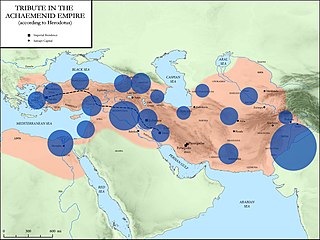
 W
WHerodotus divided the Achaemenid Empire into 20 districts for the purpose of tribute payments. The following is a description of the ethnic makeup of the districts and the amount they paid in taxes, translated from Herodotus' Histories.
 W
WArabia or Achaemenid Arabia was a satrapy (province) of the Achaemenid Empire by the name of Arabâya . Achaemenid Arabia corresponded to the lands between Nile Delta (Egypt) and Mesopotamia, later known to Romans as Arabia Petraea. According to Herodotus, Cambyses did not subdue the Arabs when he attacked Egypt in 525 BCE. His successor Darius the Great does not mention the Arabs in the Behistun inscription from the first years of his reign, but does mention them in later texts. This suggests that Darius might have conquered this part of Arabiaor that it was originally part of another province, perhaps Achaemenid Babylonia, but later became its own province.
 W
WAthura, also called Assyria, was a geographical area within the Achaemenid Empire in Upper Mesopotamia from 539 to 330 BCE as a military protectorate state. Although sometimes regarded as a satrapy, Achaemenid royal inscriptions list it as a dahyu, a concept generally interpreted as meaning either a group of people or both a country and its people, without any administrative implication.
 W
WAria is an Achaemenid region centered on the city of Herat in present-day western Afghanistan. In classical sources, Aria has been several times confused with the greater region of ancient Ariana, of which Aria formed a part.
 W
WBabylonia was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in central-southern Mesopotamia. A small Amorite-ruled state emerged in 1894 BC, which contained the minor administrative town of Babylon. It was merely a small provincial town during the Akkadian Empire but greatly expanded during the reign of Hammurabi in the first half of the 18th century BC and became a major capital city. During the reign of Hammurabi and afterwards, Babylonia was called "the country of Akkad", a deliberate archaism in reference to the previous glory of the Akkadian Empire.
 W
WBactria was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire. The first mention of Bactria comes in 520 BCE at the Behistun inscription. Bactria was a special satrapy in that it was ruled by a crown prince or an intended heir. The capital of Bactria was Bactra, and the region also sometimes included Sogdia. During the reign of Darius the Great, the Bactrians and the Aeglians were placed in one tax district, which was supposed to pay 360 talents every year.
 W
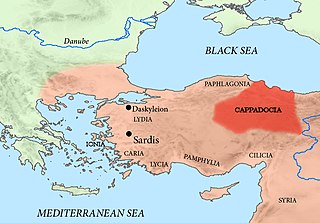
WCappadocia was a satrapy (province) of the Achaemenid Empire used by the Achaemenids to administer the regions beyond the Taurus Mountains and the Euphrates river.
 W
WCarmania is a historical region that approximately corresponds to the modern province of Kerman and was a province of the Achaemenid, Seleucid, Arsacid, and Sasanian Empire. The region bordered Persia in the west, Gedrosia in the south-east, Parthia in the north, and Aria to the north-east. Carmania was considered part of Ariana.
 W
WChorasmia was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire in Persia. Chorasmia had become part of the Achaemenid Empire before 522 BCE, and it seems to have been ruled by the satrap of Parthia.
 W
WCilicia was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire, with its capital being Tarsus. It was conquered sometime in the 540's BC by Cyrus the Great. Cilicia was a vassal, and although it had a vassal king it had to pay a tribute of 360 horses and 500 talents of silver, according to Herodotus. The fertile Cilician plains were the most important part of the satrapy.
 W
WDrangiana or Zarangiana (Greek: Δραγγιανή, Drangianē; also attested in Old Western Iranian as 𐏀𐎼𐎣, Zraka or Zranka, was a historical region and administrative division of the Achaemenid Empire. This region comprises territory around Hamun Lake, wetlands in endorheic Sistan Basin on the Iran-Afghan border, and its primary watershed Helmand river in what is nowadays southwestern region of Afghanistan.
 W
WEber-Nari, also referred to as Transeuphratia by modern scholars, was a region of Western Asia and a satrapy of the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Neo-Babylonian Empire and Achaemenid Empire. The Akkadian Eber-Nari is referred to as Athura or Athuriya in Old Persian, and Aššur in the Elamite. The Targum Onkelos lists Nineveh, Calah, Reheboth, and Resen as being in the jurisdiction of Athura.
 W
WGandāra, or Gadāra in Achaemenid inscriptions was one of the easternmost provinces of the Achaemenid Empire in South Asia, following the Achaemenid invasion of the Indus Valley. It appears in various Achaemenid inscriptions such as the Behistun Inscription, or the DNa inscription of Darius the Great.
 W
WGandhāra was an ancient region in the Peshawar basin in the far north-west of the ancient Indian subcontinent, corresponding to present-day north-west Pakistan and east Afghanistan. The centre of the region was at the confluence of the Kabul and Swat rivers, bounded by the Sulaiman Mountains on the west and the Indus River on the east. The Safed Koh mountains separated it from the Kohat region to the south. This being the core area of Gandhara, the cultural influence of "Greater Gandhara" extended across the Indus river to the Taxila region and westwards into the Kabul and Bamiyan valleys in Afghanistan, and northwards up to the Karakoram range. During the Achaemenid period and Hellenistic period, its capital city was Pushkalavati, modern Charsadda. Later the capital city was moved to Peshawar by the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great in about 127 AD.
 W
WGedrosia is a dry, mountainous country along the northwestern shores of the Indian Ocean. It was occupied in the Bronze Age by people who settled in the few oases in the region. Other people settled on the coast and became known in Greek as Ichthyophagi.
 W
WHindush was an Indian province of the Achaemenid Empire following the Achaemenid conquest of the Indus Valley circa 500 BC. According to Herodotus, it was the "easternmost province" of the empire. It is believed to have continued as a province until the invasion of the empire by Alexander the Great circa 326 BC.
 W
WHyrcania is a historical region composed of the land south-east of the Caspian Sea in modern-day Iran and Turkmenistan, bound in the south by the Alborz mountain range and the Kopet Dag in the east.
 W
WIonia, known in Old Persian as Yauna (𐎹𐎢𐎴), was a region within the satrapy of Lydia, with its capital at Sardis, within the First Persian Empire. The first mention of the Yauna is at the Behistun inscription.
 W
WKush was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire. The territory was conquered from the Kingdom of Kush.
 W
WLibya was a satrapy of the Achaemenid Empire according to King Darius I of Persia Naqshe Rustam and King Xerxes I of Persia' Daiva inscription. It is also mentioned as being part of the 6th district by Herodotus, which also included Cyrene, a Greek colony in Libya. When King Cambyses II of Persia conquered Egypt, the king of Cyrene, Arcesilaus III, sided with Persia. When he was killed trying to maintain power, Queen Pheretima invited the Persians to take Cyrene. The satrap of Egypt, Aryandes, accepted, sending an army under two Persians to support Pheretime. The expedition lasted nearly a year and resulted in the subjugation of the Libyans; the Persians penetrated as far west as the Euhesperides (Benghazi). A puppet king, Battus IV, was installed, and Libya was made into a Persian satrapy. It is possible that Cyrene gained independence with the rebellion of Egypt in 404 BCE, but ultimately, Achaemenid control of the region was lost after Alexander's conquests.
 W
WThe Satrapy of Lydia, known as Sparda in Old Persian, was an administrative province (satrapy) of the Achaemenid Empire, located in the ancient kingdom of Lydia, with Sardis as its capital.
 W
WMedia is a region of north-western Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Medes. During the Achaemenid period, it comprised present-day Azarbaijan, Iranian Kurdistan and western Tabaristan. As a satrapy under Achaemenid rule, it would eventually encompass a wider region, stretching to southern Dagestan in the north. However, after the wars of Alexander the Great, the northern parts were separated due to the Partition of Babylon and became known as Atropatene, while the remaining region became known as Lesser Media.
 W
WParopamisadae or Parapamisadae was a satrapy of the Alexandrian Empire in modern Afghanistan and Pakistan, which largely coincided with the Achaemenid province of Parupraesanna. It consisted of the districts of Sattagydia, Gandhara, Buner and Udyana. Paruparaesanna is mentioned in the Akkadian language and Elamite language versions of the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great, whereas in the Old Persian version it is called Gandāra. The entire satrapy was subsequently ceded by Seleucus I Nicator to Chandragupta Maurya following a treaty.
 W
WParthia is a historical region located in north-eastern Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great in the 6th century BC, and formed part of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire following the 4th-century-BC conquests of Alexander the Great. The region later served as the political and cultural base of the Eastern-Iranian Parni people and Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire. The Sasanian Empire, the last state of pre-Islamic Iran, also held the region and maintained the Seven Parthian clans as part of their feudal aristocracy.
 W
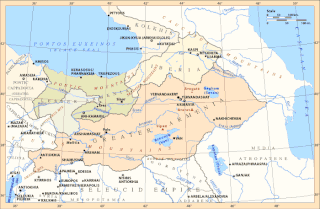
WThe Satrapy of Armenia (Armenian: Սատրապական Հայաստան Satrapakan Hayastan; Old Persian: Armina or Arminiya, a region controlled by the Orontid Dynasty was one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC, which later became an independent kingdom. Its capitals were Tushpa and later Erebuni.
 W
WSattagydia was one of the easternmost regions of the Achaemenid Empire, part of its Seventh tax district according to Herodotus, along with Gandārae, Dadicae and Aparytae. It is believed to have been situated east of the Sulaiman Mountains up to the Indus River in the basin around Bannu.
 W
WSkudra or Scudra was a province (satrapy) of the Persian Empire in Europe between 510s BC and 479 BC. Its name is attested in Persian and Egyptian inscriptions. It is believed to have comprised the lands now known as Thrace and Macedon.
 W
WSogdia or Sogdiana was an ancient Iranian civilization that at different times included territory located in present-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, such as Samarkand, Bukhara, Khujand, Panjikent, and Shahrisabz. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empire, eighteenth in the list on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great. In the Avesta, Sogdiana is listed as the second best land that the supreme deity Ahura Mazda had created. It comes second, after Airyanem Vaejah, "homeland of the Aryans", in the Zoroastrian book of Vendidad, indicating the importance of this region from ancient times. Sogdiana was first conquered by Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. The region would then be annexed by the Macedonian ruler Alexander the Great in 328 BC. The region would continue to change hands under the Seleucid Empire, Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Kushan Empire, Hephthalite Empire, and Sasanian Empire.
 W
WThe Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt, also known as the Second Egyptian Satrapy, was effectively a satrapy of the Achaemenid Persian Empire between 343 BC to 332 BC. It was founded by Artaxerxes III, the King of Persia, after his reconquest of Egypt and subsequent crowning as Pharaoh of Egypt, and was disestablished upon the conquest of Egypt by Alexander the Great.
 W
WThe Twenty-seventh Dynasty of Egypt, also known as the First Egyptian Satrapy, was effectively a province (satrapy) of the Achaemenid Persian Empire between 525 BC and 404 BC. It was founded by Cambyses II, the King of Persia, after the Battle of Pelusium and his conquest of Egypt, and his subsequent crowning as Pharaoh of Egypt. It was disestablished upon the rebellion and crowning of Amyrtaeus as Pharaoh. A second period of Achaemenid rule in Egypt occurred under the Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt.
 W
WYehud, or Yehud Medinata, alternatively Yehud Medinta, was the name retained and used by the Persian Achaemenid Empire for one of their administrative provinces, after it first being introduced by the Babylonians. The territory of the Persian colony, which was ruled by mostly Jewish governors, was considerably smaller and with a far thinner population than the kingdom of Judah before the Babylonian conquest. The area of Persian Yehud corresponded to the previous Babylonian province of Yehud, which was formed after the fall of the kingdom of Judah to the Neo-Babylonian Empire. Yehud, part of the Persian satrapy of Eber-Nari, continued to exist for two centuries, until being incorporated into the Hellenistic empires following the conquests of Alexander the Great.