 W
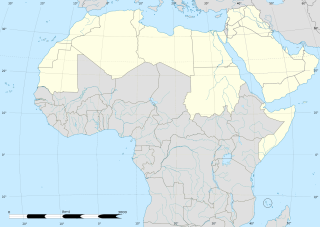
WThe Arab world, formally the Arab homeland, also known as the Arab nation, the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, consists of the 22 Arab countries which are members of the Arab League. A majority of these countries are located in Western Asia, North Africa, and the Horn of Africa; the southernmost member, the Comoros, is an island country off the coast of East Africa. The region stretches from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the east, and from the Mediterranean Sea in the north to the Indian Ocean in the southeast. The eastern part of the Arab world is known as the Mashriq, and the western part as the Maghreb. Arabic is used as the lingua franca throughout the Arab world.
 W
WThe East Asian cultural sphere, Chinese cultural sphere or Sinosphere encompasses the countries within East and Southeast Asia that were historically influenced by Chinese culture. The region is not to be confused with Greater China, a region that encompasses countries with majority Han Chinese or Chinese-speaking populations.
 W
WThe Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc, the Socialist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, and Southeast Asia under the hegemony of the Soviet Union (USSR) that existed during the Cold War (1947–1991) in opposition to the capitalist Western Bloc. In Western Europe, the term Eastern Bloc generally referred to the USSR and its satellite states in the Comecon ; in Asia, the Soviet Bloc comprised the Mongolian People's Republic, the Socialist Republic of Vietnam, the Lao People's Democratic Republic and the People's Republic of Kampuchea, the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, and the People's Republic of China. In the Americas, the Communist Bloc included the Caribbean Republic of Cuba since 1961 and Grenada.
 W
WEastern world, also known as the East, is an umbrella term for various cultures or social structures, nations and philosophical systems, which vary depending on the context. It most often includes at least part of Asia or, geographically, the countries and cultures east of Europe, the Mediterranean region and Arab world, specifically in historical (pre-modern) contexts, and in modern times in the context of Orientalism. It is often seen as a counterpart to the Western world, and correlates strongly to the southern half of the North–South divide.
 W
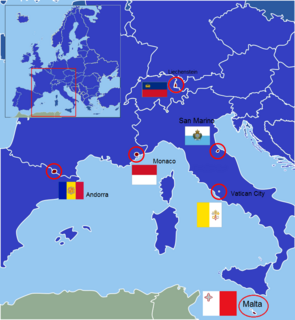
WThe European microstates or European ministates are a set of very small sovereign states in Europe. The term is typically used to refer to the six smallest states in Europe by area: Andorra, Liechtenstein, Malta, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City. Four of these states are monarchies. These states trace their status back to the first millennium or the early second millennium except for Liechtenstein, created in the 17th century.
 W
WGreater India, or Indian cultural sphere is an area composed of many countries and regions in South and Southeast Asia that were historically influenced by Indian culture. The term Greater India as a reference to the Indian cultural sphere was popularised by a network of Bengali scholars in the 1920s. It is an umbrella term encompassing the Indian subcontinent, and surrounding countries which are culturally linked or have received significant Sanskritisation and Indian influence in matters such as written language and religion. These countries have been transformed to varying degrees by the acceptance and induction of cultural and institutional elements that originated in India and spread elsewhere via trade routes. Since around 500 BCE, Asia's expanding land and maritime trade had resulted in prolonged socio-economic and cultural stimulation and diffusion of Hindu and Buddhist beliefs into the region's cosmology, in particular in Southeast Asia and Sri Lanka. In Central Asia, transmission of ideas were predominantly of a religious nature. The Spread of Islam significantly altered the course of the history of greater India.
 W
WGreater Iran or Greater Persia refers to the regions of West Asia, Central Asia, South Asia and Transcaucasia where Iranian culture has had significant influence. Historically, these were regions long ruled by dynasties of various Iranian empires, that incorporated considerable aspects of Persian culture through extensive contact with them, or where sufficient Iranian peoples settled to still maintain communities who patronize their respective cultures. It roughly corresponds to the Iranian plateau and its bordering plains. The Encyclopædia Iranica uses the term Iranian Cultural Continent for this region.
 W
WHispanic America, also known as Spanish America, is the portion of the Americas comprising the Spanish-speaking countries of the continents of North and South America. In all of these countries, Spanish is the main language, sometimes sharing official status with one or more indigenous languages, or English and Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion.
 W
WIbero-America or Iberian America is a region in the Americas comprising countries or territories where Spanish or Portuguese are predominant languages. Portugal and Spain are themselves included in some definitions, such as that of the Ibero-American Summit and the Organization of Ibero-American States. The Organization of Ibero-American States also includes Spanish-speaking Equatorial Guinea, in Central Africa, but not the Portuguese-speaking African countries.
 W
WAn island country or island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. As of 1996, 25.2% of all independent countries were island countries. Island nations, because of their geography, tend to be significantly more vulnerable to climate change than other nations, in part because of sea level rise, saltwater intrusion, and impacts on food supply.
 W
WA landlocked country or landlocked state is a sovereign state that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 5 partially recognized landlocked states.. Kazakhstan is the world's largest landlocked country.
 W
WLatin America is a group of countries and dependencies in the Western Hemisphere where Romance languages such as Spanish, French or Portuguese are predominantly spoken. Some territories such as Quebec, where French is spoken, or areas of the United States where Spanish is predominantly spoken are not included due to the country being a part of Anglo America. The term is broader than categories such as Hispanic America which specifically refers to Spanish-speaking countries or Ibero-America which specifically refers to both Spanish and Portuguese-speaking countries. The term is also more recent in origin.
 W
WThe Latin Union was an international organization of nations that used Romance languages that existed as a functional institution from 1983 to 2012. Its aim was to protect, project, and promote the common cultural heritage of Latin peoples and unifying identities of the Latin, and Latin-influenced, world. It was created in 1954 in Madrid, Spain, and its membership rose from 12 to 36 states, including countries in North America, South America, Europe, Africa, and the Asia-Pacific region.
 W
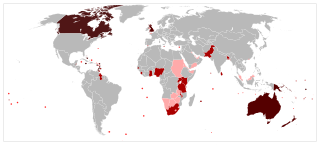
WThe number of states headed by Queen Elizabeth II has varied during her 68 years on the throne, altogether seeing her as sovereign of a total of 32 independent countries during this period. In her capacity as Queen of the United Kingdom, she is also monarch of three Crown dependencies—Guernsey, Jersey, and Man—and, in her capacity as Queen of New Zealand, she is monarch of two associated states—the Cook Islands and Niue—since they acquired this status in 1965 and 1974, respectively.
 W
WA microstate or ministate is a sovereign state having a very small population or very small land area, and usually both. The meanings of "state" and "very small" are not well-defined in international law. Recent attempts, since 2010, to define microstates have focused on identifying political entities with unique qualitative features linked to their geographic or demographic limitations. According to a qualitative definition, microstates are "modern protected states, i.e. sovereign states that have been able to unilaterally depute certain attributes of sovereignty to larger powers in exchange for benign protection of their political and economic viability against their geographic or demographic constraints." In line with this and most other definitions, examples of microstates include Andorra, the Federated States of Micronesia, Liechtenstein, the Marshall Islands, Monaco, Palau, and San Marino. The smallest political entity recognized as a sovereign state is Vatican City, with around 1,000 citizens as of 2017 and an area of only 44 hectares.
 W
WThe term "New World" is a name used for the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas. The term gained prominence in the early 16th century, during the Age of Discovery, shortly after Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci concluded that America represented a new continent, and subsequently published his findings in a pamphlet titled Mundus Novus. This realization expanded the geographical horizon of classical European geographers, who had thought the world consisted of Africa, Europe, and Asia, collectively now referred to as the Old World, or Afro-Eurasia. The Americas were also referred to as the fourth part of the world.
 W
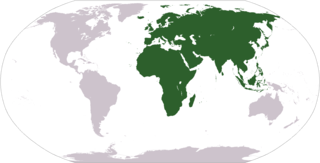
WThe term "Old World" is used commonly in the West to refer to Africa, Asia and Europe, regarded collectively as the part of the world known to its population before contact with the "New World".
 W
WRomance-speaking Africa or Latin Africa consists of the countries and territories in Africa whose official or main languages are Romance ones, and countries which have significant populations that speak Romance languages: French, Portuguese, Spanish, and Italian.
 W
WThe Romance-speaking world, romanophone, neolatin world, or Latin-speaking world, is the part of the world where Romance languages are either official, co-official, or significantly used, comprising Latin Europe and Latin America, as well as parts of North America and Romance-speaking Africa and Romance-speaking Asia.
 W
WThe terms First World, Second World, and Third World were originally used to divide the world's nations into three categories. The complete overthrow of the post–World War II status quo, known as the Cold War, left two superpowers vying for ultimate global supremacy. They created two camps, known as blocs. These blocs formed the basis of the concepts of the First and Second Worlds.
 W
WThe Western Bloc, also known as the Capitalist Bloc, was a coalition of countries that were allied with the United States, a member of NATO, and/or opposed the Soviet Union, Warsaw Pact, and communism during the Cold War. The latter were referred to as the Eastern Bloc. The governments and press of the Western Bloc were more inclined to refer to themselves as the "Free World" or the "Western world", whereas the Eastern Bloc was often called the "Communist world or Second world".
 W
WThe Western world, also known as the West, refers to various regions, nations and states, depending on the context, most often consisting of the majority of Europe, Australasia, and the Americas. The Western world is also known as the Occident, in contrast to the Orient, or Eastern world. It might mean the Northern half of the North–South divide. Western culture is commonly said to include: Australia, Canada, all European member countries of the EFTA and EU, the European microstates, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, and the United States.