 W
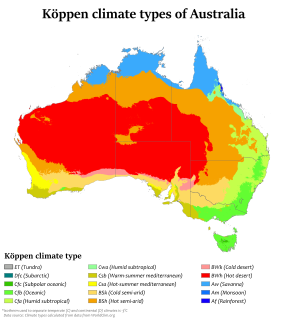
WAustralia's climate is governed mostly by its size and by the hot, sinking air of the subtropical high pressure belt. This moves north-west and north-east with the seasons. The climate is variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons, thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Australia has a wide variety of climates due to its large geographical size. The largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid. Only the south-east and south-west corners have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate, varying between grasslands and desert. Australia holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, and the highest sunshine duration.
 W
WThe Antarctic oscillation, also known as the Southern Annular Mode (SAM), is a low-frequency mode of atmospheric variability of the southern hemisphere that is defined as a belt of strong westerly winds or low pressure surrounding Antarctica which moves north or south as its mode of variability.
 W
WA Black nor'easter is a persistent and potentially violent north-easterly storm that occurs on the east coast of Australia during spring and summer, usually about two days a year. It is not a convection wind, but a storm system that develops offshore which can last several days. This is heralded by the rapid build-up of dense black cloud that can convert to a gale in well under one hour, and also bringing with it a heavy rainfall event usually accompanied by a thunderstorm. This type of storm was first recorded during the 1800s.
 W
WClimate change in Australia has been a critical issue since the beginning of the 21st century. Australia is becoming hotter, and more prone to extreme heat, bushfires, droughts, floods and longer fire seasons because of climate change. Since the beginning of the 20th century Australia has experienced an increase of nearly 1 °C in average annual temperatures, with warming occurring at twice the rate over the past 50 years than in the previous 50 years. Recent climate events such as extremely high temperatures and widespread drought have focused government and public attention on the impacts of climate change in Australia.
 W
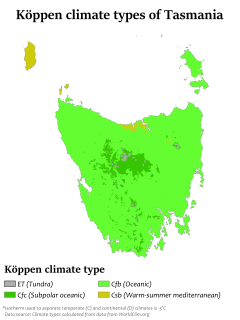
WTasmania has a cool temperate climate with four distinct seasons. The highest recorded maximum temperature in Tasmania is 42.2 °C (108.0 °F) at Scamander on 30 January 2009, during the 2009 southeastern Australia heat wave. Tasmania's lowest recorded minimum temperature is −14.2 °C (6.4 °F) on 7 August 2020, at Central Plateau.
 W
WThe desert climate or arid climate, is a climate which there is an excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert climates hold little moisture and evaporate the little rainfall they receive. Covering 14.2% of earth's land area, hot deserts are the most common type of climate on earth after polar climate.
 W
WDrought in Australia is defined by the Australian Bureau of Meteorology as rainfall over a three-month period being in the lowest decile of what has been recorded for that region in the past. This definition takes into account that drought is a relative term and rainfall deficiencies need to be compared to typical rainfall patterns including seasonal variations. Specifically, drought in Australia is defined in relation to a rainfall deficiency of pastoral leases and is determined by decile analysis applied to a certain area. Note that this definition uses rainfall only because long-term records are widely available across most of Australia. However, it does not take into account other variables that might be important for establishing surface water balance, such as evaporation and condensation.
 W
WThe Fremantle Doctor, the Freo Doctor, or simply The Doctor is the Western Australian vernacular term for the cooling afternoon sea breeze that occurs during summer months in south west coastal areas of Western Australia. The sea breeze occurs because of the major temperature difference between the land and sea.
 W
WHector is a cumulonimbus thundercloud that forms regularly nearly every afternoon on the Tiwi Islands in the Northern Territory of Australia, from approximately September to March each year. Hector, or sometimes "Hector the Convector", is known as one of the world's most consistently large thunderstorms, reaching heights of approximately 20 kilometres (66,000 ft).
 W
WSevere storms in Australia refers to the storms, including cyclones, which have caused severe damage in Australia.
 W
WA southerly buster is the colloquial name of an abrupt southerly wind change in the southern regions of New South Wales and Victoria, Australia, which approaches from the southeast, mainly on a hot day, bringing in cool, usually severe weather and a dramatic temperature drop, thus ultimately replacing and relieving the prior hot conditions. Marking the boundary between hot and cool air masses, a southerly buster is sometimes represented by a roll-up cloud perpendicular to the coast, which appears from the south and coexists with the wind change, though sometimes there is little visual signal of the southerly's arrival.
 W
WThe Todd Weather Folios are a collection of continental Australian synoptic charts that were published from 1879 to 1909.