 W
WRates and causes of deforestation vary from region to region around the world. In 2009, 2/3 of the world forests were in 10 top countries: 1) Russia, 2) Brazil, 3) Canada, 4) United States, 5) China, 6) Australia, 7) Congo, 8) Indonesia, 9) Peru and 10) India.
 W
WThe forestry sector in Argentina has great potential. The geography of the country extends from north to south, encompassing 4,000 kilometres (2,500 mi). Its variety of climates, land quality, and reliable precipitation allow for the cultivation of different tree species at high growth rates. The climate varies and most areas are quite temperate. The country also enjoys short harvest periods for the most important species. This has allowed the industry to become more competitive and continue its high growth rates.
 W
WDeforestation in Borneo has taken place on an industrial scale since the 1960s. Borneo, the third largest island in the world, divided between Indonesia, Malaysia and Brunei, was once covered by dense tropical and subtropical rainforests.
 W
WBrazil once had the highest deforestation rate in the world and in 2005 still had the largest area of forest removed annually. Since 1970, over 700,000 square kilometres (270,000 sq mi) of the Amazon rainforest have been destroyed. In 2012, the Amazon was approximately 5,400,000 square kilometres (2,100,000 sq mi), which is only 87% of the Amazon's original size.
 W
WThe deforestation in British Columbia has occurred at a heavy rate during periods of the past, but with new sustainable efforts and programs the rate of deforestation is decreasing in the province. In British Columbia, forests cover over 55 million hectares, which is 57.9% of British Columbia's 95 million hectares of land. The forests are mainly composed of coniferous trees, such as pines, spruces and firs.
 W
WCambodia is one of the world's most forest endowed countries that has not yet been drastically deforested. However, massive deforestation for economic development threatens its forests and ecosystems. As of 2015, the country has one of the highest rates of deforestation in the world.
 W
WCentral American countries have experienced cycles of deforestation and reforestation since the decline of Maya civilization, influenced by many factors such as population growth and agriculture. From 2001 to 2010, 5,376 square kilometres (2,076 sq mi) of forest were lost in the region. In 2010 Belize had 63% of remaining forest cover, Costa Rica 46%, Panama 45%, Honduras 41%, Guatemala 37%, Nicaragua 29%, and El Salvador 21%. Most of the loss occurred in the moist forest biome, with 12,201 square kilometers. Woody vegetation loss was partially set off by a plus in the coniferous forest biome with 4,730 km2, and at 2,054 km2. Mangroves and deserts contributed only 1% to the loss in forest vegetation. The bulk of the deforestation was located at the Caribbean slopes of Nicaragua with a minus of 8,574 square kilometers of forest lost in the period from 2001 to 2010. The most significant regrowth of 3,050 km2 of forest was seen in the coniferous woody vegetation of Honduras.
 W
WColombia loses 2,000 km2 of forest annually to deforestation, according to the United Nations in 2003. Some suggest that this figure is as high as 3,000 km² due to illegal logging in the region. Deforestation results mainly from logging for timber, small-scale agricultural ranching, mining, development of energy resources such as hydro-electricity, infrastructure, cocaine production, and farming. Around one-third of the country's original forest has been removed as a result of deforestation.
 W
WDeforestation in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is a significant transnational issue. In the DRC, forests are cleared for agricultural purposes by utilizing slash and burn techniques.
 W
WDeforestation is a major threat to biodiversity and ecosystems in Costa Rica. The country has a rich biodiversity with some 12,000 species of plants, 1,239 species of butterflies, 838 species of birds, 440 species of reptiles and amphibians, and 232 species of mammals, which have been under threat from deforestation.
 W
WDeforestation in Ethiopia is due to locals clearing forests for their personal needs, such as for fuel, hunting, agriculture, and at times for religious reasons. The main causes of deforestation in Ethiopia are shifting agriculture, livestock production and fuel in drier areas. Deforestation is the process of removing the forest ecosystem by cutting the trees and changing the shape of the land to suit different uses.
 W
WDeforestation in Laos is a major environmental concern, with Laos losing forest area to legal and illegal logging.
 W
WDeforestation in Haiti is a severe but complex and often misunderstood environmental problem. Haitians produce and consume charcoal as their primary source of domestic energy.
 W
WDeforestation in Indonesia involves the long-term loss of forests and foliage across much of the country; it has had massive environmental and social impacts. Indonesia is home to some of the most biologically diverse forests in the world and ranks third in number of species behind Brazil and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
 W
WKenya’s forests are fragmented across the country, combined together the forests expand to over 37 million hectares. Out of those 37 million hectares, 2.1 million are woodlands, 24.8 million are bush lands and 10.7 are wooded grasslands. Kenya’s forests are important at a global level as they host 1847 species of amphibians, birds, mammals, and reptiles of which 4% are only found in Kenya. Beyond its fauna, Kenya’s forest also hosts 6505 types of vascular plants, with 4.1% only being found in Kenya. Today Kenya faces high rates of deforestation which endanger both its fauna and flora. It has been estimated that since Kenya’s independence in 1963 the forest has dropped from covering 10% of the nation to 6%, losing approximately 12,000 hectares annually. These levels of deforestation have impacted Kenya as they rely on the forest for the storage of rainwater, the prevention of flooding, the fertility of the soil, and the regulation of climate conditions. nd night to meet the high demand. The World War II period and its aftermath made it clear to British colonial administration that reform was needed to sustain Kenyan forests. One of the first steps for conservation took place with the 1941 revision of the Forest Ordinance that passed legislation to create forest reserves and create a committee with professionals on matters of conservation. By 1950 the forest department had gained control of 100,000 acres, but it had a difficult time sustaining the conservation of these areas; it required meaningful policy to meet the constant attention these areas needed.
 W
WDeforestation in Madagascar is an ongoing environmental issue. Deforestation creates agricultural or pastoral land but can also result in desertification, water resource degradation, biodiversity erosion and habitat loss, and soil loss.
 W
WBetween 1990 and 2010 Malaysia lost 8.6% of its forest cover, or around 1,920,000 hectares.
 W
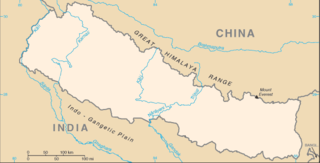
WDeforestation in Nepal has always been a serious issue, which has a severe effect on the lives of poor people. In the past, Nepal was a widely forested nation. However now with the requirement for the extension of rural areas, migration of hills people to the plains, the developing regional interest for timber, and the local residents dependence on firewood as the essential source of energy, less than 30% of the nation's forest cover remains. Due to the continuous deforestation in Nepal, many people and creatures are dying. Around 70 percent of the people in Nepal work in agriculture, even if it is difficult to farm in the prevailing unfavourable weather conditions.
 W
WAs of 2005, Nigeria has the highest rate of deforestation in the world according to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Between 2000 and 2005 the country lost 55.7% of its primary forests, and the rate of forest change increased by 31.2% to 3.12% per annum. Forest has been cleared for logging, timber export, subsistence agriculture and notably the collection of wood for fuel which remains problematic in western Africa.
 W
WDeforestation in Papua New Guinea has been extensive in recent decades and is continuing at an estimated rate of 1.4% of tropical forest being lost annually. Deforestation in Papua New Guinea is mainly a result of illegal logging, which contributed to 70-90% of all timber exports, one of the highest rates in the world. Illegal logging is linked to corruption, environmental issues and human rights concerns.
 W
WAlong with other Southeast Asian countries deforestation in the Philippines is a major environmental issue. Over the course of the 20th century, the forest cover of the country dropped from 70 percent down to 20 percent. Based on an analysis of land use pattern maps and a road map an estimated 9.8 million hectares of forests were lost in the Philippines from 1934 to 1988.
 W
WDeforestation is one of the most serious environmental issues in Sri Lanka. In the 1920s, the island had a 49 percent forest cover but by 2005 this had fallen by approximately 26 percent. Between 1990 and 2000, Sri Lanka lost an average of 26,800 ha of forests per year. This amounts to an average annual deforestation rate of 1.14%. Between 2000 and 2005 the rate accelerated to 1.43% per annum. However, with a long history of policy and laws towards environmental protection, deforestation rates of primary cover have actually decreased 35% since the end of the 1990s thanks to a strong history of conservation measures. The problem of deforestation in Sri Lanka is not as significant in the southern mountainous regions as it is in northern and lowland southern Sri Lanka, largely due to the nature of environmental protection.
 W
WDeforestation in Thailand refers to the conversion of its forested land to other uses. Deforestation numbers are inexact due to the scope of the issue. According to the Royal Forest Department (RFD) in 2019, Thai forests cover 31.6% of Thailand's landmass. The department claims that forest coverage grew by 330,000 rai in 2018, an area equivalent in size to the island of Phuket. A year earlier, an academic claimed that, since 2016, forested area has declined by 18,000 rai, a significant improvement over the period 2008–2013, when a forested million rai were lost each year. In 1975, the government set a goal of 40% forest coverage—25% natural forest and 15% commercial forest—within 20 years. To achieve that target in 2018, 27 million rai would have to be afforested.
 W
WDeforestation in the United States is an ongoing process in the United States. Like deforestation in the rest of the world, it is a complex environmental issue caused by both social and economic pressures.