 W
WEast Belarus usually refers to the part of Belarus that was part of the Soviet Union between 1919 and 1939, as opposed to West Belarus that was part of the Second Polish Republic at that time.
 W
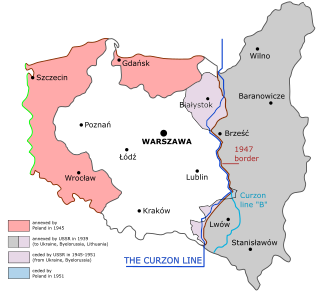
WKresy Wschodnie or simply Kresy was a term coined for the eastern part of the Second Polish Republic during the interwar period (1918–1939). Largely agricultural and extensively multi-ethnic, it amounted to nearly half of the territory of pre-war Poland. Historically situated in the eastern Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, following the 18th-century foreign partitions it was annexed by Russia and partly by the Habsburg Monarchy (Galicia), and ceded back to Poland in 1921 after the Peace of Riga. As a result of the post-World War II border changes, none of the Kresy lands remain in Poland today.
 W
WLithuania proper refers to a region which existed within the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and where the Lithuanian language was spoken. The primary meaning is identical to the Duchy of Lithuania, a land around which the Grand Duchy of Lithuania evolved. The territory can be traced by Catholic Christian parishes established in pagan Baltic lands of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania subsequent to the Christianization of Lithuania in 1387. The Lithuania Proper was always distinguished from the Ruthenian lands, the Lithuanians differed from the Ruthenians in their language and faith. . The term in Latin was widely used during the Middle Ages and can be found in numerous historical maps until World War I.
 W
WPodlachia or Podlasie, is a historical region in the eastern part of Poland. Between 1513 and 1795 it was a voivodeship with the capital in Drohiczyn. Now the part north of the Bug River is included in the modern Podlaskie Voivodeship with the capital in Białystok.
 W
WPolesia, Polesie or Polesye is a natural and historical region, which starts from the farthest edge of Central Europe, encompasses Eastern Europe, including Eastern Poland, Belarus–Ukraine border and Western Russia.
 W
WThe Russian Partition constituted the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that were annexed by the Russian Empire in the course of late-18th-century Partitions of Poland. The Russian acquisition encompassed the largest share of Poland's population, living on 463,200 km2 of land constituting the eastern and central territory of the previous commonwealth. The first partitioning led by imperial Russia took place in 1772; the next one in 1793, and the final one in 1795, resulting in Poland's elimination for the next 123 years.
 W
WVilnius Region is the territory in the present-day Lithuania and Belarus that was originally inhabited by ethnic Baltic tribes and was a part of Lithuania proper, but came under East Slavic and Polish cultural influences over time.
 W
WWestern Belorussia or Western Belarus is a historical region of modern-day Belarus comprising the territory which belonged to the Second Polish Republic during the interwar period in accordance with the international peace treaties. Before the 1939 Nazi-Soviet invasion of Poland, it used to form the northern part of the Polish Kresy macroregion. Following the end of World War II in Europe, the territory of Western Belorussia was ceded to the Soviet Union by the Allied Powers, while the city of Białystok with surroundings was returned to Poland. Until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 Western Belorussia formed a significant part of the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR). Today, it constitutes the western part of the sovereign Republic of Belarus.