 W
WThe 1797 Sumatra earthquake occurred at 22:00 local time on February 10. It was the first in a series of great earthquakes that ruptured part of the Sumatran segment of the Sunda megathrust. It caused a damaging tsunami that was particularly severe near Padang, where a 150–200 ton English ship was driven 1 km inland up the Arau River.
 W
WThe 1833 Sumatra earthquake occurred on November 25 at about 22:00 local time, with an estimated magnitude in the range of 8.8–9.2 Mw . It caused a large tsunami that flooded the southwestern coast of the island. There are no reliable records of the loss of life, with the casualties being described only as 'numerous'. The magnitude of this event has been estimated using records of uplift taken from coral microatolls.
 W
WThe 1861 Sumatra earthquake occurred on February 16 and was the last in a sequences of earthquakes that ruptured adjacent parts of the Sumatran segment of the Sunda megathrust. It caused a devastating tsunami which led to several thousand fatalities. The earthquake was felt as far away as the Malay peninsula and the eastern part of Java. The rupture area for the 2005 Nias–Simeulue earthquake is similar to that estimated for the 1861 event.
 W
WOn 30 September 1899 the island of Ceram, Dutch Indies, was struck by an Ms = 7.8 earthquake, which was accompanied by a 10-metre tsunami. According to the Batavian Magnetic and Meteorological Observatory, the shock occurred at 01:42.2 hours, Amahei local time. Dr. R. D. M. Verbeek's study about the quake and its effects was published in his Short Report about the earth- and sea-quake in Ceram, the 30th September 1899, and is the only extensive source on the Ceram earthquake.
 W
WThe 1917 Bali earthquake occurred at 06:50 local time on 21 January. It had an estimated magnitude of 6.6 on the surface wave magnitude scale and had a maximum perceived intensity of IX (Violent) on the Mercalli intensity scale. It caused widespread damage across Bali, particularly in the south of the island. It triggered many landslides, which caused 80% of the 1500 casualties.
 W
WThe 1931 Southwest Sumatra earthquake occurred on 25 September at 05:59 UTC. It was located between the Enggano Island and Sumatra, Indonesia, then under the rule of Dutch East Indies. It had a magnitude of Mw 7.3, or Ms 7.5.
 W
WThe 1965 Ceram Sea earthquake occurred on January 24 at 00:11 UTC with a moment magnitude of 8.2 and its epicenter was located just off the southwestern coast of Sanana Island in eastern Indonesia. The event occurred at a depth of 28 kilometers under the Ceram Sea, and a tsunami was generated which caused damage in Sanana, Buru, and Mangole. During the tsunami three consecutive run-ups were reported in Seram Island, and a four-meter run-up was reported at Buru Island.
 W
WThe 1968 Sulawesi earthquake struck Indonesia on August 14. It had a Richter magnitude of 7.4, spawned a large tsunami, and killed roughly 200 people.
 W
WThe 1977 Sumba earthquake occurred approximately 290 kilometres (180 mi) south of Bima, Sumbawa, and beneath the Indian Ocean, at 14:08 local time on 19 August. With a moment magnitude of 8.3, the earthquake is notable for having an unusually great magnitude for a shock with a normal faulting focal mechanism. The shock occurred near the southern section of the Sunda Trench where several other tsunami-generating earthquakes have occurred. The earthquake was at the time the largest outer-rise earthquake ever recorded in Indonesia, and aftershocks along the trench extended about 130 kilometres (81 mi) eastward and 110 kilometres (68 mi) westward from the epicenter.
 W
WThe 1992 Flores earthquake and tsunami occurred on December 12 on the island of Flores in Indonesia. With a magnitude of 7.8 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe), it was the largest and also the deadliest earthquake in 1992.
 W
WThe 1994 Java earthquake occurred on June 3 at 01:17:37 local time off the coast of Indonesia. The epicenter was off the eastern part of the southern Java coast, near the east end of the Java Trench.
 W
WOn January 1, 1996, at 4:05 p.m. Central Indonesia Time, a powerful earthquake with an epicenter in the Makassar Strait struck north of Minahasa on the island of Sulawesi, Indonesia. The earthquake registered a magnitude 7.9 on the moment magnitude scale and was centered off Tolitoli Regency in Central Sulawesi, or 25 km from the Tonggolobibi village. A tsunami of 2 to 4 meters was triggered by this earthquake as a result. This event was larger but far less deadly compared to the Mw 7.5 Sulawesi earthquake in 2018 slightly south of where this earthquake occurred. At least 350 buildings were badly damaged, nine people were killed and 63 people injured.
 W
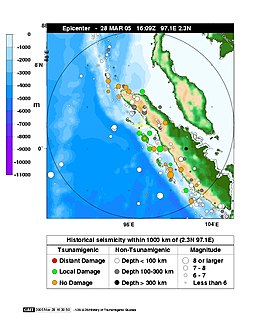
WThe 2005 Nias–Simeulue earthquake occurred on 28 March off the west coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia. At least 915 people were killed, mostly on the island of Nias. The event caused panic in the region, which had already been devastated by the massive tsunami triggered by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, but this earthquake generated a relatively small tsunami that caused limited damage. It was the third most powerful earthquake since 1965 in Indonesia.
 W
WThe 2006 Pangandaran earthquake and tsunami occurred on July 17 at 15:19:27 local time along a subduction zone off the coast of west and central Java, a large and densely populated island in the Indonesian archipelago. The shock had a moment magnitude of 7.7 and a maximum perceived intensity of IV (Light) in Jakarta, the capital and largest city of Indonesia. There were no direct effects of the earthquake's shaking due to its low intensity, and the large loss of life from the event was due to the resulting tsunami, which inundated a 300 km (190 mi) portion of the Java coast that had been unaffected by the earlier 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami that was off the coast of Sumatra. The July 2006 earthquake was also centered in the Indian Ocean, 180 kilometers (110 mi) from the coast of Java, and had a duration of more than three minutes.
 W
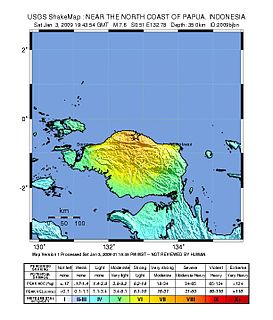
WThe 2009 Papua earthquakes occurred on January 4 local time in Indonesia's West Papua province. The very large earthquake doublet comprised a magnitude 7.6 initial shock that had a maximum Mercalli intensity of VI (Strong) and a second very large event that had a moment magnitude of 7.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The events took place less than three hours apart to the east-northeast of Sorong on the Bird's Head Peninsula and left at least four people dead and dozens injured.
 W
WThe 2010 Mentawai earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 7.8 on 25 October off the western coast of Sumatra at 21:42 local time. The earthquake occurred on the same fault that produced the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. It was widely felt across the provinces of Bengkulu and West Sumatra and resulted in a substantial localized tsunami that struck the Mentawai Islands.
 W
WOn 28 September 2018, a shallow, large earthquake struck in the neck of the Minahasa Peninsula, Indonesia, with its epicentre located in the mountainous Donggala Regency, Central Sulawesi. The magnitude 7.5 quake was located 70 km (43 mi) away from the provincial capital Palu and was felt as far away as Samarinda on East Kalimantan and also in Tawau, Malaysia. This event was preceded by a sequence of foreshocks, the largest of which was a magnitude 6.1 tremor that occurred earlier that day.
 W
WOn 22 December 2018, a tsunami that followed an eruption and partial collapse of the Anak Krakatau volcano in the Sunda Strait struck several coastal regions of Banten in Java and Lampung in Sumatra, Indonesia. At least 426 people were killed and 14,059 were injured. The tsunami was caused by an undersea landslide that followed an eruption of Anak Krakatau, the "Child of Krakatoa". On 23 December, it was found that much of the island of Anak Krakatau had collapsed into the sea.
 W
WThe 1996 Biak earthquake, or the 1996 Irian Jaya earthquake, occurred on February 17 at 14:59:30 local time near Biak Island, Indonesia. The earthquake had a moment magnitude of 8.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). The run-up height of the generated tsunami reached 7 meters (23 ft). One-hundred and sixty-six people were reported dead, 423 were injured, and 5,090 were made homeless.
 W
WThe 1883 eruption of Krakatoa in the Sunda Strait began on the afternoon of Sunday, 26 August 1883—with origins as early as that May—and peaked on the late morning of Monday, 27 August 1883, when over 70% of the island of Krakatoa and its surrounding archipelago were destroyed as it collapsed into a caldera.
 W
WThis is an incomplete list of more recent recorded major earthquakes that have occurred within the boundaries of Indonesia—as indicated by the geology of the region, and the volcanic activity—much large numbers of earthquakes of smaller magnitude occur very regularly due to the meeting of major tectonic plates in the region. Based on the records of the USGS, Indonesia has had more than 150 earthquakes with magnitude > 7 in the period 1901–2017.