 W
WHurricane Baker was a Category 2 hurricane that affected the Leeward Islands, Greater Antilles, and the Gulf Coast of the United States. The tropical cyclone was the second tropical storm and second hurricane of the 1950 Atlantic hurricane season. Originating as a tropical depression east of the Windward Islands on August 18, Baker became a tropical storm on August 19, and further intensified into a hurricane on August 21. It attained an initial peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 100 mph (155 km/h) on August 22 before weakening to a tropical storm as it made landfall on the island of Antigua. Baker weakened to a tropical depression late on August 23 while southwest of Puerto Rico. By the following morning, it had restrengthened into a tropical storm, though a landfall in Cuba caused it to weaken once again. Entering the Gulf of Mexico, Baker began to strengthen once more, regaining hurricane strength on August 29 and reaching its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 105 mph (165 km/h) early the following day. The cyclone weakened before making its final landfall in the United States near Gulf Shores, Alabama, with winds of 85 mph (140 km/h). Hurricane Baker produced extensive damage in the Lesser Antilles and Cuba, but impacts were minimal in the United States.
 W
WHurricane Bertha was an intense and early-forming major hurricane that affected areas from the Leeward Islands to the United States in July of the 1996 Atlantic hurricane season. The second named storm, first hurricane, and first major hurricane during the season. Bertha originated from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa in early July. Steadily organizing while moving generally towards the west, the disturbance was designated as a tropical depression at 0000 UTC on July 5, and was further upgraded to a tropical storm by 1200 UTC later that day. Over the next few days, continued intensification occurred, and Bertha became a Category 1 hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson hurricane scale, the first hurricane of the season, prior to moving through the northern Leeward Islands. Late on July 8, a period of rapid intensification began, and at 0600 UTC on July 9, Bertha reached its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 115 mph (185 km/h) with a minimum barometric pressure of 960 mbar (28 inHg). Moving around the western periphery of the subtropical ridge, Bertha passed north of the Bahamas as a weakening hurricane before turning towards the north-northeast and undergoing another period of rapid intensification. Late on July 12, Bertha made landfall between Wrightsville Beach and Topsail Beach, North Carolina with winds of 105 mph (169 km/h). Gradual weakening ensued the following day as Bertha moved up the Mid-Atlantic and into New England before becoming an extratropical cyclone on July 14.
 W
WTropical Storm Claudette was the third-wettest tropical cyclone on record in the contiguous United States. Claudette caused significant flooding in eastern Texas and western Louisiana in July 1979. The third named storm of the 1979 Atlantic hurricane season, Claudette developed from a tropical wave located east of the Windward Islands on July 16. It gradually strengthened and was upgraded to a tropical storm on July 17 and crossed the northern Leeward Islands later that day. As it neared landfall in Puerto Rico early on July 18, upper-level winds weakened it back to a tropical depression. Claudette remained disorganized and the National Hurricane Center operationally reported that it degenerated back into a tropical wave after crossing Puerto Rico. Late on July 18, the depression struck Dominican Republic, emerged into the Caribbean Sea on the following day. Claudette struck western Cuba on July 21, shortly before reaching the Gulf of Mexico and "regenerating" into a tropical cyclone. By July 23, Claudette regained tropical storm intensity and turned northward toward the Gulf Coast of the United States. The storm made landfall near the Texas-Louisiana border late on July 23 as a moderately strong tropical storm. It weakened slowly and drifted over land, lasting until dissipation in West Virginia on July 29.
 W
WHurricane Debby caused minor damage in the Greater and Lesser Antilles in August 2000. The seventh tropical cyclone, fourth named storm, and second hurricane of the annual season, Debby developed from a tropical wave east of the Lesser Antilles on August 19. Favorable conditions allowed the depression to become Tropical Storm Debby early on August 20, and further strengthening into a hurricane occurred 24 hours later. Sustained winds peaked at 85 mph (140 km/h) on August 21. Debby made three landfalls on August 22, in Barbuda, Saint Barthélemy, and Virgin Gorda, before re-entering the Atlantic north of Puerto Rico. As Debby moved parallel to the north coast of Hispaniola late on August 23, it weakened back to a tropical storm. The storm tracked westward and weakened further, instead of approaching Florida and strengthening into a major hurricane. While south of eastern Cuba on August 24, Debby was downgraded to a tropical depression, six hours before completely dissipating.
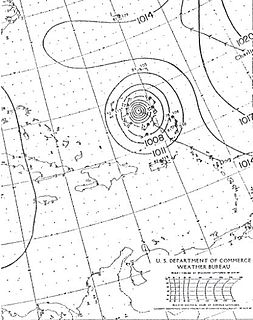 W
WHurricane Dog was the most intense hurricane in the 1950 Atlantic hurricane season. Prior to reanalysis by the Hurricane Research Division in 2014, it was considered one of the strongest Atlantic hurricanes on record, equivalent to Category 5 status on the modern Saffir-Simpson scale, with winds of 185 miles per hour (298 km/h). The fourth named storm of the season, Dog developed on August 30 to the east of Antigua; after passing through the northern Lesser Antilles, it turned to the north and intensified into a Category 4 hurricane. Dog reached its peak intensity with winds of 145 mph (230 km/h) over the open Atlantic, and after weakening it passed within 200 miles (320 km) of Cape Cod, Massachusetts. The storm became extratropical on September 12.
 W
WHurricane Donna, known in Puerto Rico as Hurricane San Lorenzo, was the strongest hurricane of the 1960 Atlantic hurricane season, and caused severe damage to the Lesser Antilles, the Greater Antilles, and the East Coast of the United States, especially Florida, in August–September. The fifth tropical cyclone, third hurricane, and first major hurricane of the season, Donna developed south of Cape Verde on August 29, spawned by a tropical wave to which 63 deaths from a plane crash in Senegal were attributed. The depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Donna by the following day. Donna moved west-northwestward at roughly 20 mph (32 km/h) and by September 1, it reached hurricane status. Over the next three days, Donna deepened significantly and reached maximum sustained winds of 130 mph (210 km/h) on September 4. Thereafter, it maintained intensity as it struck the Lesser Antilles later that day. On Sint Maarten, the storm left a quarter of the island's population homeless and killed seven people. An additional five deaths were reported in Anguilla, and there were seven other fatalities throughout the Virgin Islands. In Puerto Rico, severe flash flooding led to 107 fatalities, 85 of them in Humacao alone.
 W
WHurricane Earl was the first major hurricane to threaten New England since Hurricane Bob in 1991. The fifth named storm of the season, Earl originated from a tropical wave to west of the Cape Verde Islands on August 25, 2010. Tracking nearly due west, the system attained tropical storm intensity within hours of genesis. After maintaining winds of 50 mph (85 km/h) for nearly two days, Earl began to strengthen as it neared the Lesser Antilles. The storm intensified into a hurricane on August 29 and later a major hurricane on August 30 as it brushed the Leeward Islands. A temporary weakening trend took place as Earl moved northwestward, contributed to moderate southwesterly wind shear, but intensification later resumed by September 1. Once reorganized, Earl reached its peak winds of 145 mph (230 km/h). Executing a gradual curve to the northeast, the hurricane slowly weakened over decreasing sea surface temperatures; the storm's center passed roughly 85 mi (140 km) east of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina on September 3. Accelerating northeastward, the system briefly weakened to a tropical storm before reattaining hurricane strength as it made landfall near Western Head, Nova Scotia. After traversing the peninsula, the hurricane became extratropical and was later absorbed by a larger low pressure area on September 6, while located north of Newfoundland.
 W
WHurricane Faith reached the northernmost latitude and had the longest track of any Atlantic tropical cyclone. The sixth named storm and fifth hurricane of the 1966 Atlantic hurricane season, Faith developed from an area of disturbed weather between Cape Verde and the west coast of Africa on August 21. Tracking westward, the depression gradually intensified and became Tropical Storm Faith on the following day. Moving westward across the Atlantic Ocean, it continued to slowly strengthen, reaching hurricane status early on August 23. About 42 hours later, Faith reached an initial peak with winds of 105 mph (165 km/h), before weakening slightly on August 26. Located near the Lesser Antilles, the outer bands of Faith produced gale force winds in the region, especially Puerto Rico, the Virgin Islands, and Antigua. Minor coastal damage occurred as far south as Trinidad and Tobago.
 W
WHurricane Frederic was an intense and damaging tropical cyclone that carved a path of damage from the Lesser Antilles to Quebec, in particular devastating areas of the United States Gulf Coast. Though only five were killed directly, the US$1.77 billion in damage accrued by Frederic made it the Atlantic basin's costliest tropical cyclone on record at the time. Prior to its final landfall, the threat that Frederic imposed on areas of the U.S. Gulf Coast triggered a mass exodus from the region larger than any other evacuation in the past. While the storm primarily impacted the U.S. states of Mississippi and Alabama, lesser effects were felt throughout the Greater and Lesser Antilles, as well as inland North America.
 W
WHurricane Georges was a powerful and long-lived Cape Verde Category 4 hurricane which caused severe destruction as it traversed the Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico in September 1998, making seven landfalls along its path. Georges was the seventh tropical storm, fourth hurricane, and second major hurricane of the 1998 Atlantic hurricane season. It became the most destructive storm of the season, the costliest Atlantic hurricane since Hurricane Andrew in 1992 and remain the costliest until Hurricane Charley in 2004, and the deadliest since Hurricane Gordon in 1994. Georges killed 604 people, mainly on the island of Hispaniola, and caused extensive damage resulting at just under $10 billion in damages mostly in St. Kitts and Nevis, Puerto Rico and Hispaniola.
 W
WHurricane Gonzalo was the second tropical cyclone, after Hurricane Fay, to directly strike the island of Bermuda in a one-week time frame in October 2014, and was the first Category 4 Atlantic hurricane since Hurricane Ophelia in 2011. At the time, it was the strongest hurricane in the Atlantic since Igor in 2010. Gonzalo struck Bermuda less than a week after the surprisingly fierce Hurricane Fay; 2014 was the first season in recorded history to feature two hurricane landfalls in Bermuda. A powerful Atlantic tropical cyclone that wrought destruction in the Leeward Islands and Bermuda, Gonzalo was the seventh named storm, sixth and final hurricane and only the second major hurricane of the below-average 2014 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm formed from a tropical wave on October 12, while located east of the Lesser Antilles. It made landfall on Antigua, Saint Martin, and Anguilla as a Category 1 hurricane, causing damage on those and nearby islands. Antigua and Barbuda sustained US$40 million in losses, and boats were abundantly damaged or destroyed throughout the northern Leeward Islands. The storm killed three people on Saint Martin and Saint Barthélemy. Gonzalo tracked northwestward as it intensified into a major hurricane. Eyewall replacement cycles led to fluctuations in the hurricane's structure and intensity, but on October 16, Gonzalo peaked with maximum sustained winds of 145 mph.
 W
WHurricane Jose was a powerful and erratic tropical cyclone which was the longest-lived Atlantic hurricane since Hurricane Nadine in 2012. Jose was the tenth named storm, fifth hurricane, and third major hurricane of the 2017 Atlantic hurricane season. Jose developed into a tropical storm on September 5 from a tropical wave that left the west coast of Africa nearly a week prior. A period of rapid intensification ensued on September 6, when Jose reached hurricane intensity. On September 8, it reached its peak intensity as a high-end Category 4 hurricane. However, due to wind shear, Jose weakened over the next few days as it completed an anti-cyclonic loop north of Hispaniola. Despite weakening to a tropical storm on September 14, Jose managed to regain hurricane intensity the next day as it began to curve northwards. Never strengthening above Category 1 status for the remainder of its lifespan, Jose degraded to a tropical storm once again on September 20. Two days later, Jose transitioned into a post-tropical cyclone as it drifted northeastwards off the coast of New England. By September 26, Jose's remnants dissipated off the East Coast of the United States.
 W
WHurricane Irma was an extremely powerful Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread destruction across its path in September 2017. Irma was the first Category 5 hurricane to strike the Leeward Islands on record, followed by Maria two weeks later. At the time, it was considered as the most powerful hurricane on record in the open Atlantic region, outside of the Caribbean Sea and Gulf of Mexico until it was surpassed by Hurricane Dorian two years later. It was also the third strongest Atlantic hurricane at landfall ever recorded, just behind the 1935 Labor Day Hurricane and Hurricane Dorian.
 W
WHurricane Jose was the fourteenth tropical cyclone, tenth named storm, and seventh hurricane of the annual season that caused moderate damage in the Lesser Antilles in October 1999. Jose developed from a tropical wave several hundred miles east of the Windward Islands on October 17. The depression intensified and was subsequently upgraded to Tropical Storm Jose on October 18. The storm tracked northwestward and was upgraded to a hurricane the following day as it approached the northern Leeward Islands. Jose briefly peaked as a Category 2 hurricane with winds of 100 mph (160 km/h) on October 20. However, wind shear weakened the storm back to a Category 1 hurricane before it struck Antigua. Further deterioration occurred and Jose weakened to a tropical storm before landfall in Tortola on October 21. While located north of Puerto Rico on October 22, the storm turned northward, shortly before curving north-northeastward. Wind shear decreased, allowing Jose to re-intensify into a hurricane while passing east of Bermuda on October 24. However, on the following day, wind shear increased again, while sea surface temperatures decreased, causing Jose to weaken and quickly transition into an extratropical cyclone.
 W
WHurricane Klaus was a minimal Atlantic hurricane that dropped heavy rainfall across the Lesser Antilles in October 1990. The eleventh tropical cyclone and sixth hurricane of the 1990 Atlantic hurricane season, Klaus developed from a tropical wave on October 3 a short distance east of Dominica. It drifted northwestward, and quickly intensified to attain hurricane status on October 5. Though its closest approach to the Lesser Antilles was within 12 miles (19 km), the strongest winds remained to its northeast due to strong wind shear, which caused Klaus to steadily weaken. After deteriorating into a tropical depression, Klaus briefly restrengthened over the Bahamas before dissipating on October 9 under the influence of developing tropical storm, Marco.
 W
WHurricane Lenny is tied with 2001's Michelle as the fourth strongest November Atlantic hurricane on record, behind the 1932 Cuba hurricane and 2020 Hurricanes Iota and Eta. It was the twelfth tropical storm, eighth hurricane, and record-breaking fifth Category 4 hurricane in the 1999 Atlantic hurricane season. Lenny formed on November 13 in the western Caribbean Sea and maintained an unprecedented west-to-east track for its entire duration, which gave it the common nickname, "Wrong Way Lenny". It attained hurricane status south of Jamaica on November 15 and passed south of Hispaniola and Puerto Rico over the next few days. Lenny rapidly intensified over the northeastern Caribbean on November 17, attaining peak winds of 155 mph (249 km/h) about 21 mi (34 km) south of Saint Croix in the United States Virgin Islands. It gradually weakened while moving through the Leeward Islands, eventually dissipating on November 23 over the open Atlantic Ocean.
 W
WHurricane Luis was a very large, long-lived, powerful and very destructive Category 4 Cape Verde hurricane, as well as one of the strongest and most notable hurricanes of the 1995 Atlantic hurricane season. Luis was also the strongest hurricane to make landfall, and the third-most intense hurricane recorded during the extremely active season. It was the twelfth tropical storm, sixth hurricane, and second major hurricane of the season. At one point, the storm was one of four simultaneous tropical systems in the Atlantic basin, along with Humberto, Iris, and Karen. The storm lasted for 14 days as a tropical storm between late August and mid-September.
 W
WHurricane Marilyn was the most powerful hurricane to strike the Virgin Islands since Hurricane Hugo of 1989, and the third such tropical cyclone in roughly a two-week time span to strike or impact the Leeward Islands, the others being Hurricane Iris and the much more powerful and destructive Hurricane Luis. The thirteenth named storm, seventh hurricane and third major hurricane of the extremely active 1995 Atlantic hurricane season, Marilyn formed on September 12 as a tropical depression from a tropical wave that moved off the coast of Africa on September 7. After formation, the storm quickly became a tropical storm, and steadily intensified into a hurricane by the time it struck the Lesser Antilles on September 14 at Category 1 strength. Entering the northeastern Caribbean Sea, rapid intensification ensued and it peaked on September 16 north of Puerto Rico as a Category 3 hurricane shortly after it had impacted the U.S. Virgin Islands. A Hurricane Hunter reconnaissance flight reported hail, which is unusual for tropical cyclones. After heading north past Bermuda, Marilyn weakened and became extratropical on September 22. The remnant circulation wandered the Atlantic Ocean from September 23 – October 1, just south of Nova Scotia.
 W
WHurricane Omar was a powerful tropical cyclone that took an unusual southwest to northeast track through the eastern Caribbean Sea during mid-October 2008. Forming out of a tropical disturbance on October 13, Omar initially moved slowly in the eastern Caribbean Sea. By October 15, Omar began to quickly intensify as deep convection developed around the center of circulation. Later that day, an eye developed and the storm began to accelerate to the northeast. Early on October 16, Omar reached its peak intensity with maximum winds of 130 mph (215 km/h) and a barometric pressure of 958 mbar. Shortly after, the hurricane rapidly weakened to Category 1 intensity. After slightly re-strengthening the next day, Omar weakened to a tropical storm before degenerating into a non-convective low pressure area. The remnants of Omar persisted until October 21, at which time they dissipated to the west of the Azores.
 W
WHurricane Rafael produced minor damage in the northeastern Caribbean Sea in mid-October 2012. The seventeenth named storm and ninth hurricane of the annual hurricane season, Rafael originated from a tropical wave roughly 230 mi (370 km) south-southeast of Saint Croix on October 12; because the system already contained tropical storm-force winds, it skipped tropical depression status. Though initially disorganized due to moderate wind shear, a subsequent decrease allowed for shower and thunderstorm activity to develop in earnest by October 14. While moving north-northwestward the following morning, Rafael intensified into a Category 1 hurricane. A cold front off the East Coast of the United States caused the system to turn northward and eventually northeastward by October 16, at which time Rafael attained its peak intensity with maximum sustained winds of 90 mph (150 km/h). As the cyclone entered a more stable atmosphere and tracked across increasingly cooler sea surface temperatures, it began extratropical transition, a process the system completed by the following afternoon.