 W
WClimatology or climate science is the scientific study of climate, scientifically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of time. This modern field of study is regarded as a branch of the atmospheric sciences and a subfield of physical geography, which is one of the Earth sciences. Climatology now includes aspects of oceanography and biogeochemistry.
 W
WClimate is the long-term average of weather, typically averaged over a period of 30 years. More rigorously, it denotes the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, which includes the ocean and ice on Earth. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude, terrain, and altitude, as well as nearby water bodies and their currents.
 W
WAlbedo is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that reflects all incident radiation.
 W
WAttribution of recent climate change is the effort to scientifically ascertain mechanisms responsible for recent global warming and related climate changes on Earth. The effort has focused on changes observed during the period of instrumental temperature record, particularly in the last 50 years. This is the period when human activity has grown fastest and observations of the atmosphere above the surface have become available. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), it is "extremely likely" that human influence was the dominant cause of global warming between 1951 and 2010. Likely human contribution is 93%–123% of the observed 1951–2010 temperature change.
 W
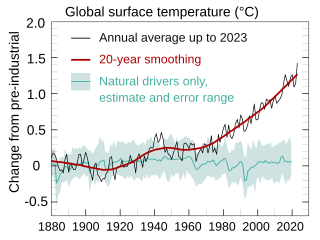
WClimate variability includes all the variations in the climate that last longer than individual weather events, whereas the term climate change only refers to those variations that persist for a longer period of time, typically decades or more. In the time since the industrial revolution the climate has increasingly been affected by human activities that are causing global warming and climate change.
 W
WClimatic geomorphology is the study of the role of climate in shaping landforms and the earth-surface processes. An approach used in climatic geomorphology is to study relict landforms to infer ancient climates. Being often concerned about past climates climatic geomorphology considered sometimes to be an aspect of historical geology. Since landscape features in one region might have evolved under climates different from those of the present, studying climatically disparate regions might help understand present-day landscapes. For example, Julius Büdel studied both cold-climate processes in Svalbard and weathering processes in tropical India to understand the origin of the relief of Central Europe, which he argued was a palimpsest of landforms formed at different times and under different climates.
 W
WThe infrared atmospheric window refers to a region of the Infrared spectrum where there is relatively little absorption of terrestrial thermal radiation by atmospheric gases. The window plays an important role in the atmospheric greenhouse effect by maintaining the balance between incoming solar radiation and outgoing IR to space. In the earth's atmosphere this window is roughly the region between 8 and 14 μm although it can be narrowed or closed at times and places of high humidity because of the strong absorption in the water vapor continuum or because of blocking by clouds. It covers a substantial part of the spectrum from surface thermal emission which starts at roughly 5 μm. Principally it is a large gap in the absorption spectrum of water vapor. Carbon dioxide plays an important role in setting the boundary at the long wavelength end. Ozone partly blocks transmission in the middle of the window.
 W
WLake-effect snow is produced during cooler atmospheric conditions when a cold air mass moves across long expanses of warmer lake water. The lower layer of air, heated up by the lake water, picks up water vapor from the lake and rises up through the colder air above; the vapor then freezes and is deposited on the leeward (downwind) shores.
 W
WThe March for Science is an international series of rallies and marches held on Earth Day. The inaugural march was held on April 22, 2017 in Washington, D.C., and more than 600 other cities across the world. According to organizers, the march is a non-partisan movement to celebrate science and the role it plays in everyday lives. The goals of the marches and rallies were to emphasize that science upholds the common good and to call for evidence-based policy in the public's best interest. The March for Science organizers, using crowd science techniques, estimated global attendance at 1.07 million, with 100,000 participants estimated for the main March in Washington, D.C., 70,000 in Boston, 60,000 in Chicago, 50,000 in Los Angeles, 50,000 in San Francisco, 20,000 in Seattle, 14,000 in Phoenix, and 11,000 in Berlin.
 W
WThe March for Science Portland was a protest held in Portland, Oregon. This local protest was part of the March for Science, a series of rallies and marches in Washington, D.C. and over 600 cities across the world on April 22, 2017. Portland Science Advocates organized the march in support of science and to protest President Donald Trump's plan to cut funding for the Environmental Protection Agency and the National Institutes of Health. Funding for the event, which cost approximately $30,000, was crowdsourced.
 W
WMelt ponds are pools of open water that form on sea ice in the warmer months of spring and summer. The ponds are also found on glacial ice and ice shelves. Ponds of melted water can also develop under the ice.
 W
WNuclear winter is a severe and prolonged global climatic cooling effect hypothesized to occur after widespread firestorms following a nuclear war. The hypothesis is based on the fact that such fires can inject soot into the stratosphere, where it can block some direct sunlight from reaching the surface of the Earth. It is speculated that the resulting cooling would lead to widespread crop failure and famine. When developing computer models of nuclear-winter scenarios, researchers use the conventional bombing of Hamburg, and the Hiroshima firestorm in World War II as example cases where soot might have been injected into the stratosphere, alongside modern observations of natural, large-area wildfire-firestorms.
 W
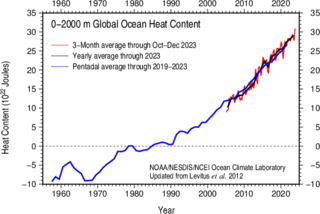
WIn oceanography and climatology, ocean heat content (OHC) is a term for the energy absorbed by the ocean, which is stored as internal energy or enthalpy. Changes in the ocean heat content play an important role in the sea level rise, because of thermal expansion.
 W
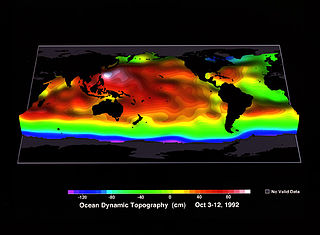
WOcean surface topography or sea surface topography, also called ocean dynamic topography, are highs and lows on the ocean surface, similar to the hills and valleys of Earth's land surface depicted on a topographic map. These variations are expressed in terms of average sea surface height (SSH) relative to the Earth's geoid. The main purpose of measuring ocean surface topography is to understand the large-scale ocean circulation.
 W
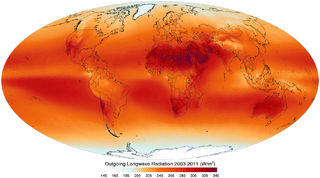
WOutgoing Long-wave Radiation (OLR) is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths from 3–100 μm emitted from Earth and its atmosphere out to space in the form of thermal radiation. It is also referred to as up-welling long-wave radiation and terrestrial long-wave flux, among others. The flux of energy transported by outgoing long-wave radiation is measured in W/m2. In the Earth's climate system, long-wave radiation involves processes of absorption, scattering, and emissions from atmospheric gases, aerosols, clouds and the surface.
 W
WPhenology is the study of periodic events in biological life cycles and how these are influenced by seasonal and interannual variations in climate, as well as habitat factors.
 W
WPotential evaporation (PE) or potential evapotranspiration (PET) is defined as the amount of evaporation that would occur if a sufficient water source were available. If the actual evapotranspiration is considered the net result of atmospheric demand for moisture from a surface and the ability of the surface to supply moisture, then PET is a measure of the demand side. Surface and air temperatures, insolation, and wind all affect this. A dryland is a place where annual potential evaporation exceeds annual precipitation.
 W
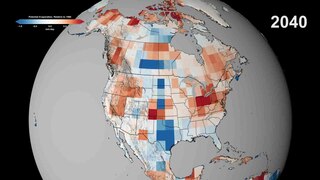
WThere is currently a strong scientific consensus that the Earth is warming and that this warming is mainly caused by human activities. This consensus is supported by various studies of scientists' opinions and by position statements of scientific organizations, many of which explicitly agree with the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) synthesis reports.
 W
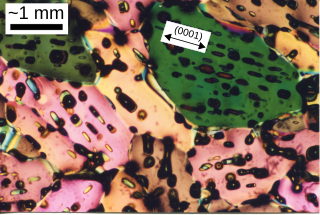
WSea ice is a complex composite composed primarily of pure ice in various states of crystallization along with air bubbles and included pockets of brine. Understanding its growth processes is important both for climate scientists for use in simulations as well remote sensing specialists since the composition and microstructural properties of the ice ultimately affect how it interacts with electromagnetic radiation.
 W
WIn phenology, season creep refers to observed changes in the timing of the seasons, such as earlier indications of spring widely observed in temperate areas across the Northern Hemisphere. Phenological records analyzed by climate scientists have shown significant temporal trends in the observed time of seasonal events, from the end of the 20th century and continuing into the 21st century. In Europe, season creep has been associated with the arrival of spring moving up by approximately one week in a recent 30-year period. Other studies have put the rate of season creep measured by plant phenology in the range of 2–3 days per decade advancement in spring, and 0.3–1.6 days per decade delay in autumn, over the past 30–80 years.
 W
WThe soil-plant-atmosphere continuum (SPAC) is the pathway for water moving from soil through plants to the atmosphere. Continuum in the description highlights the continuous nature of water connection through the pathway. The low water potential of the atmosphere, and relatively higher water potential inside leaves, leads to a diffusion gradient across the stomatal pores of leaves, drawing water out of the leaves as vapour. As water vapour transpires out of the leaf, further water molecules evaporate off the surface of mesophyll cells to replace the lost molecules since water in the air inside leaves is maintained at saturation vapour pressure. Water lost at the surface of cells is replaced by water from the xylem, which due to the cohesion-tension properties of water in the xylem of plants pulls additional water molecules through the xylem from the roots toward the leaf.
 W
WThe State of the Climate is an annual report that is primarily led by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Climatic Data Center (NOAA/NCDC), located in Asheville, North Carolina, but whose leadership and authorship spans roughly 100 institutions in about 50 countries.
 W
WSurveys of scientists' views on climate change – with a focus on human-caused or anthropogenic global warming (AGW) – have been undertaken since the 1990s. A 2016 paper concluded that "the finding of 97% consensus [that humans are causing recent global warming] in published climate research is robust and consistent with other surveys of climate scientists and peer-reviewed studies."
 W
WA tipping point in the climate system is a threshold that, when exceeded, can lead to large changes in the state of the system. Potential tipping points have been identified in the physical climate system, in impacted ecosystems, and sometimes in both. For instance, feedback from the global carbon cycle is a driver for the transition between glacial and interglacial periods, with orbital forcing providing the initial trigger. Earth's geologic temperature record includes many more examples of geologically rapid transitions between different climate states.
 W
WAn urban heat island (UHI) is an urban area or metropolitan area that is significantly warmer than its surrounding rural areas due to human activities. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparent when winds are weak. UHI is most noticeable during the summer and winter. The main cause of the urban heat island effect is from the modification of land surfaces. Waste heat generated by energy usage is a secondary contributor. As a population center grows, it tends to expand its area and increase its average temperature. The term heat island is also used; the term can be used to refer to any area that is relatively hotter than the surrounding, but generally refers to human-disturbed areas.
 W
WA varve is an annual layer of sediment or sedimentary rock.
 W
WWarming stripes are data visualization graphics that use a series of coloured stripes chronologically ordered to visually portray long-term temperature trends. Warming stripes reflect a "minimalist" style, conceived to use colour alone to avoid technical distractions and intuitively convey global warming trends to non-scientists.
 W
WWeathering is the breaking down of rocks, soils, and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, water, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs in situ, that is, in the same place, with little or no movement, and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the transport of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations.
 W
WA window of opportunity is a period of time during which some action can be taken that will achieve a desired outcome. Once this period is over, or the "window is closed", the specified outcome is no longer possible.