 W
WThe following sortable table lists the 113 mountain peaks of the United States with at least 100 kilometers of topographic isolation and at least 500 meters of topographic prominence. 107 mountain peaks are located in the 50 states, while 6 mountain peaks are located in the U.S. territories.
 W
WThe following sortable table comprises the 302 mountain peaks of the United States with at least 3000 meters of topographic elevation and at least 500 meters of topographic prominence.
 W
WThe following sortable table comprises the 104 mountain peaks of the United States with at least 4000 meters of topographic elevation and at least 500 meters of topographic prominence.
 W
WAn American Viticultural Area (AVA) is a designated wine grape-growing region in the United States, providing an official appellation for the mutual benefit of wineries and consumers. Winemakers frequently want their consumers to know about the geographic pedigree of their wines, as wines from a particular area can possess distinctive characteristics. Consumers often seek out wines from specific AVAs, and certain wines of particular pedigrees can claim premium prices and loyal customers. If a wine is labeled with an AVA, at least 85% of the grapes that make up the wine must have been grown in the AVA, and the wine must be fully finished in the state where the AVA is located.
 W
WThis is a list of some aquifers in the United States.
 W
WThe following is a list of the 3,142 counties and county-equivalents in the 50 states and District of Columbia sorted by U.S. state, plus an additional 100 county-equivalents in the U.S. territories sorted by territory.
 W
WThis list of North American deserts identifies areas of the continent that receive less than 10 in (250 mm) annual precipitation. The "North American Desert" is also the term for a large U.S. Level 1 ecoregion (EPA) of the North American Cordillera, in the Deserts and xeric shrublands biome (WWF). The continent's deserts are largely between the Rocky Mountains and Sierra Madre Oriental on the east, and the rain shadow-creating Sierra Nevada, Transverse, and Peninsular Ranges on the west. The North American xeric region of over 95,751 sq mi (247,990 km2) includes: three major deserts; numerous smaller deserts; and large non-desert arid regions; in the western United States and in northeast, central, and northwest Mexico.
 W
WThe following is a list of ecoregions in the United States as identified by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF). The United States is a megadiverse country with a high level of endemism across a wide variety of ecosystems.
 W
WIn the mountaineering parlance of the Western United States, a fourteener is a mountain peak with an elevation of at least 14,000 feet. There are 96 fourteeners in the United States, all west of the Mississippi River. Colorado has the most (53) of any single state; Alaska is in second place with 29. Many peak baggers try to climb all fourteeners in the contiguous United States, one particular state, or another region.
 W
WThe Great Basin is the largest region of contiguous endorheic drainage basins in North America, and is encompassed by the Great Basin Divide. This is a list of the drainage basins in the Great Basin that are over 500 sq mi (1,300 km2), listed by the state containing most of the basin.
 W
WThe following sortable table comprises the 200 highest mountain peaks of the United States with at least 500 meters of topographic prominence.
 W
WThe following sortable table comprises the 209 most topographically isolated mountain peaks of the United States of America with at least 500 meters of topographic prominence.
 W
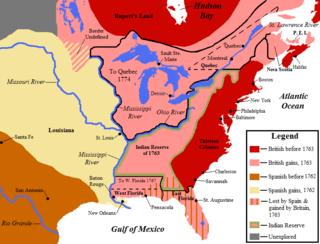
WThis is a list of historic regions of the United States that existed at some time during the territorial evolution of the United States and its overseas possessions, from the colonial era to the present day. It includes formally organized territories, proposed and failed states, unrecognized breakaway states, international and interstate purchases, cessions, and land grants, and historical military departments and administrative districts. The last section lists informal regions from American vernacular geography known by popular nicknames and linked by geographical, cultural, or economic similarities, some of which are still in use today.
 W
WOrganized incorporated territories are territories of the United States that are both incorporated and organized. There have been no such territories since 1959.
 W
WThe United States has 154 protected areas known as National Forests covering 188,336,179 acres. The National Forests are managed by the U.S. Forest Service, an agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture. The first National Forest was established as the Yellowstone Park Timber and Land Reserve on March 30, 1891, then in the Department of the Interior. In 1897, the Organic Act provided purposes for which forest reserves could be established, including to protect the forest, secure water supplies, and supply timber. With the Forest Reserve Act of 1891, the President of the United States was given the power to set aside forest reserves in the public domain. With the Transfer Act of 1905, forest reserves became part of the U.S. Department of Agriculture in the newly created U.S. Forest Service.
 W
WThese are the major U.S. river basins in the U.S., as designated by the U.S. Water Resources Council. Each of these river basins contain a number of smaller river basins.
 W
WSince the establishment of the United States in 1776, numerous state partition proposals have been put forward that would partition an existing state in order that a particular region within might either join another state, or create a new state. Article IV, Section 3, Clause 1 of the United States Constitution, often called the New States Clause, grants to the United States Congress the authority to admit new states into the United States beyond the thirteen already in existence at the time the Constitution went into effect. It also includes a stipulation originally designed to give Eastern states that still had Western land claims a veto over whether their western counties could become states.New States may be admitted by the Congress into this Union; but no new State shall be formed or erected within the Jurisdiction of any other State; nor any State be formed by the Junction of two or more States, or Parts of States, without the Consent of the Legislatures of the States concerned as well as of the Congress.
 W
WThe United States of America is a federal republic consisting of 50 states, a federal district, five major territories, and various minor islands. The 48 contiguous states and Washington, D.C., are in North America between Canada and Mexico, while Alaska is in the far northwestern part of North America and Hawaii is an archipelago in the mid-Pacific. Territories of the United States are scattered throughout the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea.
 W
WThe states and territories included in the United States Census Bureau's statistics include the fifty states, the District of Columbia, and the five permanently inhabited territories of the United States, including Puerto Rico.
 W
WA state of the United States is one of the 50 constituent entities that shares its sovereignty with the federal government. Americans are citizens of both the federal republic and of the state in which they reside, due to the shared sovereignty between each state and the federal government. Kentucky, Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, and Virginia use the term commonwealth rather than state in their full official names.