 W
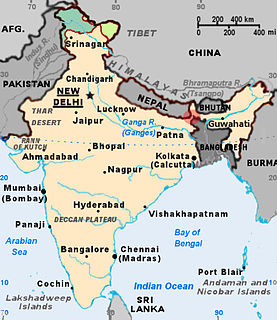
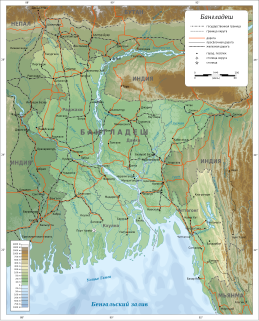
WThe Bangladesh–India border, known locally as the International Border (IB), is an international border running between Bangladesh and India that demarcates the eight divisions of Bangladesh and the Indian states.
 W
WThe 2001 Bangladesh–India border clashes were a series of armed skirmishes between India and Bangladesh in April 2001. The clashes took place between troops of the Bangladesh Rifles (BDR) and the Indian Border Security Force (BSF) on the poorly-marked international border between the two countries.
 W
WBanglabandha is a major inland port in northern Bangladesh established to provide a trade link with India, Nepal and Bhutan. The three nations are separated by 52 km (32 mi) of Indian territory, known as the Siliguri Corridor. On the Indian side of the border is Phulbari. Border crossing of vehicles between Phulbari and Banglabandha was inaugurated in January 2011.
 W
WThe Barak River flows 900 kilometres (560 mi) through the states of Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram and Assam in India and into the Bay of Bengal via Bangladesh. Of its length 524 km (326 mi) is in India, 31 km (19 mi) on the Indo–Bangladesh border and the rest is in Bangladesh. The upper part of its navigable part is in India — 121 km (75 mi) between Lakhipur and Bhanga, declared as National Waterway 6, (NW-6) since the year 2016. It drains a basin of 52,000 km2 (20,000 sq mi), of which 41,723 km2 (16,109 sq mi) lies in India, 1.38% (rounded) of the country. The water and banks host or are visited by a wide variety of flora and fauna.
 W
WThe Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line between Sangaman Kanda, Sri Lanka and the north westernmost point of Sumatra (Indonesia). It is the largest water region called a bay in the world. There are countries dependent on the Bay of Bengal in South Asia and Southeast Asia. In ancient India, Bay of Bengal was known as Kalinga Sagar. Later during the British India, it came forth as the Bay of Bengal after the historic Bengal region, as the Port of Kolkata served as the gateway to the Crown rule in India. Cox's Bazar, the longest sea beach in the world and Sundarbans, the largest mangrove forest and the natural habitat of the Bengal tiger, are located along the bay.
 W
WDahagram–Angarpota is a Bangladeshi enclave in India about 200 m (660 ft) away from the border of Bangladesh. It has a population of 17,000 people as of 2014. Dahagram–Angarpota was the largest and is the only remaining Bangladeshi enclave after the 2015 resolution of the India-Bangladesh enclaves issue. The enclave is connected to mainland Bangladesh by the Tin Bigha Corridor, which is situated in the town of Patgram Upazila.
 W
WDahala Khagrabari (#51) was an Indian enclave belonging to the District of Cooch Behar in the State of West Bengal. This was a piece of India within a piece of Bangladesh within a piece of India within Bangladesh, making it the only third-order enclave in the world until 1 August 2015, when it was ceded to Bangladesh.
 W
WDeaths along the Bangladesh–India border occur many times a year as result of people attempting to illegally cross into India from Bangladesh, cross border firing and cattle smuggling. Bangladesh and India share a 4,096 kilometer border. To prevent smuggling and illegal migration from Bangladesh, the Indian Border Security Force exercises its controversial "Shoot-on-sight" policy. Under this policy, the BSF can shoot any person on site with or without cause. A large portion of the victims are cattle traders and farmers with land near the border. Regarding border killings, Brad Adams, Executive Director of the Asia Department of Human Right Watch state that, "Routinely shooting poor, unarmed villagers is not how the world's largest democracy should behave."
 W
WThe Dhalai River a trans-boundary river in India and Bangladesh. It rises in the mountains of the Indian state of Tripura. It enters Kulaura Upazila of Maulvibazar District of Bangladesh. Later it joins Manu River in Rajnagar Upazila. The co-ordinates of Dhalai River at Ambassa are 23.55'128'' N and 91.51'204'' E in degrees minutesseconds(DMS). It originate from Atharamura Hill and is 117 kilometres (73 mi) long. Some of the popular riverside townships of Dhalai River are the towns of Ambassa, Baralutma and Kamalpur.
 W
WThe India–Bangladesh enclaves, also known as the chiṭmahals and sometimes called pasha enclaves, were the enclaves along the Bangladesh–India border, in Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, Assam and Meghalaya. Within the main body of Bangladesh were 102 enclaves of Indian territory, which in turn contained 21 Bangladeshi counter-enclaves, one of which contained an Indian counter-counter-enclave – the world's only third-order enclave. Within the Indian mainland were 71 Bangladeshi enclaves, containing 3 Indian counter-enclaves. A joint census in 2010 found 51,549 people residing in these enclaves: 37,334 in Indian enclaves within Bangladesh and 14,215 in Bangladeshi enclaves within India.
 W
WFeni River is a river in southeastern Bangladesh and Tripura state of India. It is a trans-boundary river with an ongoing dispute about water rights. The Feni River originates in South Tripura district and flows through Sabroom town and then enters Bangladesh. Muhuri River, also called Little Feni, from Noakhali District joins it near its mouth. The river is navigable by small boats as far as Ramgarh, about 80 kilometres (50 mi) upstream.
 W
WThe Ganges or Ganga is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The 2,525 km (1,569 mi) river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, and flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain of North India into Bangladesh, where it empties into the Bay of Bengal. It is the third largest river on Earth by discharge.
 W
WIchamati River, is a trans-boundary river which flows through India and Bangladesh and also forms the boundary between the two countries. The river is facing the problem of siltation leading to thin flow of water in the dry season and floods in the rainy season. Experts are handling the situation and remedial matters are being discussed between the governments of India and Bangladesh.
 W
WIndia-Bangladesh Border Haat is a border trade market between Bangladesh and India. It is a market place organised by the two countries one day each week. It is not only a market for buying daily commodities but also a reunion spot for families living on both sides. Currently, four border haats are operational along the India-Bangladesh border. Two border haats are located in Meghalaya at Kalaichar and Balat and two are located in Tripura at Srinagar and Kamalasagar.
 W
WThe Radcliffe Line was the boundary demarcation line between the Indian and Pakistani portions of the Punjab and Bengal provinces of British India. It was named after its architect, Sir Cyril Radcliffe, who, as the joint chairman of the two boundary commissions for the two provinces, received the responsibility to equitably divide 175,000 square miles (450,000 km2) of territory with 88 million people.
 W
WThe Tin Bigha Corridor is a strip of land belonging to India on the West Bengal–Bangladesh border which, in September 2011, was leased to Bangladesh so the country could access its Dahagram–Angarpota enclave from the mainland. The enclave remains the only one still in existence after the 2015 resolution of the India-Bangladesh enclaves issue. It is situated in the town of Patgram Upazila.