 W
WThe Mare Boreum quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Mare Boreum quadrangle is also referred to as MC-1. Its name derives from an older name for a feature that is now called Planum Boreum, a large plain surrounding the polar cap.
 W
WAbalos Colles is a stratified fragment of the Rupes Tenuis basal unit of Planum Boreum, located south of the Rupes Tenuis scarp and west of the Escorial crater. It contains 16 mounds. Abalos Colles is one of the named features in the vicinity of Planum Boreum, the Martian North pole. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars located at latitude 72°N, longitude 70°W. Its name was officially approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in 2003.
 W
WAbalos Mensa is a wedge-shaped mound, or mensa and one of the named features in the vicinity of Planum Boreum, the Martian North pole. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars. Its name was officially approved by IAU in 2006. It extends from latitude 80.21°N to 82.4°N and from longitude 279.34°E to 290.52°E. Its centre is located at latitude 81.17°N, longitude 284.4°E (75.6°W), and has a diameter of 129.18 km.
 W
WAbalos Undae is a dune field on Mars in the periphery of Planum Boreum, the Martian North pole. It is one of the officially named northern circumpolar dune fields, along with Olympia, Hyperboreae, and Siton Undae, and also one of the densest of the region. Its northernmost boundary is located in the southwest channel that separates the Abalos Colles formation from the main polar ice cap, and from there the dune field extends southwest all the way to the lowlands of Vastitas Borealis.
 W
WAspledon Undae is one of the named northern circumpolar dune fields in the vicinity of Planum Boreum, the Martian North pole. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars. Its name was officially approved by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) on 20 March 2007. Its name is Greek, and derives from the name of a town in Boeotia, Ancient Greece, which, in turn, took its name from Aspledon, son of Poseidon, the ancient Greek god of the sea. The dunes of Aspledon Undae extend from latitude 71.47°N to 75.14°N and from longitude 305.83°E to 315.04°E. Its centre is located at latitude 73.06°N, longitude 309.65°E (50.35°W), and has a diameter of 215.2 km.
 W
WChasma Boreale is a large canyon in Mars's north polar ice cap in the Mare Boreum quadrangle of Mars at 83° north latitude and 47.1° west longitude. It is about 560 km (350 mi) long and was named after a classical albedo feature name. The canyon's sides reveal layered features within the ice cap that result from seasonal melting and deposition of ice, together with dust deposits from Martian dust storms. Information about the past climate of Mars may eventually be revealed in these layers, just as tree ring patterns and ice core data do on Earth. Both polar caps also display grooved features, probably caused by wind flow patterns. The grooves are also influenced by the amount of dust. The more dust, the darker the surface. The darker the surface, the more melting as dark surfaces absorb more energy.
 W
WGreen Valley is a region on Mars within Vastitas Borealis that was chosen as the landing site of NASA's Phoenix lander. It is located at 68.35 degrees north, 233 degrees east. The valley is about 50 kilometres wide but only about 250 metres deep; either it was filled in or was never any deeper than that. The edges are not visible from the middle of the valley.
 W
WHagal is the informal name of a dune field on Mars located below the north pole of Mars. Its name derives from the sand dunes in Frank Herbert's novel Dune and the fictional planet Hagal. It is located at coordinates 78.0° N latitude, 84.0° E longitude, and consists of linear and round dunes with a southeast slipface orientation. It was one of the dune formations targeted for imaging by the HiRISE camera, on board the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, at the rate of one image every six weeks. in the third year of its seasonal expedition. It is also known as the "Martian Morse Code" due to the linear and rounded formations of its dunes, which have the appearance of dots and dashes.
 W
WHeimdal is a relatively recent impact crater on the planet Mars. It lies in Vastitas Borealis, the northern plain. It is named after the Norwegian town of Heimdal.
 W
WHyperboreae Undae is one of the largest and densest dune fields of Planum Boreum, the Martian North Pole. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars. Its name was officially approved by IAU in 1988. It extends from latitude 77.12°N to 82.8°N and from longitude 302.92°E to 316.02°E. Its centre is at latitude 79.96°N, longitude 49.49°W, and has a diameter of 463.65 kilometres (288.10 mi).
 W
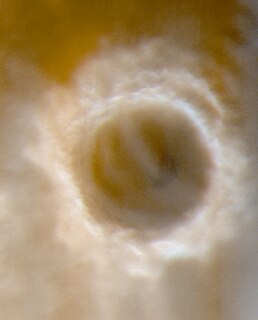
WKorolev is an ice-filled impact crater in the Mare Boreum quadrangle of Mars, located at 73° north latitude and 165° east longitude. It is 81.4 kilometres (50.6 mi) in diameter and contains about 2,200 cubic kilometres (530 cu mi) of water ice, comparable in volume to Great Bear Lake in northern Canada. The crater was named after Sergei Korolev (1907–1966), the head Soviet rocket engineer and designer during the Space Race in the 1950s and 1960s.
 W
WLomonosov is a crater on Mars, with a diameter close to 150 km. It is located in the Martian northern plains. Since it is large and found close to the boundary between the Mare Acidalium quadrangle and the Mare Boreum quadrangle, it is found on both maps. The topography is smooth and young in this area, hence Lomonosov is easy to spot on large maps of Mars.
 W
WOlympia Undae is a vast dune field in the north polar region of the planet Mars. It consists of a broad "sand sea" or erg that partly rings the north polar plateau from about 120° to 240°E longitude and 78° to 83°N latitude. Stretching about 1,100 km (680 mi) across and covering an area of 470,000 km2, Olympia Undae is the largest continuous dune field on Mars. It is similar in size to the Rub' Al Khali in the Arabian Peninsula, the largest active erg on Earth.
 W
WPhoenix was a robotic spacecraft that landed on Mars on May 25, 2008 and operated until November 2. Its instruments were used to assess the local habitability and to research the history of water on Mars. The mission was part of the Mars Scout Program; its total cost was $420 million, including the cost of launch.
 W
WPlanum Boreum is the northern polar plain on Mars. It extends northward from roughly 80°N and is centered at 88.0°N 15.0°E. Surrounding the high polar plain is a flat and featureless lowland plain called Vastitas Borealis which extends for approximately 1500 kilometres southwards, dominating the northern hemisphere.
 W
WRupes Tenuis is a Martian north polar scarp. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars. Its name was officially approved by IAU in 1988. It extends from latitude 74.94°N to 82.2°N and from longitude 242.12°E to 300.77°E. Its centre is located at latitude 81.6°N longitude 85.47°W. It marks the outer perimeter of Planum Boreum from longitude 242.12°E to 300.77°E, and it is formed by the eastern extension of the Olympia Cavi, a series of local troughs and depressions, which become longer and deeper as they merge to create the Rupes Tenuis scarp formation. The scarp is located to the west of Chasma Boreale, at the base of Planum Boreum, and its height varies from a few hundred metres to a maximum of approximately 1000 metres.
 W
WSiton Undae is one of the largest and densest dune fields in the vicinity of Planum Boreum, the Martian northern polar ice-cap. It is named after one of the classical albedo features on Mars. Its name was officially approved by IAU on 20 March 2007. It extends from latitude 73.79°N to 77.5°N and from longitude 291.38°E to 301.4°E. Its centre is located at latitude 75.55°N, longitude 297.28E (62.72°W), and has a diameter of 222.97 kilometres (138.55 mi).
 W
WUdzha is an impact crater on Mars, that measures 45 kilometer in diameter, but has been almost entirely covered by layers of ice and dust. Only the highest part of the crater rim rises above the polar deposits and hint at its circular form. Udzha Crater is located at 81.8 degrees north latitude, 77.2 degrees east longitude on Mars. It was named after a village in northern Russia.
 W
WVastitas Borealis is the largest lowland region of Mars. It is in the northerly latitudes of the planet and encircles the northern polar region. Vastitas Borealis is often simply referred to as the northern plains, northern lowlands or the North polar erg of Mars. The plains lie 4–5 km below the mean radius of the planet, and is centered at 87.73°N 32.53°E. To the north lies Planum Boreum. A small part of Vastitas Borealis lies in the Ismenius Lacus quadrangle.