 W
W108 Mile Lake is a glacial lake located in the Cariboo region of British Columbia, Canada. The lake is named after the nearby town 108 Mile Ranch.108 Mile Lake is connected to Sepa Lake. The channel between the two lakes was dredged in the late 1980s allowing a free flow of water between the two basins. The lake is a popular fishing, hiking, and mountain biking spot. Fish found in this lake include rainbow trout, bull trout, redside shiners, northern pikeminnows, suckers and coastal cutthroat trout.
 W
WAdmiralty Lake was a proglacial lake in the basin of what is now Lake Ontario. The shoreline of Admiralty Lake was about 20 metres (66 ft) lower than Lake Ontario. The shoreline of Glacial Lake Iroquois, an earlier proglacial lake was much higher than Lake Ontario's, because a lobe of the Laurentian Glacier blocked what is now the valley of the St Lawrence River. Lake Iroquois drained over the Niagara Escarpment, and down the Mohawk River. When the lobe of the glacier retreated the weight of the glacier kept the outlet of the St Lawrence River lower than the current level. As the glacier continued to retreat the region of the Thousand Islands rebounded, and the lake filled to its current level.
 W
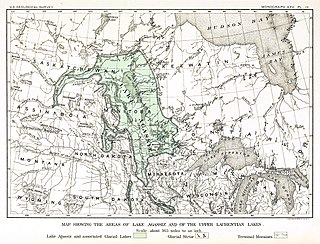
WLake Agassiz was a very large glacial lake in central North America. Fed by glacial meltwater at the end of the last glacial period, its area was larger than all of the modern Great Lakes combined though its mean depth was not as great as that of many major lakes today.
 W
WLake Algonquin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed in east-central North America at the time of the last ice age. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, and Lake Nipissing.
 W
WLake Arkona was a stage of the lake waters in the Huron-Erie-Ontario basin following the end of the Lake Maumee levels and before the Lake Whittlesey stages, named for Arkona, Ontario, about 50 miles (80 km) east of Sarnia.
 W
WBow Lake is a small lake in western Alberta, Canada. It is located on the Bow River, in the Canadian Rockies, at an altitude of 1920 m.
 W
WDriedmeat Lake is a long ribbon lake in Alberta; part of the Battle River system. Its northern end is located approximately 10 km (6.2 mi) south of the city of Camrose. The city draws its water supply from the lake. It was originally created by a glacial meltwater channel, which carved the surrounding valley. In the valley and around it, Saskatoon berries, an ingredient of pemmican, grow and are endemic in the area.
 W
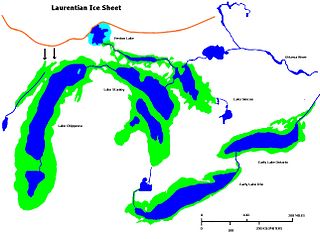
WLake Duluth was a proglacial lake that formed in the Lake Superior drainage basin as the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated. The oldest existing shorelines were formed after retreat from the Greatlakean advance, sometime around 11,000 years B.P. Lake Duluth formed at the western end of the Lake Superior basin. Lake Duluth overflowed south through outlets in Minnesota and Wisconsin at an elevation of around 331 m above sea level.
 W
WEarly Lake Erie was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed at the end of the last ice age approximately 13,000 years ago. The early Erie fed waters to Glacial Lake Iroquois.
 W
WLake Frontenac was a proglacial lake in the basin of what is now Lake Ontario. The sudden influx of fresh water into the Atlantic, as the retreat of the Laurentian Glacier triggered a sudden drop in the lake's water level, may in turn have triggered the onset of the Younger Dryas, 1000-year period of renewed cooling approximately 12000 years ago.
 W
WHector Lake is a small glacial lake in western Alberta, Canada. It is located on the Bow River, in the Waputik Range of the Canadian Rockies.
 W
WHidden Lake is a small glacial lake in the Skoki Valley of Banff National Park, Canada. It is located in the Slate Range of the Canadian Rockies.
 W
WGlacial Lake Iroquois was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed at the end of the last ice age approximately 13,000 years ago. The lake was essentially an enlargement of the present Lake Ontario that formed because the St. Lawrence River downstream from the lake was blocked by the ice sheet near the present Thousand Islands. The level of the lake was approximately 30 m (~100 ft) above the present level of Lake Ontario.
 W
WLake Louise is a glacial lake within Banff National Park in Alberta, Canada. It is located 5 km (3.1 mi) west of the Hamlet of Lake Louise and the Trans-Canada Highway.
 W
WLake Maumee was a proglacial lake and an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 14,000 Years Before Present (YBP) as the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. As water levels continued to rise the lake evolved into Lake Arkona and then Lake Whittlesey.
 W
WLake Memphremagog is a fresh water glacial lake located between Newport, Vermont, United States and Magog, Quebec, Canada. The lake spans both Quebec and Vermont, but is mostly in Quebec. Most of the watershed that feeds the lake is located in Vermont, and is a source for accumulated phosphorus, sediments and other pollutants. Cleanup efforts since the late 1980s have improved the water quality. The lake furnishes potable (drinking) water for 200,000 people.
 W
WLake Minnewanka is a glacial lake located in the eastern area of Banff National Park in Canada, about five kilometres northeast of the Banff townsite. The lake is 21 km (13 mi) long and 142 m (466 ft) deep, making it the 2nd longest lake in the mountain parks of the Canadian Rockies.
 W
WLake Minong was a proglacial lake that formed in the Lake Superior basin during the Wisconsin glaciation around 10,000 B.P.. This was the last glacial advance that entered Michigan and covered only part of the upper peninsula. Lake Minong occurred in the eastern corner of the Lake Superior basin while Lake Duluth was in the western end. The lakes became separated when the glacier reached the upper peninsula. Lake Minong expanded to the north as the ice retreated after 9,800 B.P. When the ice retreated from the Keweenaw Peninsula, Lake Duluth merged into Lake Minong.
 W
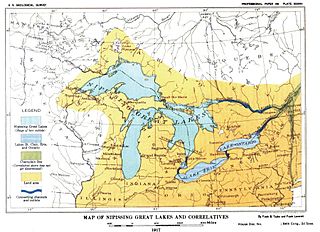
WNipissing Great Lakes was a prehistoric proglacial lake. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Superior, Lake Huron, Georgian Bay and Lake Michigan. It formed about 7,500 years before present (YBP). The lake occupied the depression left by the Labradorian Glacier. This body of water drained eastward from Georgian Bay to the Ottawa valley. This was a period of isostatic rebound raising the outlet over time, until it opened the outlet through the St. Clair valley.
 W
WLake Ojibway was a prehistoric lake in what is now northern Ontario and Quebec in Canada. Ojibway was the last of the great proglacial lakes of the last ice age. Comparable in size to Lake Agassiz, and north of the Great Lakes, it was at its greatest extent c. 8,500 years BP. The former lakebed forms the modern Clay Belt, an area of fertile land.
 W
WPaudash Lake is a lake in south central Ontario southwest of Bancroft along Highway 28. The lake is located just north of Silent Lake Provincial Park in Haliburton County, 27 km (17 mi) south of the panhandle of Algonquin Provincial Park. The nearest communities to Paudash Lake are the village of Cardiff, close to the lake's Inlet Bay, and the hamlet of Paudash to the northeast of Lower Paudash Lake. Actually two lakes, 'Paudash' and 'Lower Paudash', the lakes are located on the Crowe River, near its head waters, which flows into the Trent River at Crowe Bay north of Campbellford.
 W
WPeyto Lake is a glacier-fed lake in Banff National Park in the Canadian Rockies. The lake itself is near the Icefields Parkway. It was named for Bill Peyto, an early trail guide and trapper in the Banff area.
 W
WQuesnel Lake is a glacial lake or fjord in British Columbia, Canada, and is the major tributary of the Fraser River. With a maximum depth of 511 m (1,677 ft), it is claimed to be the deepest fjord lake in the world, the deepest lake in BC, and the third-deepest lake in North America, after Great Slave Lake.
 W
WReindeer Lake is a lake in Western Canada located on the border between northeastern Saskatchewan and northwestern Manitoba, with the majority in Saskatchewan. The name of the lake appears to be a translation of the Algonquian name. It is the 24th largest lake in the world by area, as well as being the second-largest lake in Saskatchewan and the ninth largest in Canada. 8% of the lake lies in Manitoba and 92% of lake in Saskatchewan.
 W
WLac la Ronge is a glacial lake in Saskatchewan, Canada. It is the fifth largest lake in the province.
 W
WSaganaga Lake is a large lake on the Minnesota – Ontario international border. It is protected by the Boundary Waters Canoe Area Wilderness in the United States and by Quetico Provincial Park and La Verendrye Provincial Park in Canada.
 W
WSydney Lake is a small glacial lake located about 46 miles from Minaki, Ontario. It was named after Sydney Forester, who surveyed the area in the early 20th century for the Government of Canada.
 W
WVolcano Lake, formerly called Crater Lake, is a lake on Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada, located just south of Puzzle Mountain and west of Elkhorn Mountain on west side of Strathcona Provincial Park. The name is a misnomer – the lake is the result of glaciation.
 W
WLake Wayne formed in the Lake Erie and Lake St. Clair basins around 12,500 years before present (YBP) when Lake Arkona dropped in elevation. About 20 feet (6.1 m) below the Lake Warren beaches it was early described as a lower Lake Warren level. Based on work in Wayne County, near the village of Wayne evidence was found that Lake Wayne succeeded Lake Whittlesey and preceded Lake Warren. From the Saginaw Basin the lake did not discharge water through Grand River but eastward along the edge of the ice sheet to Syracuse, New York, thence into the Mohawk valley. This shift in outlets warranted a separate from Lake Warren. The Wayne beach lies but a short distance inside the limits of the Warren beach. Its character is not greatly different when taken throughout its length in Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania and New York. At the type locality in Wayne County, Michigan, it is a sandy ridge, but farther north, and to the east through Ohio it is gravel. The results of the isostatic rebound area similar to the Lake Warren beaches.
 W
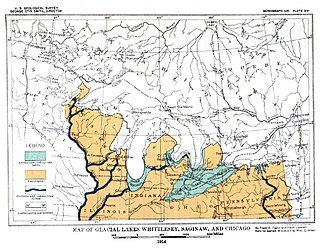
WLake Whittlesey was a proglacial lake that was an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 14,000 years ago. As the Erie Lobe of the Wisconsin Glacier retreated at the end of the last ice age, it left melt-water in a previously-existing depression area that was the valley of an eastward-flowing river known as the Erigan River that probably emptied into the Atlantic Ocean following the route of today's Saint Lawrence River. The lake stood at 735 feet (224 m) to 740 feet (230 m) above sea level. The remanent beach is not horizontal as there is a ‘hinge line’ southwest of a line from Ashtabula, Ohio, through the middle part of Lake St. Clair. The hinge line is where the horizontal beaches of the lake have been warped upwards towards the north by the isostatic rebound as the weight of the ice sheet was removed from the land. The rise is 60 feet (18 m) north into Michigan and the Ubly outlet. The current altitude of the outlet is 800 feet (240 m) above sea level. Where the outlet entered the Second Lake Saginaw at Cass City the elevation is 740 feet (230 m) above sea level. The Lake Whittlesey beach called the Belmore Beach and is a gravel ridge 10 feet (3.0 m) to 15 feet (4.6 m) high and one-eighth mile wide. Lake Whittlesey was maintained at the level of the Ubly outlet only until the ice melted back on the "Thumb" far enough to open a lower outlet. This ice recession went far enough to allow the lake to drop about 20 feet (6.1 m) below the lowest of the Arkona beaches to Lake Warren levels.
 W
WWollaston Lake is a lake in northeastern Saskatchewan, Canada. It is 550 kilometres (340 mi) northeast of Prince Albert. With a surface area of 2,286 square kilometres (883 sq mi), it is the largest bifurcation lake in the world – that is, a lake that drains naturally in two directions.