 W
WThe line of longitude running through El Hierro (Ferro), the westernmost of the Canary Islands, was known in European history as the prime meridian in common use outside of the future British Empire. Already in the 2nd century A.D., Ptolemy considered a definition of the zero meridian based on the westernmost position of the known world, giving maps with only positive (eastern) longitudes. In the year 1634, France ruled by Louis XIII and Richelieu decided that Ferro's meridian should be used as the reference on maps, since this island was considered the most western position of the Old World. Flores Island lies further west, but the Azores were not discovered by Europeans until the early 15th century, and their identification as part of the Old World is uncertain. It was thought to be exactly 20 degrees west of the Paris meridian, so indeed the exact position of Ferro was never considered. Old maps often have a common grid with Paris degrees at the top and Ferro degrees offset by 20 at the bottom. Louis Feuillée also worked on this problem in 1724.
 W
WThe Meridian 11°15' East was proposed as prime meridian by Arno Peters in the Peters World Map. The Meridian is the antipode of 168°45' West of Greenwich which runs through the Bering Strait and was proposed as a new date line. On Peters' world map the easternmost part of Asia and Russia is not displayed left of Alaska, as is usually done on Greenwich-centered maps, but on the right side as the rest of Russia and Asia.
 W
WThe Gila and Salt River Meridian intersects the initial point on the south side of the Gila River, opposite the mouth of Salt River, at latitude 33° 22′ 37.82733″ north, longitude 112° 18′ 21.99931″ west from Greenwich based on NAD 83, and governs the surveys in the territory of Arizona. The current declination for the initial point is 12° east. It is located on Monument Hill, an easily visible hill just south of the confluence of the Gila and Salt Rivers, in Avondale, Arizona, about 14 miles southwest of downtown Phoenix. The original marker was set in 1851 by John R. Bartlett. In 1934, the U.S. Coast and Geodetic Survey set triangulation station "INITIAL" approximately 15 feet from the initial point. Ty White, Associate Cadastral Engineer for the U.S. Bureau of Land Management (BLM), re-monumented the initial point on December 1, 1944. On April 24,1962, the monument was re-established by Leonard W. Murphy, based on the Ty White's field notes, because the previous monument had been vandalized. On April 26, 1984, Paul L. Reeves and John P. Bennet re-monumented the original corner. On February 19, 2006, the initial point was again re-monumented due to deterioration of the 1985 plaque. This re-monumentation was performed by staff from the BLM, members of the Arizona Professional Surveyors Society, and students at Phoenix College. The initial point was added to the National Register of Historic Places as of October 15, 2002. The plaque for that listing was installed as part of the 2006 re-monumenting.
 W
WThis is a list, which includes a photographic gallery, of some of the remaining structures and monuments, of historic significance in Avondale, a city in Maricopa County, Arizona, United States, adjacent to Phoenix, Arizona.Farming was the main industry in Avondale in the late 1890s. Avondale was incorporated in 1946.
 W
WThe Huntsville meridian begins on the northern boundary of Alabama, in latitude 34° 59′ 27" north, longitude 86° 34′ 16″ west from Greenwich, extends south to latitude 33° 06′ 20″ north, and governs the surveys in the northern district of Alabama.
 W
WThe IERS Reference Meridian (IRM), also called the International Reference Meridian, is the prime meridian maintained by the International Earth Rotation and Reference Systems Service (IERS). It passes about 5.3 arcseconds east of George Biddell Airy's 1851 transit circle or 102 metres (335 ft) at the latitude of the Royal Observatory, Greenwich. It is also the reference meridian of the Global Positioning System (GPS) operated by the United States Department of Defense, and of WGS84 and its two formal versions, the ideal International Terrestrial Reference System (ITRS) and its realization, the International Terrestrial Reference Frame (ITRF).
 W
WThe Indian meridian, in longitude 97° 14′ 30″ west from Greenwich, extends from Red River to the south boundary of Kansas, and, with the base line in latitude 34° 30′ north, governs the surveys in Oklahoma east of 100° west longitude from Greenwich.
 W
WIran Standard Time (IRST) or Iran Time (IT) is the time zone used in Iran. Iran uses a UTC offset UTC+03:30. IRST is defined by the 52.5 degrees east meridian, the same meridian which defines the Iranian calendar and is the official meridian of Iran.
 W
WThe Louisiana meridian, in longitude 92° 24′ 15″ west of Greenwich, extends from the Gulf of Mexico to the north boundary of Louisiana, and with the baseline through the initial point conforming to the parallel of 31° north latitude, governs all the surveys in the state west of the Mississippi River.
 W
WMecca Time was a proposed time standard that uses the line of longitude that goes through Mecca, Saudi Arabia as its Prime Meridian. A clock based on this meridian would be at approximately UTC+02:39:18.3.
 W
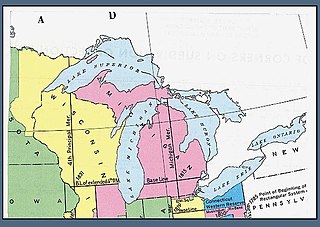
WThe Michigan meridian is the principal meridian used as a reference in the Michigan Survey, the survey of the U.S. state of Michigan in the early 19th century. It is located at 84 degrees, 21 minutes and 53 seconds west longitude at its northern terminus at Sault Ste. Marie, and varies very little from that line down the length of the state.
 W
WThe Mount Diablo meridian, established in 1851, is a principal meridian extending north and south from its initial point atop Mount Diablo in California. Established under the U.S. Public Land Survey System, it is used to describe lands in most of northern California and all of Nevada. Mount Diablo also marks the baseline at latitude 37°52′54″N.
 W
WThe New Mexico Meridian, is longitude 106° 53′ 40″ west from Greenwich. It extends throughout New Mexico and into Colorado, and together with the baseline, at latitude 34° 15′ 25″ north, governs township and range surveys in New Mexico, except those in the northwest corner of the state which refer to the Navajo meridian and baseline. The New Mexico meridian and Baseline also provide the basis for township and range surveys in the upper valley of the Rio Grande del Norte in Colorado.
 W
WThe Paris meridian is a meridian line running through the Paris Observatory in Paris, France – now longitude 2°20′14.03″ East. It was a long-standing rival to the Greenwich meridian as the prime meridian of the world. The "Paris meridian arc" or "French meridian arc" is the name of the meridian arc measured along the Paris meridian.
 W
WThe prime meridian is a geographical reference line that passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, in London, England. It was first established by Sir George Airy in 1851, and by 1884, over two-thirds of all ships and tonnage used it as the reference meridian on their charts and maps. In October of that year, at the behest of US President Chester A. Arthur, 41 delegates from 25 nations met in Washington, D.C., United States, for the International Meridian Conference. This conference selected the meridian passing through Greenwich as the official prime meridian due to its popularity. However, France abstained from the vote, and French maps continued to use the Paris meridian for several decades. In the 18th century, London lexicographer Malachy Postlethwayt published his African maps showing the "Meridian of London" intersecting the Equator a few degrees west of the later meridian and Accra, Ghana.
 W
WThe Pulkovo meridian, which passes through the center of the main building of the Pulkovo Observatory and is at 30°19,6‘ east of Greenwich, was the point of departure for all former geographical maps of Russia.
 W
WSaint Helena meridian begins at the initial point of the Washington meridian, in latitude 31° north, and longitude 91° 09′ 15″ west of Greenwich, passing one mile east of Baton Rouge, extends south to the Mississippi River, and governs the surveys in the Greensburg and southeastern districts of Louisiana, east of the Mississippi River.
 W
WThe Saint Stephens meridian, in longitude 88° 02′ west from Greenwich, begins at the initial point, on the base line, in latitude 31° north, passes through Saint Stephens, Alabama, extends south to Mobile Bay and north to latitude 33° 06′ 20″, and governs the surveys in the southern district of Alabama, and in Pearl River district lying east of the river and south of the Choctaw Baseline, in latitude 31° 52′ 40″ north, in the state of Mississippi.
 W
WThe Salt Lake meridian, established in 1855, in longitude 111° 54′ 00″ west from Greenwich, has its initial point at southeast corner of Temple Square, in Salt Lake City, Utah, extends north and south through the state, and, with the base line, through the initial, and coincident with the parallel of 40° 46′ 04″ north latitude, governs the surveys in the territory, except those referred to the Uintah meridian and Baseline projected from an initial point in latitude 40° 26′ 20″ north, longitude 109° 57′ 30″ west from Greenwich.
 W
WThe San Bernardino meridian, established in 1852, is one of three principal meridians in the state of California. Because of the state's shape, three meridian–baseline sets are required for surveys in all parts of the state. The San Bernardino meridian is used for Southern California, and some townships in Arizona are also referenced to it.
 W
WThe Tallahassee meridian, in longitude 84° 16′ 37.59″ west from the prime meridian at Greenwich, runs north and south from the initial point on the base line at Tallahassee, in latitude 30° 26′ 04.12″ north, and as a principal meridian governs the surveys in Florida and Alabama as part of the Public Land Survey System.
 W
WThe Tenerife meridian was the prime meridian of choice for Dutch cartographers and navigators from the 1640s until the beginning of the 19th century. It lies at 16° 38′ 22″ W of the current international prime meridian, the IERS Reference Meridian through Greenwich.
 W
WThe Treaty of Tordesillas, signed at Tordesillas in Spain on June 7, 1494, and authenticated at Setúbal, Portugal, divided the newly-discovered lands outside Europe between the Portuguese Empire and the Spanish Empire, along a meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde islands, off the west coast of Africa. That line of demarcation was about halfway between the Cape Verde islands and the islands entered by Christopher Columbus on his first voyage, named in the treaty as Cipangu and Antilia.
 W
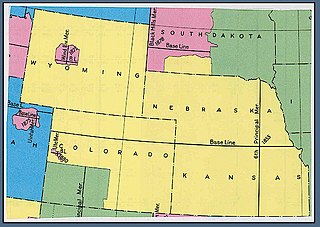
WThe Uintah meridian has a center point north of Roosevelt, Utah. The Uintah meridian was established in 1875, and governs land surveys in the Uintah and Ouray Indian Reservation in the state of Utah.
 W
WThe Ute meridian, also known as the Grand River meridian, was established in 1880 and is a principal meridian of Colorado. The initial point lies inside the boundaries of Grand Junction Regional Airport, Grand Junction, Colorado.
 W
WThe Warsaw meridian is a meridian line running through Warsaw. The local mean time at the meridian was known as Warsaw Mean Time. It corresponds to an offset from UTC of +01:24.
 W
WThe Willamette Stone was a small stone obelisk originally installed by the Department of Interior in 1885 in the western hills of Portland, Oregon in the United States to mark the intersection and origin of the Willamette meridian and Willamette baseline. It replaced a cedar stake placed by the Surveyor General of the Oregon Territory in 1851; this stake defined the grid system of sections and townships from which all real property in the states of Oregon and Washington has been measured following the Donation Land Claim Act of 1850. The Willamette meridian runs north–south, and the Willamette baseline runs east–west through the marker. The easternmost northeast corner of Washington County is sited on the marker.