 W
WThe Hasmonean dynasty was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during classical antiquity, from c. 140 BCE to 37 BCE. Between c. 140 and c. 116 BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously from the Seleucid Empire, and from roughly 110 BCE, with the empire disintegrating, Judea gained full independence and expanded into the neighboring regions of Samaria, Galilee, Iturea, Perea, and Idumea. The Hasmonean rulers took the title "basileus,, and some modern scholars refer to this period as an independent kingdom of Israel. The kingdom was ultimately conquered by the Roman Republic and the dynasty was displaced by Herod the Great in 37 BCE.
 W
WIsrael, officially known as the State of Israel, is a country in Western Asia, located on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea. It has land borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan on the east, the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel's economic and technological center is Tel Aviv, while its seat of government and proclaimed capital is Jerusalem, although international recognition of the state's sovereignty over Jerusalem is limited.
 W
WAccording to the Hebrew Bible, the Kingdom of Israel, was one of two successor states to the former United Kingdom of Israel and Judah. Historians often refer to the Kingdom of Israel as the "Northern Kingdom" or as the "Kingdom of Samaria" to differentiate it from the Southern Kingdom of Judah.
 W
WThe United Monarchy is the name given to the Israelite kingdom of Israel and Judah, during the reigns of Saul, David and Solomon, as depicted in the Hebrew Bible. This is traditionally dated between 1047 BCE and 930 BCE. On the succession of Solomon's son, Rehoboam, around 930 BCE, the biblical account reports that the country split into two kingdoms: the Kingdom of Israel in the north and the Kingdom of Judah in the south.
 W
WThe Jewish Autonomous Oblast is a federal subject of Russia in the Russian Far East, bordering Khabarovsk Krai and Amur Oblast in Russia and Heilongjiang province in China. Its administrative center is the town of Birobidzhan.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Judah was an Iron Age kingdom of the Southern Levant. The Hebrew Bible depicts it as the successor to the United Monarchy, a term denoting the Kingdom of Israel under biblical kings Saul, David and Solomon and covering the territory of two historical kingdoms, Judah and Israel. However, some scholars, including Israel Finkelstein and Alexander Fantalkin, believe that the existent archaeological evidence for an extensive Kingdom of Judah before the late 8th century BCE is too weak and that the methodology used to obtain the evidence is flawed. The Tel Dan Stele shows that the kingdom, in some semblance, existed by at least the mid-9th century BCE, but it does little to show to what extent.
 W
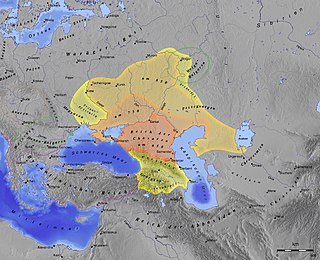
WThe Khazars were a semi-nomadic Turkic people with a confederation of Turkic-speaking tribes that in the late 6th century CE established a major commercial empire covering the southeastern section of modern European Russia, southern Ukraine, Crimea and Kazakhstan. The Caspian Sea is still called the Khazar Sea in some local languages such as Azerbaijani (Khazar-deniz). The Khazars created what for its duration was the most powerful polity to emerge from the break-up of the Western Turkic Khaganate. Astride a major artery of commerce between Eastern Europe and Southwestern Asia, Khazaria became one of the foremost trading empires of the medieval world, commanding the western marches of the Silk Road and playing a key commercial role as a crossroad between China, the Middle East and Kievan Rus'. For some three centuries the Khazars dominated the vast area extending from the Volga-Don steppes to the eastern Crimea and the northern Caucasus.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Semien, sometimes referred to as the Kingdom of Beta Israel, was an ancient kingdom of the Beta Israel centered in the northwestern part of the Ethiopian Empire that came to an end in 1627 during the reign of emperor Susenyos I.
 W
WThe Taifa of Granada was a Berber emirate in Al-Andalus, roughly corresponding to the modern province of Granada, Spain, in southern Spain. The emirate originated in 1013 and lasted until 1091.