 W
WThe main points that are discussed in the geology of Iran include the study of the geological and structural units or zones; stratigraphy; magmatism and igneous rocks; ophiolite series and ultramafic rocks; and orogenic events in Iran.
 W
WThe Geological Survey and Mineral Exploration of Iran or in brief GSI is a government agency responsible for conducting geological and mineral surveys throughout the country, collecting the results of activities carried out in this field, establishing coordination, preparing and publishing geological maps of Iran. It is a subdivision of the Ministry of Industry, Mine and Trade, which was established in 1962 in cooperation with United Nations.
 W
WThe Hormuz Formation, Hormuz Series, Hormuz Evaporites or Hormuz Group is a sequence of evaporites that were deposited during the Ediacaran to Early Cambrian, a period previously referred to as the Infra-Cambrian. Most exposures of this sequence are in the form of emergent salt diapirs within anticlines of the Zagros fold and thrust belt. As a result of their involvement in post-depositional salt tectonics, the internal stratigraphy of the sequence is relatively poorly understood. They are the lateral equivalent of the evaporite-bearing Ara Group in the South Oman Basin.
 W
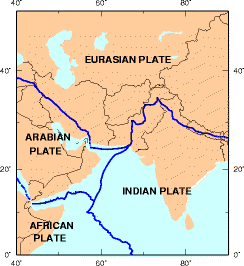
WThe Iranian Plate is a small tectonic plate thought to underlie Iran and Afghanistan, and parts of Iraq and Pakistan.
 W
WEngineer Nasrollah Khadem was one of the first prominent geological experts in Iran. He is the founder of the Geological Survey and Mineral Exploration of Iran. He played a major role in the development of Geology science and Mining engineering in Iran. Through his efforts, important mines were discovered and exploited in Iran.
 W
WThe Makran Trench is the physiographic expression of a subduction zone along the northeastern margin of the Gulf of Oman adjacent to the southwestern coast of Balochistan of Pakistan and the southeastern coast of Iran. In this region the oceanic crust of the Arabian Plate is being subducted beneath the continental crust of the Eurasian Plate.
 W
WThe National Geoscience Database of Iran or in brief NGDIR is a scientific and research government agency in Iran which works in the field of Geology of Iran and centrally manages Geoscience data. This center was established in 1999 in the field of data collection authority with the aim of managing, preserving and sharing Geoscience data.
 W
WProven oil reserves in Iran, according to its government, rank fourth largest in the world at approximately as of 2013, although it ranks third if Canadian reserves of unconventional oil are excluded. This is roughly 10% of the world's total proven petroleum reserves. At 2020 rates of production, Iran's oil reserves would last 145 years if no new oil was found.
 W
WPirgel is a mud volcano in Iran, in the province Sistan and Balochistan close to the town of Khash. The mud volcano is accessible via a foot track.
 W
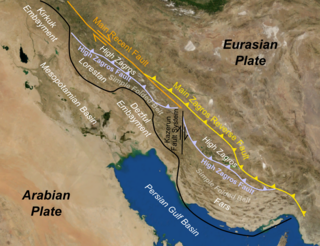
WThe Zagros fold and thrust belt is an approximately 1,800-kilometre (1,100 mi) long zone of deformed crustal rocks, formed in the foreland of the collision between the Arabian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is host to one of the world's largest petroleum provinces, containing about 49% of the established hydrocarbon reserves in fold and thrust belts (FTBs) and about 7% of all reserves globally.