 W
WThe geography of the European Union describes the geographic features of the European Union (EU), a multinational polity that occupies a large portion of Europe and covers 4,422,773 km2 (1,707,642 sq mi). Its European territory extends northeast to Finland, northwest to Ireland, southeast to Cyprus and southwest to the Spanish exclaves on the Mediterranean shores of North Africa. Additionally, the EU includes numerous islands around the world, and French Guiana in South America.
 W
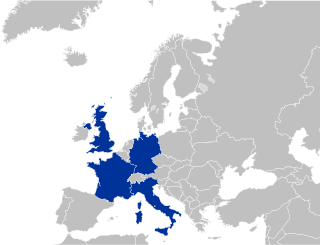
WThe Big Four, also known as G4, refers to France, Germany, Italy and the United Kingdom. France and the United Kingdom are official nuclear-weapon states and are permanent members of the United Nations Security Council with the power of veto, which enables any one of them to prevent the adoption of any "substantive" draft Council resolution, regardless of its level of international support. France, Germany, Italy and the United Kingdom are considered major European economic powers and they are the Western European countries individually represented as full members of the G7, the G8, the G10 and the G20. They have been referred to as the "Big Four of Europe" since the interwar period. The term G4 was used for the first time when French President Nicolas Sarkozy called for a meeting in Paris with Italian Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Gordon Brown and Chancellor of Germany Angela Merkel to consider the response to the financial crisis during the Great Recession. The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development describes them as the "Four Big European Countries".
 W
WIslam is the fastest-growing major religion in Europe, primarily due to immigration and higher fertility rates among Muslims. Since the 1960s, immigrants from Muslim countries started to appear in numbers in Western Europe, especially in Germany, France and Belgium. Although large Muslim communities have existed on the continent since Ottoman conquests in the late Middle Ages, especially in the Balkans, this was the first major wave of immigration of Muslims to northwestern Europe.
 W
WThis is a list of the extreme points of the European Union — the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
 W
WThe G6 in the European Union is an unofficial group of the interior ministers of the six European Union member states—France, Germany, Italy, Poland, Spain, and the United Kingdom—with the largest populations and thus with the majority of votes in the Council of the European Union. The G6 was established in 2003 as G5 to deal with immigration, terrorism and law and order. In 2006, Poland joined the group, making it the G6.
 W
WIn 2016, the impact of Brexit on the European Union (EU) was expected to result in social and economic changes to the Union, but also longer term political and institutional shifts. The extent of these effects remain somewhat speculative until the precise terms of the United Kingdom's post-Brexit relationship with the EU becomes clear. With an end to UK participation in the EU's policies on freedom of movement and the European Union Customs Union, as well as sharing criminal intelligence and other matters, there is a clear impact with consequences for both institutions.
 W
WThe Inner Six, or simply "the Six", were the six founding member states of the European Communities. They were in contrast to the outer seven who formed the European Free Trade Association rather than engage in supranational European integration. Five of the Outer Seven later joined the European Communities.
 W
WThe European Union created a Committee of the Regions to represent Regions of Europe as the layer of EU government administration directly below the nation-state level. The Committee has its headquarters in Brussels.
 W
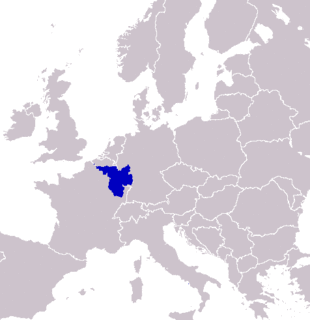
WSaarLorLux or Saar-Lor-Lux, a portmanteau of Saarland, Lorraine and Luxembourg, is a euroregion of five regional authorities located in four European states. The term has also been applied to cooperations of several of these authorities or of their subdivisions, administrations, organisations, clubs and people. Member regions represent different political structures: the sovereign state of Luxembourg; Belgium's Walloon region, comprising the French and German speaking parts of Belgium; Lorraine, a region of France; the French départements Moselle and Meurthe-et-Moselle; and the German federated states of Saarland and Rhineland-Palatinate.
 W
WWithdrawal from the European Union is the legal and political process whereby an EU member state ceases to be a member of the Union. Article 50 of the Treaty on European Union (TEU) states that "Any Member State may decide to withdraw from the Union in accordance with its own constitutional requirements".
 W
WWithdrawal from the Eurozone denotes the process whereby a Eurozone member-state, whether voluntarily or forcibly, stops using the euro as its national currency and leaves the Eurozone. As of August 2020, no country has withdrawn from the Eurozone.