 W
WA geologic map is a special-purpose map made to show various geological features. Rock units or geologic strata are shown by color or symbols. Bedding planes and structural features such as faults, folds, are shown with strike and dip or trend and plunge symbols which give three-dimensional orientations features.
 W
WDigimap is a web mapping and online data delivery service developed by the EDINA national data centre for UK academia. It offers a range of on-line mapping and data download facilities which provide maps and spatial data from Ordnance Survey, British Geological Survey, Landmark Information Group and OceanWise Ltd Ltd.,, Getmapping Ltd, the Environment Agency, OpenStreetMap, CollinsBartholomew Ltd, and various other sources.
 W
WDigital geologic mapping is the process by which geological features are observed, analyzed, and recorded in the field and displayed in real-time on a computer or personal digital assistant (PDA). The primary function of this emerging technology is to produce spatially referenced geologic maps that can be utilized and updated while conducting field work.
 W
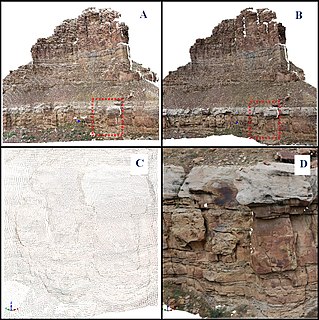
WA digital outcrop model (DOM), also called a virtual outcrop model, is a digital 3D representation of the outcrop surface, mostly in a form of textured polygon mesh.
 W
WGeological map of Senegal at 1/500 000
 W
WSir James Hector FRS FRSE(16 March 1834 – 6 November 1907) was a Scottish geologist, naturalist, and surgeon who accompanied the Palliser Expedition as a surgeon and geologist. He went on to have a lengthy career as a government employed man of science in New Zealand, and during this period he dominated the Colony's scientific institutions in a way that no single man has since.
 W
WThe Map that Changed the World is a 2001 book by Simon Winchester about English geologist William Smith and his great achievement, the first geological map of England, Wales and southern Scotland.
 W
WA swathe or swath is the width of a scythe stroke or a mowing-machine blade, the path of this width made in mowing or the mown grass or grain lying on such a path. The mower with a scythe moves along the mowing-edge with the uncut grass to the right and the cut grass laid in a neat row to the left, on the previously mown land. The swathe width depends on the blade length, the nature of the crop and the mower but is usually about 1.5 metres wide. Mowing may be done by a team of mowers, usually starting at the edges of a meadow then proceeding clockwise leaving a series of staggered swathes and finishing in the middle.
 W
WThe Turin Papyrus Map is an ancient Egyptian map, generally considered the oldest surviving map of topographical interest from the ancient world. It is drawn on a papyrus reportedly discovered at Deir el-Medina in Thebes, collected by Bernardino Drovetti in Egypt sometime before 1824 AD and now preserved in Turin's Museo Egizio. The map was drawn about 1150 BC by the well-known Scribe-of-the-Tomb Amennakhte, son of Ipuy. It was prepared for Ramesses IV's quarrying expedition to the Wadi Hammamat in the Eastern Desert, which exposes Precambrian rocks of the Arabian-Nubian Shield. The purpose of the expedition was to obtain blocks of bekhen-stone to be used for statues of the king.
 W
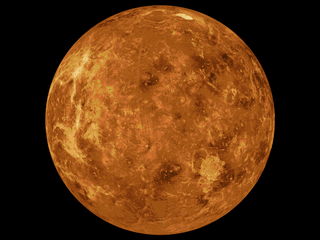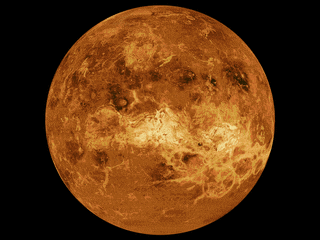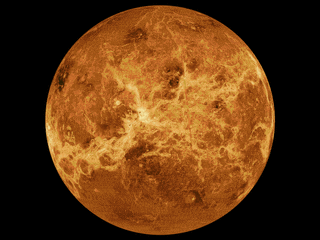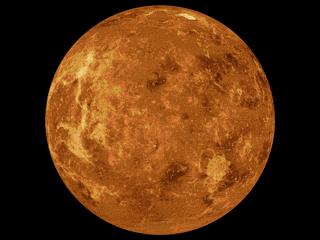
WThe mapping of Venus refers to the process and results of human description of the geological features of the planet Venus. It involves surface radar images of Venus, construction of geological maps, and the identification of stratigraphic units, volumes of rock with a similar age.