 W
WThe Kingdom of Bhutan is divided into 20 districts. Bhutan is located between the Tibet Autonomous Region of China and India on the eastern slopes of the Himalayas in South Asia.
 W
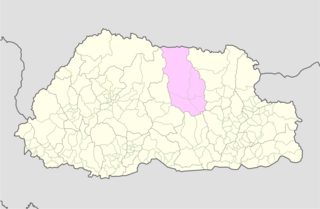
WBumthang District is one of the 20 dzongkhag (districts) comprising Bhutan. It is the most historic dzongkhag if the number of ancient temples and sacred sites is counted. Bumthang consists of the four mountain valleys of Ura, Chumey, Tang and Choekhor ("Bumthang"), although occasionally the entire district is referred to as Bumthang Valley.
 W
WChukha District is one of the 20 dzongkhag (districts) comprising Bhutan. The major town is Phuentsholing which is the gateway city along the sole road which connects India to western Bhutan. Chukha is the commercial and the financial capital of Bhutan. With Bhutan's oldest hydropower plant, Chukha hydel, and Tala Hydroelectricity Project, the country's largest power plant, Chukha is the dzongkhag which contributes the most to the GDP of the country. Also located in Chukha district are some of the country's oldest industrial companies like the Bhutan Carbide Chemical Limited (BCCL) and the Bhutan Boards Products Limited (BBPL).
 W
WDagana District is a district located in Bhutan. Most of the district is populated by Dzongkha speakers. However, in the southwest part near the Sarpang District, Nepali is also spoken as a native language.
 W
WGasa District or Gasa Dzongkhag is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. The capital of Gasa District is Gasa Dzong near Gasa. It is located in the far north of the county and spans the Middle and High regions of the Tibetan Himalayas. The dominant language of the district is Dzongkha, which is the national language. Related languages, Layakha and Lunanakha, are spoken by semi-nomadic communities in the north of the district. The People's Republic of China claims the northern part of Gasa District.
 W
WHaa District is one of the 20 dzongkhag or districts comprising Bhutan. Per the 2017 census, the population of Haa dzongkhag was 13,655 in 2,952 households making it the second least populated dzongkhag in Bhutan after Gasa. The dominant language of the district is Dzongkha, the national language.
 W
WLhuntse District is one of the 20 dzongkhag (districts) comprising Bhutan. It consists of 2506 households. Located in the northeast, Lhuntse is one of the least developed dzhongkhags of Bhutan. There are few roads, the first gas station was opened in September 2005, electricity is not well distributed, and the difficult terrain makes distribution of social welfare problematic. Despite its favourable climate, farming is hindered by the lack of infrastructure.
 W
WMongar District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. Mongar is the fastest-developing dzongkhag in eastern Bhutan. A regional hospital has been constructed and the region is bustling with many economic activities. Mongar is noted for its lemon grass, a plant that can be used to produce an essential oil. It also has a hydroelectric power-plant on the Kuri Chhu river.
 W
WParo District is a district (dzongkhag), valley, river and town in Bhutan. It is one of the most historic valleys in Bhutan. Both trade goods and invading Tibetans came over the pass at the head of the valley, giving Paro the closest cultural connection with Tibet of any Bhutanese district. The dominant language in Paro is Dzongkha, the national language.
 W
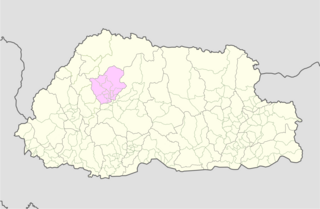
WPemagatshel District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) constituting Bhutan.
 W
WPunakha District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It is bordered by Thimphu, Gasa, and Wangdue Phodrang Districts. The dominant language in the district is Dzongkha, the national language.
 W
WSamdrup Jongkhar District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. The dominant languages of the district are Tshangla (Sharchopkha) in the north and west, and Nepali in the east.
 W
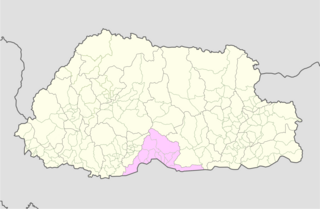
WSamtse District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan.
 W
WSarpang District is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan.
 W
WThimphu District is a dzongkhag (district) of Bhutan. Thimphu is also the capital of Bhutan and the largest city in the whole kingdom.
 W
WTrashigang District is Bhutan's easternmost dzongkhag (district).
 W
WTrashiyangtse District is one of the twenty dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It was created in 1992 when Trashiyangtse district was split off from Trashigang District. Trashiyangtse covers an area of 1,437.9 square kilometres (555.2 sq mi). At an elevation of 1750–1880 m, Trashi yangtse dzongkhag is rich of culture filled with sacred places blessed by Guru Rimpoche and dwelled by Yangtseps, Tshanglas, Bramis from Tawang, Khengpas from Zhemgang and Kurtoeps from Lhuentse.
 W
WTrongsa District is one of the districts of Bhutan. It is the most central district of Bhutan and the geographic centre of Bhutan is located within it at Trongsa Dzong.
 W
WTsirang District (Dzongkha: རྩི་རང་རྫོང་ཁག་; Wylie: Rtsi-rang rdzong-khag; previously, is one of the 20 dzongkhags of Bhutan. The administrative center of the district is Damphu.
 W
WWangdue Phodrang District is a dzongkhag (district) of central Bhutan. This is also the name of the dzong which dominates the district, and the name of the small market town outside the gates of the dzong—it is the capital of Wangdue Phodrang District). The name is said to have been given by the Shabdrung Ngawang Namgyal who was searching for the best location for a dzong to prevent incursions from the south. The word "wangdue" means unification of Country, and "Phodrang" means Palace in Dzongkha.
 W
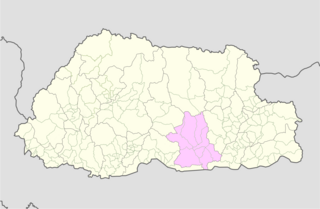
WZhemgang District, is one of the 20 dzongkhags (districts) comprising Bhutan. It is bordered by Sarpang, Trongsa, Bumthang, Mongar and Samdrup Jongkhar Districts, and borders Assam in India to the south. Administrative center of the district is Zhemgang.