 W
WBush encroachment is a natural phenomenon characterised by the increase in density of woody plants at the expense of the herbaceous layer. It is often considered an ecological regime shift and a symptom of land degradation. Bush encroachment is found to have severe negative consequences on key ecosystem services, especially biodiversity, animal habitat, land productivity and groundwater recharge. Bush encroachment can refer both to the expansion of native plants as well as the invasion and spread of invasive species. The phenomenon is observed across different ecosystems and with different characteristics and intensities globally. Among the more severely affected landscapes is the Veld in Southern Africa.
 W
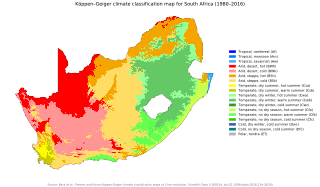
WThe climate of South Africa is determined by South Africa's situation between 22°S and 35°S, in the Southern Hemisphere's subtropical zone, and its location between two oceans, Atlantic and the Indian.
 W
WThe Department of Environment, Forestry & Fisheries is one of the departments of the South African government. It is responsible for protecting, conserving and improving the South African environment and natural resources. It was created in 2019 by the merger of the Department of Environmental Affairs with the forestry and fisheries components of the Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries.
 W
WThe environmental movement in South Africa traces its history from the early beginnings of conservation, to the rise of radicalism and activism amongst local ecologists. Before the Chernobyl disaster and the fall of the Berlin Wall, there were very few green activist groups in the country. Koeberg Alert and the Dolphin Action and Protection Group are probably two of the oldest post-conservation groups.
 W
WThe Highveld is the portion of the South African inland plateau which has an altitude above roughly 1500 m, but below 2100 m, thus excluding the Lesotho mountain regions to the south-east of the Highveld. It is home to some of the country's most important commercial farming areas, as well as its largest concentration of metropolitan centres, especially the Gauteng conurbation, which accommodates one-third of South Africa's population.
 W
WThis is a list of invasive species in South Africa, including invasive species of plants, animals, and other organisms in South Africa.
 W
WThe Lesotho Highlands are formed by the Drakensberg and Maloti mountain ranges in the east and central parts of the country of Lesotho. Foothills form a divide between the lowlands and the highlands. Snow is common in the highlands in the winter.
 W
WNetSys International (Pty) Ltd. is a South African–based company, specialising in solutions for the weather and aviation industries.
 W
WWater supply and sanitation in South Africa is characterised by both achievements and challenges. After the end of Apartheid South Africa's newly elected government struggled with the then growing service and backlogs with respect to access to water supply and sanitation developed. The government thus made a strong commitment to high service standards and to high levels of investment subsidies to achieve those standards. Since then, the country has made some progress with regard to improving access to water supply: It reached universal access to an improved water source in urban areas, and in rural areas the share of those with access increased from 66% to 79% from 1990 to 2010.
 W
WThe practice of whaling in South Africa gained momentum at the start of the 19th century and ended in 1975. By the mid-1960s, South Africa had depleted their population of fin whales, and subsequently those of sperm and sei whales, and had to resort to hunting the small and less-profitable minke whale. Minke whales continued to be caught and brought to the Durban whaling station from 1968 until 1975. South Africa comprehensively banned whaling in 1979.