 W
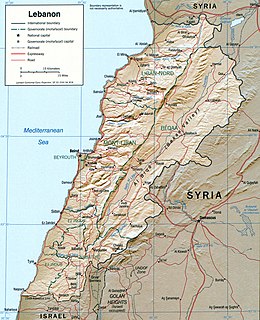
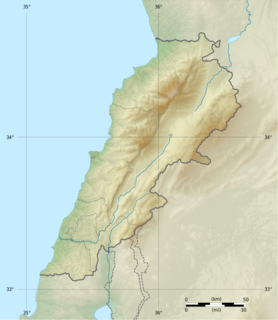
WLebanon is a small country in the Middle East, located at approximately 34˚N, 35˚E. It stretches along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and its length is almost three times its width. From north to south, the width of its terrain becomes narrower. Lebanon's mountainous terrain, and the economic and religious movements that either originated in the region or crossed through to leave an imprint upon Lebanese society, give form to the country's history.
 W
WBaraachit, also spelt Brashit, is a rural town located in the Nabatiye Governorate, in the Bint Jbeil District of southern Lebanon, ca. 3.5 kilometres (2.2 mi) southeast of Tibnine and about 80 kilometres (50 mi) from Beirut. The village sits on an elevation of 710 metres (2,330 ft) above sea level. The town has a mixed population of Shi'a and Christians.
 W
WFaqra is a ski resort on the outskirts of the Kfardebian village in the Keserwan District in Mount Lebanon, 47 km (29 mi) from Beirut and 36 km (22 mi) from Jounieh.
 W
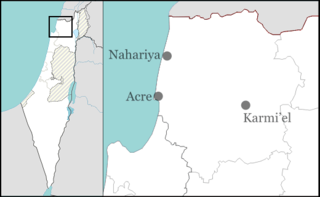
WLadder of Tyre, , also known as the Ladder of the Tyrians and the Promontory of Tyre, is a geographical feature mentioned in Greek and Hebrew sources, distinguished by a littoral mountainous range, the highest point of which is distant 18.5 kilometres (11.5 mi) north of Acre in northern Israel. The range stretches beyond Tyre in southern Lebanon. Along its Mediterranean coastline, the Ladder of Tyre skirts an area of about five miles wide at its greatest width, and is distinguished by capes that jut westward into the sea from the ridge which runs parallel to the general line of the coast. These capes project more than a mile into the sea, and rise precipitously at a mean elevation of 250 feet (76 m) above sea level. The Ladder of Tyre is mentioned in the Babylonian Talmud, in the Jerusalem Talmud, in the First Book of Maccabees (11:59), and in the writings of Josephus.
 W
WLaqlouq, also spelled Laklouk and also known as ′Arab Laqlouq is a small mountainous village in mountainous area in the Byblos District of Mount Lebanon Governorate, Lebanon. It is located 69 kilometers northeast of Beirut. Laqlouq has an average elevation of 1,780 meters above sea level and a total land area of 210 hectares. Most of the inhabitants are Sunni Muslims, in contrast to the majority of Byblos District's population, which is largely Maronite Christian with a significant Shia Muslim minority.
 W
WThe Levant is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, it is equivalent to the historical region of Syria, which included present-day Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Palestine and most of Turkey south-east of the middle Euphrates. In its widest historical sense, the Levant included all of the Eastern Mediterranean with its islands; that is, it included all of the countries along the Eastern Mediterranean shores, extending from Greece to Cyrenaica in eastern Libya.
 W
WMargaliot is a moshav in northern Israel. Located along the border with Lebanon in the Upper Galilee, near the town of Kiryat Shmona, it falls under the jurisdiction of Mevo'ot HaHermon Regional Council. In 2019 it had a population of 412, most of them Jews of Iranian Kurdistan descent.
 W
WMzaar Kfardebian is a ski area in Lebanon and the largest ski resort in the Middle East. It is located one hour away from Beirut, the capital of Lebanon. It is also referred to as Ouyoune el Simane.
 W
WRas el Ain,, is a place abounding with immense fountains, with reservoirs and aqueducts 6 kilometers (3.7 mi) south of Tyre, and ca. 77 kilometers (48 mi) south of Beirut, in the South Governorate (Liban-Sud), in the municipality of Batouliyat. The place lies in a very green and fertile plain, about one kilometer from the sea coast. It is a popular tourist destination, owing to its artesian wells fed by underground springs and collected in stone reservoirs that have been maintained through the ages. It has been the main source of water for ancient Tyre since Phoenician days. One of the reservoirs fed the arched aqueducts of the Roman period, and which once stretched all the way to Tyre. Remains of these aqueducts, exhibiting strong and excellent masonry, with round arches and a continuous cornice above them, can still be seen today, and a short stretch of the original aqueduct is still used today in Tyre's present-day waterworks.
 W
WShebaa Farms, also spelled Sheba'a Farms is a small strip of land at the intersection of the Lebanese-Syrian border and the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights. The territory is about 11 kilometres (7 mi) long and 2.5 kilometres (2 mi) wide. Both Islamic and Jewish tradition hold that a location in the Sheeba farms, called Maqam 'Ibrahim al-Khalil in Arabic and Makom Habětarim in Hebrew, is the site of the covenant of the pieces, God's first covenant with Abraham, in the biblical land of Israel.
 W
WThe Upper Galilee is a geographical-political term in use since the end of the Second Temple period, originally referring to a mountainous area straddling present-day northern Israel and southern Lebanon, its boundaries being the Litani River in the north, the Mediterranean Sea in the west, the Lower Galilee in the south, from which it is separated by the Beit HaKerem Valley, and the upper Jordan River and the Hula Valley in the east. According to 1st-century historian, Josephus, the bounds of Upper Galilee stretched from Bersabe in the Beit HaKerem Valley to Baca (Peki'in) in the north. The said region contains approximately 180 square miles.
 W
WZaarour is a ski resort on the eastern slopes of Mount Sannine in the Matn District of Mount Lebanon Governorate, only 35 km from Beirut. The resort lies north of the mountain village of Mrouj. The name is the Arabic for hawthorn, which in itself is a corruption of the Syriac word.