 W
WThe great bison belt is a tract of rich grassland that ran from Alaska to the Gulf of Mexico around 9000 BC. The great bison belt was supported by spring and early summer rainfall that allowed short grasses to grow. These grasses retain their moisture at the roots which allowed for grazing ungulates such as bison to find high-quality nutritious food in autumn.
 W
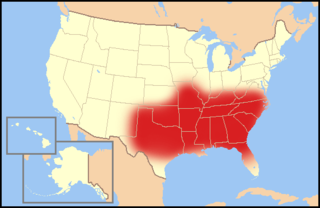
WThe Bible Belt is a region of the Southern United States in which socially conservative evangelical Protestantism plays a strong role in society and politics, and church attendance across the denominations is generally higher than the nation's average. The region contrasts with the religiously diverse Midwest and Great Lakes, and the Mormon Corridor in Utah and southern Idaho.
 W
WThe Corn Belt is a region of the Midwestern United States that, since the 1850s, has dominated corn production in the United States. In the United States, "corn" is the common word for "maize". More generally, the concept of the "Corn Belt" connotes the area of the Midwest dominated by farming and agriculture.
 W
WThe Cotton Belt is a region of the Southern United States where cotton was the predominant cash crop from the late 18th century into the 20th century.
 W
WFruit Belt is a term in the United States for an area where the microclimate provides good conditions for fruit growing.
 W
WThe largest quantities of gold found in the eastern United States were found in the Georgia Gold Belt, extending from eastern Alabama to Rabun County, Georgia. The biggest concentration of gold was found in White, Lumpkin, and northern Cherokee counties in Georgia. The gold in the Georgia Gold Belt was close to 24 karat (100%) purity. Most of the gold was found in eroded rock (saprolite) and mixed in with quartz.
 W
WThe Insular Belt is a physiogeological region on the north western North American coast. It consists of three major island groups and many smaller islands and stretches from southern British Columbia into Alaska and the Yukon. It represents the Late Cretaceous to Eocene accretion of what is known as the Insular Superterrane to the North American continent.
 W
WJell-O is a variety of gelatin desserts, puddings, and no-bake cream pies. The original Jell-O gelatin dessert is the signature of the brand. Jell-O is a registered trademark of Kraft Heinz and is based in Chicago, Illinois.
 W
WThe Juneau gold belt is located in the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska. This belt is approximately 100 miles (160 km) in length, north/northwest-trending, and extends from Berners Bay southeastward to Windham Bay, 60 miles (97 km) southeast of Juneau, and includes Douglas Island. The belt contains over 200 gold-quartz-vein deposits with production nearing 7,000,000 ounces (200,000,000 g) of gold. More than three-quarters of Alaska's lode gold was mined from the Juneau gold belt.
 W
WThe Mormon Corridor is the areas of Western North America that were settled between 1850 and approximately 1890 by members of The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, who are commonly nicknamed “Mormons”.
 W
WThe Pretzel Belt, or Pennsylvania Snack Belt, is a concentration of pretzel and snack food makers in the central southeastern region of Pennsylvania, roughly coterminous with Pennsylvania Dutch Country. The first commercial pretzel manufacturer in the United States, the Julius Sturgis Pretzel Bakery, was founded in the region in the borough of Lititz in 1861, and remains extant there today. By the beginning of the 20th century the pretzel had become a cultural institution in the region. Manufacturers also include several pretzel and chip bakeries in Hanover, Pennsylvania, which holds the nickname "the snack capital of the world", as well as other examples like Hershey, Pennsylvania, home of the Hershey Chocolate Company.
 W
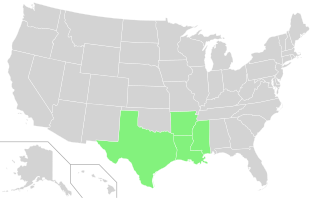
WThe Rice Belt of the United States includes Arkansas, Louisiana, Mississippi and Texas, four southern U.S. states that grow a significant portion of the nation's rice crop. The name is in conformity with the Corn Belt of the Midwestern United States, in which much of the nation's corn is grown.
 W
WThe Rust Belt is a region of the Northeastern and Midwestern United States that has been experiencing industrial decline starting around 1980. It is made up largely of the Great Lakes Megalopolis, though definitions vary. Rust refers to the deindustrialization, economic decline, population loss, and urban decay due to the shrinking of its once-powerful industrial sector, such as steel, automobile, and coal-mining Jobs. The term gained popularity in the U.S. in the 1980s.
 W
WThe Salt Belt is the U.S. region in which road salt is used in winter to control snow and ice. States in the salt belt include Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, North Dakota, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, Virginia, West Virginia, Wisconsin, and Washington DC. Other states such as Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, Idaho and Utah are also considered part of the Salt Belt but use less corrosive substances.
 W
WThe Snowbelt is the region near the Great Lakes in North America where heavy snowfall in the form of lake-effect snow is particularly common. Snowbelts are typically found downwind of the lakes, principally off the eastern and southern shores.
 W
WThe Stroke Belt or Stroke Alley is a region in the southeastern United States that has been recognized by public health authorities for having an unusually high incidence of stroke and other forms of cardiovascular disease. It is usually defined as a 9-state region consisting of Alabama, Arkansas, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Tennessee. It is often disputed if Texas belongs in the Stroke Belt.
 W
WThe Sun Belt is a region of the United States generally considered to stretch across the Southeast and Southwest. Another rough definition of the region is the area south of the 36th parallel. Several climates can be found in the region — desert/semi-desert, Mediterranean (California), humid subtropical, subtropical highland and tropical.
 W
WThe Unchurched Belt is a region in the far Northwestern United States that has low rates of religious participation. The term derives from Bible Belt and the notion of the unchurched.