 W
WThe Antarctic oscillation, also known as the Southern Annular Mode (SAM), is a low-frequency mode of atmospheric variability of the southern hemisphere that is defined as a belt of strong westerly winds or low pressure surrounding Antarctica which moves north or south as its mode of variability.
 W
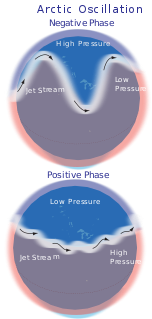
WThe Arctic oscillation (AO) or Northern Annular Mode/Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode (NAM) is a weather phenomenon at the Arctic poles north of 20 degrees latitude. It is an important mode of climate variability for the Northern Hemisphere. The southern hemisphere analogue is called the Antarctic oscillation or Southern Annular Mode (SAM). The index varies over time with no particular periodicity, and is characterized by non-seasonal sea-level pressure anomalies of one sign in the Arctic, balanced by anomalies of opposite sign centered at about 37–45° N.
 W
WThe Atlantic Equatorial Mode or Atlantic Niño is a quasiperiodic interannual climate pattern of the equatorial Atlantic Ocean. It is the dominant mode of year-to-year variability that results in alternating warming and cooling episodes of sea surface temperatures accompanied by changes in atmospheric circulation. The term Atlantic Niño comes from its close similarity with the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) that dominates the tropical Pacific basin. For this reason, the Atlantic Niño is often called the little brother of El Niño. The Atlantic Niño usually appears in northern summer, and is not the same as the Atlantic Meridional (Interhemispheric) Mode that consists of a north-south dipole across the equator and operates more during northern spring. The equatorial warming and cooling events associated with the Atlantic Niño are known to be strongly related to rainfall variability over the surrounding continents, especially in West African countries bordering the Gulf of Guinea. Therefore, understanding of the Atlantic Niño has important implications for climate prediction in those regions. Although the Atlantic Niño is an intrinsic mode to the equatorial Atlantic, there may be a tenuous causal relationship between ENSO and the Atlantic Niño in some circumstances.
 W
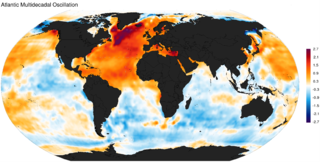
WThe Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation (AMO), also known as Atlantic Multidecadal Variability (AMV), is a climate cycle that affects the sea surface temperature (SST) of the North Atlantic Ocean based on different modes on multidecadal timescales. While there is some support for this mode in models and in historical observations, controversy exists with regard to its amplitude, and in particular, the attribution of sea surface temperature change to natural or anthropogenic causes, especially in tropical Atlantic areas important for hurricane development. The Atlantic multidecadal oscillation is also connected with shifts in hurricane activity, rainfall patterns and intensity, and changes in fish populations.
 W
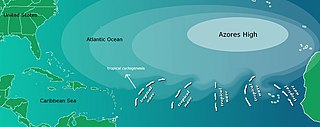
WThe Azores High also known as North Atlantic (Subtropical) High/Anticyclone or the Bermuda-Azores High, is a large subtropical semi-permanent centre of high atmospheric pressure typically found south of the Azores in the Atlantic Ocean, at the Horse latitudes. It forms one pole of the North Atlantic oscillation, the other being the Icelandic Low. The system influences the weather and climatic patterns of vast areas of North Africa and southern Europe, and to a lesser extent, eastern North America. The aridity of the Sahara Desert and the summer drought of the Mediterranean Basin is due to the large-scale subsidence and sinking motion of air in the system. In its summer position, the high is centered near Bermuda, and creates a southwest flow of warm tropical air toward the East Coast of the United States. In summer, the Azores-Bermuda High is strongest. The central pressure hovers around 1024 mbar (hPa).
 W
WCyclonic Niño is a climatological phenomenon that has been observed in climate models where tropical cyclone activity is increased. Increased tropical cyclone activity mixes ocean waters, introducing cooling in the upper layer of the ocean that quickly dissipates and warming in deeper layers that lasts considerably more, resulting in a net warming of the ocean.
 W
WThe El Niño–Southern Oscillation affects the location of the jet stream, which alters rainfall patterns across the West, Midwest, the Southeast, and throughout the tropics. The shift in the jet stream also leads to shifts in the occurrence of severe weather, and the number of tropical cyclones expected within the tropics in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans affected by changes in the ocean temperature and the subtropical jet stream. The winter will have a negative phase according to the Arctic oscillation (AO).
 W
WEl Niño is the warm phase of the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) and is associated with a band of warm ocean water that develops in the central and east-central equatorial Pacific, including the area off the Pacific coast of South America. The ENSO is the cycle of warm and cold sea surface temperature (SST) of the tropical central and eastern Pacific Ocean. El Niño is accompanied by high air pressure in the western Pacific and low air pressure in the eastern Pacific. El Niño phases are known to last close to four years, however, records demonstrate that the cycles have lasted between two and seven years. During the development of El Niño, rainfall develops between September–November. The cool phase of ENSO is La Niña, with SSTs in the eastern Pacific below average, and air pressure high in the eastern Pacific and low in the western Pacific. The ENSO cycle, including both El Niño and La Niña, causes global changes in temperature and rainfall.
 W
WEl Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is an irregularly periodic variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical eastern Pacific Ocean, affecting the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics. The warming phase of the sea temperature is known as El Niño and the cooling phase as La Niña. The Southern Oscillation is the accompanying atmospheric component, coupled with the sea temperature change: El Niño is accompanied by high air surface pressure in the tropical western Pacific and La Niña with low air surface pressure there. The two periods last several months each and typically occur every few years with varying intensity per period.
 W
WGoyder's Line is a line that runs roughly east–west across South Australia and, in effect, joins places with an average annual rainfall of 10 inches (250 mm). North of Goyder's Line, annual rainfall is usually too low to support cropping, with the land being only suitable for grazing. Related to that, the line also marks a distinct change in vegetation. To the south, it is composed mainly of mallee scrub, whilst saltbush predominates to the north of the line.
 W
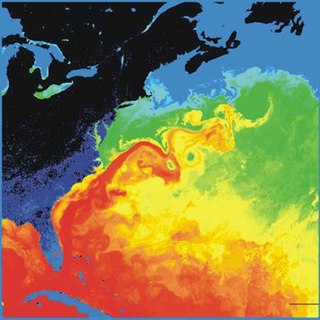
WThe Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and stretches to the tip of Florida, and follows the eastern coastlines of the United States and Newfoundland before crossing the Atlantic Ocean as the North Atlantic Current. The process of western intensification causes the Gulf Stream to be a northwards accelerating current off the east coast of North America. At about 40°0′N 30°0′W, it splits in two, with the northern stream, the North Atlantic Drift, crossing to Northern Europe and the southern stream, the Canary Current, recirculating off West Africa.
 W
WHector is a cumulonimbus thundercloud that forms regularly nearly every afternoon on the Tiwi Islands in the Northern Territory of Australia, from approximately September to March each year. Hector, or sometimes "Hector the Convector", is known as one of the world's most consistently large thunderstorms, reaching heights of approximately 20 kilometres (66,000 ft).
 W
WThe Icelandic Low is a semi-permanent centre of low atmospheric pressure found between Iceland and southern Greenland and extending in the Northern Hemisphere winter into the Barents Sea. In summer it weakens and splits into two centres, one near Davis Strait and the other west of Iceland. It is a principal centre of action in the atmosphere circulation of the Northern Hemisphere, associated with frequent cyclone activity. It forms one pole of the North Atlantic oscillation, the other being the Azores High.
 W
WThe Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), also known as the Indian Niño, is an irregular oscillation of sea surface temperatures in which the western Indian Ocean becomes alternately warmer and then colder than the eastern part of the ocean.
 W
WThe Interdecadal Pacific oscillation (IPO) is an oceanographic/meteorological phenomenon similar to the Pacific decadal oscillation (PDO), but occurring in a wider area of the Pacific. While the PDO occurs in mid-latitudes of the Pacific Ocean in the northern hemisphere, the IPO stretches from the southern hemisphere into the northern hemisphere.
 W
WLa Niña is a coupled ocean-atmosphere phenomenon that is the colder counterpart of El Niño, as part of the broader El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern. The name La Niña originates from Spanish, meaning "the little girl", by analogy to El Niño meaning "the little boy". In the past it was also called an anti-El Niño, and El Viejo.
 W
WMaritime Continent is the name given primarily by meteorologists and oceanographers to the region of Southeast Asia which comprises, amongst other countries, Indonesia, Philippines and Papua New Guinea. Located between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, it is situated within a warm ocean region known as the Tropical Warm Pool.
 W
WThe monsoon of South Asia is among several geographically distributed global monsoons. It affects the Indian subcontinent, where it is one of the oldest and most anticipated weather phenomena and an economically important pattern every year from June through September, but it is only partly understood and notoriously difficult to predict. Several theories have been proposed to explain the origin, process, strength, variability, distribution, and general vagaries of the monsoon, but understanding and predictability are still evolving.
 W
WThe North Pacific High is a semi-permanent, subtropical anticyclone located in the northeastern portion of the Pacific Ocean, located northeast of Hawaii and west of California. It is strongest during the northern hemisphere summer and shifts towards the equator during the winter, when the Aleutian Low becomes more active. It is responsible for California's typically dry summer and fall and typically wet winter and spring, as well as Hawaii's year-round trade winds.
 W
WThe North Pacific Oscillation (NPO) is a teleconnection pattern first described by Walker and Bliss and characterized by a north-south seesaw in sea level pressure over the North Pacific. Rogers, using surface atmospheric temperature from St. Paul, Alaska, and Edmonton, identified two phases of the NPO, an Aleutian below (AB) phase that correspond to a deepened and eastward shifted Aleutian low and an Aleutian above (AA) phase that is the opposite.
 W
WThe Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO) is a robust, recurring pattern of ocean-atmosphere climate variability centered over the mid-latitude Pacific basin. The PDO is detected as warm or cool surface waters in the Pacific Ocean, north of 20°N. Over the past century, the amplitude of this climate pattern has varied irregularly at interannual-to-interdecadal time scales. There is evidence of reversals in the prevailing polarity of the oscillation occurring around 1925, 1947, and 1977; the last two reversals corresponded with dramatic shifts in salmon production regimes in the North Pacific Ocean. This climate pattern also affects coastal sea and continental surface air temperatures from Alaska to California.
 W
WA polar vortex is a persistent, large-scale, upper-level low-pressure area, less than 1,000 kilometers in diameter, that rotates counter-clockwise at the North Pole and clockwise at the South Pole, i.e., both polar vortices rotate eastward around the poles. The vortices weaken and strengthen from year to year. As with other cyclones, their rotation is driven by the Coriolis effect.
 W
WSouth Atlantic High is a semipermanent pressure high centered at about 25°S, 15°W, in the Atlantic Ocean. It is also called the St. Helena High, Saint Helena island being the only land in the area. It can stretch thousands of miles across the South Atlantic. This does not mean that the position and the intensity of this anticyclone are permanent, but just that we find an anticyclone on the maps describing the average monthly pressure. This area of high pressure is part of the great subtropical belt of anticyclones called the subtropical ridge. The centre of the high pressure region tends to follow the seasonal variation in position of the sun, moving south in the southern summer and north in the southern winter. This affects the climate of the adjacent continental areas, bringing seasonal changes to the climate and weather as the position of the high oscillates.
 W
WThe South Pacific High is a semi-permanent subtropical anticyclone located in the southeast Pacific Ocean. The area of high atmospheric pressure and the presence of the Humboldt Current in the underlying ocean make the west coast of Peru and northern Chile extremely arid. The Sechura and Atacama deserts, as the whole climate of Chile, are heavily influenced by this semi-permanent high-pressure area. This high-pressure system plays a major role in the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), and it is also a major source of trade winds across the equatorial Pacific.
 W
WThe Subtropical Indian Ocean Dipole (SIOD) is featured by the oscillation of sea surface temperatures (SST) in which the southwest Indian Ocean i.e. south of Madagascar is warmer and then colder than the eastern part i.e. off Australia. It was first identified in the studies of the relationship between the SST anomaly and the south-central Africa rainfall anomaly; the existence of such a dipole was identified from both observational studies and model simulations .
 W
WA western disturbance is an extratropical storm originating in the Mediterranean region that brings sudden winter rain to the northwestern parts of the Indian subcontinent. It is a non-monsoonal precipitation pattern driven by the westerlies. The moisture in these storms usually originates over the Mediterranean Sea, the Caspian Sea and the Black Sea. Extratropical storms are a global phenomena with moisture usually carried in the upper atmosphere, unlike their tropical counterparts where the moisture is carried in the lower atmosphere. In the case of the Indian subcontinent, moisture is sometimes shed as rain when the storm system encounters the Himalayas. western disturbances are more frequent and strong in winter season.
 W
WThe Western Hemisphere Warm Pool (WHWP) is a region of sea surface temperatures (SST) warmer than 28.5 °C that develops west of Central America in the spring, then expands to the tropical waters to the east.