 W
WThe Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS-02) is a particle physics experiment module that is mounted on the International Space Station (ISS). The experiment is a recognized CERN experiment (RE1). The module is a detector that measures antimatter in cosmic rays; this information is needed to understand the formation of the Universe and search for evidence of dark matter.
 W
WThe ARCTIC refrigerator/freezer (ARCTIC) provided a thermally-controlled environment for storing biological samples prior to their return to Earth in the early stages of the International Space Station (ISS). The ARCTIC freezers supported several of these experiments on ISS during Expeditions 4 and 5.
 W
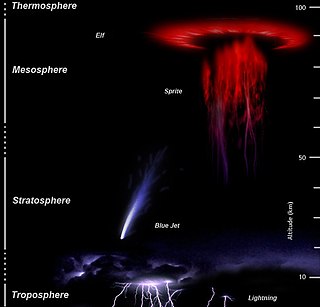
WAtmosphere-Space Interactions Monitor (ASIM) is a project led by the European Space Agency to place cameras and X-ray/γ-ray detectors on the International Space Station to observe the upper atmosphere in order to study sprites, jets and elves and terrestrial gamma-ray flashes in connection with thunderstorms. It is hoped that measurements of these phenomena from space will contribute to the understanding of Earth's upper atmosphere.
 W
WThe Cold Atom Laboratory (CAL) is an experimental instrument on board the ISS, which launched in 2018. It creates an extremely cold microgravity environment in order to study behaviour of atoms in these conditions.
 W
WECOSTRESS is an ongoing scientific experiment in which a radiometer mounted on the International Space Station measures the temperature of plants growing in specific locations on Earth over the course of a solar year. These measurements give scientists insight into the effects of events like heat waves and droughts on crops.
 W
WEXPOSE is a multi-user facility mounted outside the International Space Station dedicated to astrobiology. EXPOSE was developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) for long-term spaceflights and was designed to allow exposure of chemical and biological samples to outer space while recording data during exposure.
 W
WThe eye-tracking device (ETD) is a headmounted device, designed for measurement of 3D eye and head movements under experimental and natural conditions. The tracker permits comprehensive measurement of eye movement and optionally head movement. It represents a tool for the investigation of sensorimotor behaviour, particularly of the vestibular and oculomotor systems in both health and disease.
 W
WThe Human Research Facility Holter Monitor (Holter) is a battery-powered, noninvasive electrocardiogram (ECG) device that accurately measures the heart rate of crew members over an extended period of time. ECG information is stored on a Portable Computer Memory Card International Adapter (PCMCIA) card and downlinked to Earth for analysis after monitoring is complete.
 W
WISSpresso is the first espresso coffee machine designed for use in space, produced for the International Space Station by Argotec and Lavazza in a public-private partnership with the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The first espresso coffee was drunk in space by astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti on 3 May 2015. ISSpresso is one of nine experiments selected by the Italian Space Agency for the Futura mission.
 W
WThe Lab-on-a-Chip Applications Development (LOCAD) element is a set of related lab-on-a-chip projects at NASA. The projects develop integrated lab-on-a-chip products in three areas related to space exploration: Environmental Control and Life Systems Support (ECLSS), Medical Systems, and Remote Exploration. NASA conducts activities related to these projects both at NASA Marshall Space Flight Center and aboard the International Space Station (ISS).
 W
WThe Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) is a series of experiments mounted externally on the International Space Station (ISS) that investigates the effects of long-term exposure of materials to the harsh space environment.
 W
WThe Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER) is a NASA telescope on the International Space Station, designed and dedicated to the study of the extraordinary gravitational, electromagnetic, and nuclear physics environments embodied by neutron stars, exploring the exotic states of matter where density and pressure are higher than in atomic nuclei. As part of NASA's Explorers program, NICER enabled rotation-resolved spectroscopy of the thermal and non-thermal emissions of neutron stars in the soft X-ray band with unprecedented sensitivity, probing interior structure, the origins of dynamic phenomena, and the mechanisms that underlie the most powerful cosmic particle accelerators known. NICER achieved these goals by deploying, following the launch, and activation of X-ray timing and spectroscopy instruments. NICER was selected by NASA to proceed to formulation phase in April 2013.
 W
WThe Plasmakristall-3 Plus laboratory was a joint Russian-German laboratory for the investigation of dusty/complex plasmas on board the International Space Station (ISS), with the principal investigators at the German Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics and the Russian Institute for High Energy Densities. It was the successor to the PKE Nefedov experiment with improvements in hardware, diagnostics and software. The laboratory was launched in December 2005 and was operated for the first time in January 2006. It was used in 21 missions until it was deorbited in 2013. It is succeeded by the PK-4 Laboratory.
 W
WSAGE III on ISS is the fourth generation of a series of NASA Earth-observing instruments, known as the Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment. The first SAGE III instrument was launched on the Russian Meteor (satellite) spacecraft. The recently revised SAGE III will be mounted to the International Space Station where it will use the unique vantage point of ISS to make long-term measurements of ozone, aerosols, water vapor, and other gases in Earth's atmosphere.
 W
WThe Synchronized Position Hold Engage and Reorient Experimental Satellite (SPHERES) are a series of miniaturized satellites developed by MIT's Space Systems Laboratory for NASA and US Military, to be used as a low-risk, extensible test bed for the development of metrology, formation flight, rendezvous, docking and autonomy algorithms that are critical for future space missions that use distributed spacecraft architecture, such as Terrestrial Planet Finder and Orbital Express.
 W
WThe Thor experiment aims to investigate electrical activity from thunderstorms and convection related to water vapour transport. The experiment is named as 'Thor' after the god of thunder, lightning and storms in Nordic mythology. The experiment is conducted by European Space Agency with a thundercloud imaging system 400 km above Earth.
 W
WThe Vegetable Production System (Veggie) is a plant growth system developed and used by NASA in outer space environments. The purpose of Veggie is to provide a self-sufficient and sustainable food source for astronauts as well as a means of recreation and relaxation through therapeutic gardening. Veggie was designed in conjunction with ORBITEC and is currently being used aboard the International Space Station, with another Veggie module planned to be delivered to the ISS in 2017.
 W
WWORF is a new data storage method which allows users to write data once and allows storage of the users data without ever being refreshed. This differs from current digital storage techniques such as drives that need to be re-written often to prevent loss or corruption of data. WORF has the potential to store data forever and is currently being tested on the International Space Station (ISS).
 W
WYouTube Space Lab was a 2011–2012 international science competition launched by YouTube and Lenovo, in cooperation with NASA, European Space Agency (ESA), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). Founded by Zahaan Bharmal of Google, the competition challenged teenagers from ages 14–18 to design an experiment to be performed on the International Space Station. The global winners were Amr Mohamed from Alexandria, Egypt, and Dorothy Chen and Sara Ma from Troy, Michigan.