 W
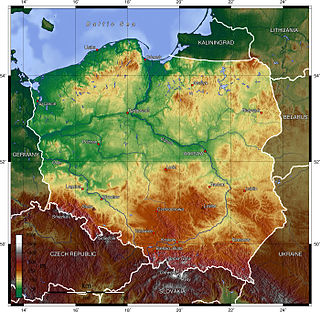
WPoland is a country that extends across the North European Plain from the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south to the sandy beaches of the Baltic Sea in the north. Poland is the fifth-most populous country of the European Union and the ninth-largest country in Europe by area. The territory of Poland covers approximately 312,696 km2 (120,733 sq mi), of which 98.52% is land and 1.48% is water. The Polish coastline was estimated at 770 km (478 mi) in length. Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, at 2,499 km (1,553 mi).
 W
WThe Central European Highlands, in a broad sense, comprise the high mountains of the Alpine Mountains and the Carpathian Mountains systems along with mountainous ranges of medium elevation, e.g. those belonging to the Bohemian Massif, still prevailingly of mountainous character.
 W
WEuroregion Cieszyn Silesia is one of the euroregions between Poland and Czech Republic. It has area of 1741,34 km² and 658,224 inhabitants as of 2009. The largest cities are Jastrzębie Zdrój from Polish side and Havířov from Czech side. It was established on 22 April 1998.
 W
WThe Euroregion Pradziad (Polish) or Euroregion Praděd (Czech) is a Euroregion joining parts of the Poland and Czech Republic. It was created on 2 July 1997 in Jeseník.
 W
WThis is a list of the extreme points of Poland, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
 W
WPodlachia or Podlasie, is a historical region in the eastern part of Poland. Between 1513 and 1795 it was a voivodeship with the capital in Drohiczyn. Now the part north of the Bug River is included in the modern Podlaskie Voivodeship with the capital in Białystok.
 W
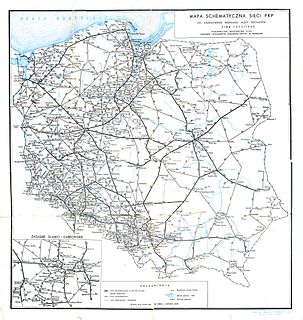
WPoland A and B refers to the historical, political and cultural distinction between the western and the eastern part of the country, with Poland "A", west of the Vistula, being much more developed and having faster growth than Poland "B", east of the river. The General Secretary of Krajowa Izba Gospodarcza Marek Kłoczko, said in his 2007 interview that the divisions are more spread out and forming three separate categories, Poland "A" is the metropolitan cities, Poland "B" is the rest of the country, and Poland "C" is the plains and the landscape parks east of the Vistula, which require a different treatment.
 W
WEuroregion Silesia is one of Euroregions in Poland and Czechia.
 W
WThe Wrześnica is a 49-kilometer (30.4 mi)-long, right tributary of the Warta in Poland. Its river basis covers an area of 355 km². It has its source near Piekary, a suburb of Gniezno. It meets the Warta near the village of Samarzewo. Important cities along the Wrześnica river include Czerniejewo, Września.
 W
WZakerzonia is an informal name for the territories of Poland to the west of the Curzon Line which used to have sizeable Ukrainian populations, including significant Lemko, Boyko and Ruthenian populations, before the invasion of Poland by the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany in 1939, and were claimed as ethnically Ukrainian territories by Ukrainian nationalists in the aftermath of World War II.
 W
WŻuławy Wiślane is the alluvial delta area of Vistula, in the northern part of Poland, in large part reclaimed artificially by means of dykes, pumps, channels and extensive drainage system. Its shape is similar to a reversed triangle formed by branching of Vistula into two separate rivers, Leniwka and Nogat at its height, confined by rivers themselves, and closed by Mierzeja Wiślana at its base. It is a deforested, agricultural plain that covers about 1000 square km.