
WThe following is a list of Mongol rulers.
 W
WThe qualifier Mongol Tribes was established as an umbrella term in the early 13th century, when Temüjin united the different tribes under his control and established the Mongol Empire. There were 19 Nirun tribes that descended from Bodonchar and 18 Darligin tribes, which were also core Mongolic tribes but not descending from Bodonchar. The unification created a new common ethnic identity as Mongols. Descendants of those clans form the Mongolian nation and other Inner Asian people .
 W
WThe Pax Mongolica, less often known as Pax Tatarica, is a historiographical term modelled after the original phrase Pax Romana which describes the stabilizing effects of the conquests of the Mongol Empire on the social, cultural and economic life of the inhabitants of the vast Eurasian territory that the Mongols conquered in the 13th and 14th centuries. The term is used to describe the eased communication and commerce the unified administration helped to create and the period of relative peace that followed the Mongols' vast conquests.
 W
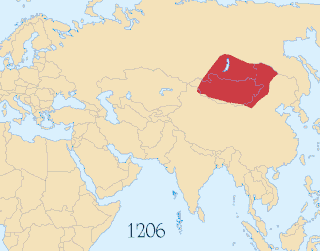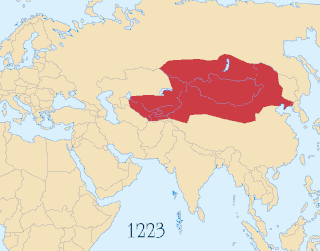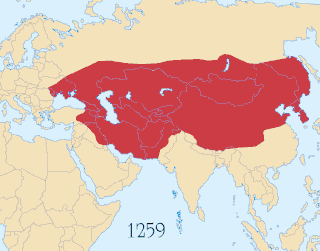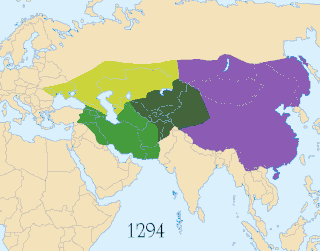
WThis article discusses the political divisions and vassals of the Mongol Empire. Through invasions and conquests the Mongols established a vast empire that included many political divisions, vassals and tributary states. It was the largest contiguous land empire in history. However, after the death of Möngke Khan, the Toluid Civil War and subsequent wars had led to the fragmentation of the Mongol Empire. By 1294, the empire had fractured into four autonomous khanates, including the Golden Horde in the northwest, the Chagatai Khanate in the middle, the Ilkhanate in the southwest, and the Yuan dynasty in the east based in modern-day Beijing, although the Yuan emperors held the nominal title of Khagan of the empire.
 W
WThis is the timeline of the Mongol Empire from the birth of Temüjin, later Genghis Khan, to the ascension of Kublai Khan as emperor of the Yuan dynasty in 1271, though the title of Khagan continued to be used by the Yuan rulers into the Northern Yuan dynasty, a far less powerful successor entity, until 1634.