 W
WThe New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges it is home of several highest peaks in the island of New Guinea including a 16,024 ft (4,884 m) Puncak Jaya the highest mountain in Oceania. The intermountain river valleys, many of which support thriving agricultural communities, on the large island of New Guinea. The highlands run generally east-west the length of the island, which is divided politically between Indonesia in the west and Papua New Guinea in the east.
 W
WThe New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges it is home of several highest peaks in the island of New Guinea including a 16,024 ft (4,884 m) Puncak Jaya the highest mountain in Oceania. The intermountain river valleys, many of which support thriving agricultural communities, on the large island of New Guinea. The highlands run generally east-west the length of the island, which is divided politically between Indonesia in the west and Papua New Guinea in the east.
 W
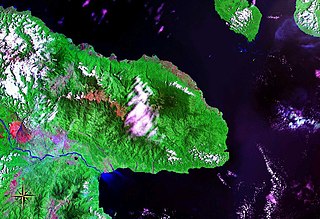
WHuon Peninsula is a large rugged peninsula on the island of New Guinea in Morobe Province, eastern Papua New Guinea. It is named after French explorer Jean-Michel Huon de Kermadec. The peninsula is dominated by the steep Saruwaged and Finisterre and Cromwell Mountains. The nearest large town is the Morobe provincial capital Lae to the south, while settlements on the north coast include the former German town of Finschhafen, the district capital of Wasu, Malalamai and Saidor with its World War II era Saidor Airport.
 W
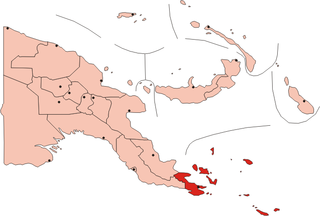
WThe Louisiade Archipelago is a string of ten larger volcanic islands frequently fringed by coral reefs, and 90 smaller coral islands in Papua New Guinea.
 W
WThe New Britain-New Ireland lowland rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Papua New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the lowland rain forests of New Britain, New Ireland, and nearby islands in the Bismarck Archipelago.
 W
WThe New Britain-New Ireland montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Papua New Guinea. The ecoregion includes the mountain rain forests on the islands of New Britain and New Ireland, which lie northeast of New Guinea.
 W
WThe New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges it is home of several highest peaks in the island of New Guinea including a 16,024 ft (4,884 m) Puncak Jaya the highest mountain in Oceania. The intermountain river valleys, many of which support thriving agricultural communities, on the large island of New Guinea. The highlands run generally east-west the length of the island, which is divided politically between Indonesia in the west and Papua New Guinea in the east.
 W
WThe New Guinea mangroves is a mangrove ecoregion that covers extensive areas of the coastline New Guinea, the large island in the western Pacific Ocean north of Australia.
 W
WThe Northern New Guinea lowland rain and freshwater swamp forests is a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of northern New Guinea.
 W
WThe Northern New Guinea montane rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in northern New Guinea. The ecoregion covers several separate mountain ranges lying north of New Guinea's Central Range and south of the Pacific Ocean.
 W
WThe Solomon Islands rain forests are a terrestrial ecoregion covering most of the Solomon Islands archipelago.
 W
WThe Southeastern Papuan rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in southeastern New Guinea. The ecoregion covers the mountainous center and coastal lowlands of the Papuan Peninsula.
 W
WThe Southern New Guinea freshwater swamp forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in southern New Guinea. The ecoregion includes the extensive swamp forests of southern and western New Guinea.
 W
WThe Southeastern Papuan rain forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in southeastern New Guinea. The ecoregion covers portions of New Guinea's southern lowlands.
 W
WThe Trans Fly savanna and grasslands are a lowland ecoregion on the south coast of the island of New Guinea in both the Indonesian and Papua New Guinean sides of the island. With their monsoon and dry season climate these grasslands are quite different from the tropical rainforest that covers most of the island and resemble the landscape of northern Australia which lies to the south.
 W
WThe Trobriand Islands rain forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion of southeastern Papua New Guinea.