 W
WThe Basin and Range Province is a vast physiographic region covering much of the inland Western United States and northwestern Mexico. It is defined by unique basin and range topography, characterized by abrupt changes in elevation, alternating between narrow faulted mountain chains and flat arid valleys or basins. The physiography of the province is the result of tectonic extension that began around 17 million years ago in the early Miocene epoch.
 W
WCave of the Crystals or Giant Crystal Cave is a cave connected to the Naica Mine at a depth of 300 metres (980 ft), in Naica, Chihuahua, Mexico.
 W
WThe Cerro Prieto Fault is a transform fault located in far northern Baja California. It runs between the Cerro Prieto spreading center located southwest of Mexicali, and the Wagner Basin, another spreading center which lies under the Gulf of California. These spreading centers are part of the East Pacific Rise, the northern leg of which has formed the Gulf of California by steadily rifting the Baja California Peninsula away from the mainland of Mexico.
 W
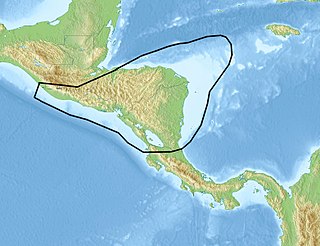
WThe Chortis Block is a 400–600 km (250–370 mi)-wide continental fragment in Central America located in the northwest corner of the oceanic Caribbean Plate.
 W
WThe Cocos Plate is a young oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Central America, named for Cocos Island, which rides upon it. The Cocos Plate was created approximately 23 million years ago when the Farallon Plate broke into two pieces, which also created the Nazca Plate. The Cocos Plate also broke into two pieces, creating the small Rivera Plate. The Cocos Plate is bounded by several different plates. To the northeast it is bounded by the North American Plate and the Caribbean Plate. To the west it is bounded by the Pacific Plate and to the south by the Nazca Plate.
 W
WThe Comarca Minera Geopark is located in the center-south of the Hidalgo state, México. It extends over nine municipalities: Atotonilco el Grande, Epazoyucan, Huasca de Ocampo, Mineral del Chico, Mineral de la Reforma, Mineral del Monte, Omitlán de Juárez, Pachuca de Soto and Singuilucan. These municipalities are articulated by a network of 31 geosites, elected because they express the geological history of the territory and highlight the relationship between mining and metallurgy, and the historical spaces and cultural development of the region. In addition, they are important for science and education and, mostly, have a significant landscape value.
 W
WLa Reforma is a Plio-Pleistocene caldera on the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. It is part of eleven volcanoes in Baja California, which formed with the Gulf of California during the Miocene, about ten million years ago. Previously, a volcanic arc had existed on the peninsula. The caldera's basement consists of granites and monzonites, formed between the Cretaceous and the Middle Miocene.
 W
WThis is an incomplete list of islands of Mexico.
 W
WThe Louann Salt is a widespread evaporite formation that formed in the Gulf of Mexico during the Callovian in the mid Jurassic. The Louann formed in a rift as the South American and North American Plates separated, from an embayment of the Pacific Ocean. The Louann underlies much of the northern Gulf coast from Texas to the Florida panhandle and extends beneath large areas of the Gulf coastal plain of Mississippi, Louisiana and Texas.
 W
WThe Mexican Geological Survey is an agency of the Mexican government; its mission includes mapping and mining consultation.
 W
WThe North American Cordillera is the North American portion of the American Cordillera which is a mountain chain (cordillera) along the western side of the Americas. The North American Cordillera covers an extensive area of mountain ranges, intermontane basins, and plateaus in western North America, including much of the territory west of the Great Plains. It is also sometimes called the Western Cordillera, the Western Cordillera of North America, or the Pacific Cordillera.
 W
WThe Pinacate Peaks are a group of volcanic peaks and cinder cones located mostly in the Mexican state of Sonora along the international border adjacent to the U.S. state of Arizona, surrounded by the vast sand dune field of the Gran Desierto de Altar, at the desert's southeast.
 W
WThe Rio Grande rift is a north-trending continental rift zone. It separates the Colorado Plateau in the west from the interior of the North American craton on the east. The rift extends from central Colorado in the north to the state of Chihuahua, Mexico, in the south. The rift zone consists of four basins that have an average width of 50 kilometers. The rift can be observed on location at Rio Grande National Forest, White Sands National Park, Santa Fe National Forest, and Cibola National Forest, among other locations.
 W
WThe Rivera Plate is a small tectonic plate located off the west coast of Mexico, just south of the Baja California Peninsula. It is bounded on the northwest by the East Pacific Rise, on the southwest by the Rivera Transform Fault, on the southeast by a deformation zone, and on the northeast by the Middle America Trench and another deformation zone.
 W
WThe volcanoes of east-central Baja California are located on the Baja California Peninsula near the Gulf of California, in the state of Baja California Sur, in Mexico.