 W
WAnnexation is the administrative action and concept in international law relating to the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state and is generally held to be an illegal act. It is distinct from conquest, which refers to the acquisition of control over a territory involving a change of sovereignty, and differs from cession, in which territory is given or sold through treaty, since annexation is a unilateral act where territory is seized and held by one state. It usually follows military occupation of a territory.
 W
WThe Annexation Bill of 1866 was a bill introduced on July 2, 1866, but never passed in the United States House of Representatives. It called for the annexation of British North America and the admission of its provinces as states and territories in the Union. The bill was sent to committee but never came back, was never voted upon, and did not become law. The bill never came to the United States Senate.
 W
WThe territory of Crimea, previously controlled by the Crimean Khanate, was annexed by the Russian Empire on 19 April [O.S. 8 April] 1783. The period before the annexation was marked by Russian interference in Crimean affairs, a series of revolts by Crimean Tatars, and Ottoman ambivalence. The annexation began 134 years of rule by the Russian Empire, which was ended by the revolution of 1917.
 W
WThe Crimean Peninsula, north of the Black Sea in Eastern Europe, was annexed by the Russian Federation between February and March 2014 and since then has been administered as two Russian federal subjects—the Republic of Crimea and the federal city of Sevastopol. The annexation from Ukraine followed a Russian military intervention in Crimea that took place in the aftermath of the 2014 Ukrainian revolution and was part of wider unrest across southern and eastern Ukraine.
 W
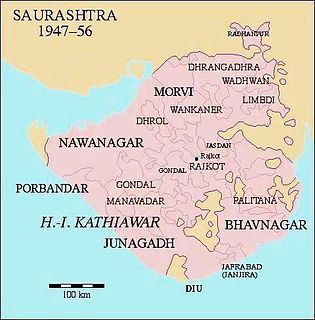
WJunagadh was a princely state of British India, located in what is now Gujarat, outside but under the suzerainty of British India.
 W
WThe annexation of the Partido de Nicoya to Costa Rica is a historical event that refers to the incorporation of the territory of Nicoya to the State of Costa Rica, which occurred on July 25, 1824.
 W
WThe annexation of Santo Domingo was an attempted treaty during the later Reconstruction Era, initiated by United States President Ulysses S. Grant in 1869, to annex "Santo Domingo" as a United States territory, with the promise of eventual statehood. President Grant feared some European power would take the island in violation of the Monroe Doctrine. He privately thought annexation would be a safety valve for African Americans who were suffering persecution in the US, but he did not include this in his official messages. Grant speculated that the acquisition of Santo Domingo would help bring about the end of slavery in Cuba and elsewhere.
 W
WAnnexation of the Jordan Valley is the proposed application of Israeli sovereignty over the Jordan Valley. The idea has been advocated by some Israeli politicians since the Israeli occupation of the West Bank began in 1967, most notably with the Allon Plan and the 2020 Trump peace plan.
 W
WThe annexation of the Leeward Islands or the Leewards War was a series of diplomatic and armed conflicts between the French Third Republic and the native kingdoms of Raiatea-Tahaa, Huahine and Bora Bora, which resulted in the conquest of the Leeward Islands, in the South Pacific archipelago of the Society Islands in modern-day French Polynesia.
 W
WThe annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China was the process by which the People's Republic of China (PRC) gained control of Tibet. These regions came under the control of China after attempts by the Government of Tibet to gain international recognition, efforts to modernize its military, negotiations between the Government of Tibet and the PRC, a military conflict in the Chamdo area of western Kham in October 1950, and the eventual acceptance of the Seventeen Point Agreement by the Government of Tibet under Chinese pressure in October 1951. In some Western opinions, the incorporation of Tibet into China is viewed as an annexation. The Government of Tibet and the Tibetan social structure remained in place in the Tibetan polity under the authority of China until the 1959 Tibetan uprising, when the Dalai Lama fled into exile and after which the Government of Tibet and Tibetan social structures were dissolved.
 W
WThe Anschluss, also known as the Anschluss Österreichs, refers to the annexation of Austria into Nazi Germany on 12 March 1938.
 W
WThe Bosnian Crisis of 1908–09, also known as the Annexation crisis or the First Balkan Crisis, erupted in early October 1908 when Austria-Hungary announced the annexation of Bosnia and Herzegovina, territories formerly within the sovereignty of the Ottoman Empire. This unilateral action—timed to coincide with Bulgaria's declaration of independence from the Ottoman Empire—sparked protestations from all the Great Powers and Austria-Hungary's Balkan neighbours, Serbia and Montenegro. In April 1909 the Treaty of Berlin was amended to reflect the fait accompli and bring the crisis to an end. The crisis permanently damaged relations between Austria-Hungary and the neighboring states of Italy, Serbia, and Russia, and in the long term helped lay the grounds for World War I. Although the crisis ended with what appeared to be a total Austro-Hungarian diplomatic victory, Russia became determined not to back down again and hastened its military build-up. The Crisis also cooled down Austrian–Serbian relations, which continued to be strained to the point of declaring war on each other in 1914.
 W
WThe history of post-confederation Canada began on July 1, 1867, when the British North American colonies of Canada, New Brunswick, and Nova Scotia were united to form a single Dominion within the British Empire. Upon Confederation, the United Province of Canada was immediately split into the provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The colonies of Prince Edward Island and British Columbia joined shortly after, and Canada acquired the vast expanse of the continent controlled by the Hudson's Bay Company, which was eventually divided into new territories and provinces. Canada evolved into a fully sovereign state by 1982.
 W
WAt the end of World War II, plans were made in the Netherlands to annex German territory as compensation for the damages caused by the war. In October 1945, the Dutch state asked Germany for 25 billion guilders in reparations. In February 1945 it had already been established at the Yalta Conference that reparations would not be given in monetary form. The plan which was worked out in most detail was the one made by Frits Bakker Schut, and hence became known as the Bakker-Schut Plan.
 W
WThe German occupation of Czechoslovakia (1938–1945) began with the German annexation of Sudetenland in 1938, continued with the March 1939 invasion of the Czech lands and creation of the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, and by the end of 1944 extended to all parts of the former Czechoslovakia.
 W
WThe Annexation of Goa was the process in which the Republic of India annexed the former Portuguese Indian territories of Goa, Daman and Diu, starting with the armed action carried out by the Indian Armed Forces in December 1961. In India, this action is referred to as the "Liberation of Goa". In Portugal, it is referred to as the "Invasion of Goa".
 W
WThe Newlands Resolution was a joint resolution passed on July 4, 1898, by the United States Congress to annex the independent Republic of Hawaii. In 1900, Congress created the Territory of Hawaii.
 W
WThe Hungarian occupation of Yugoslav territories consisted of the military occupation, then annexation, of the Bačka, Baranja, Međimurje and Prekmurje regions of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia by the Kingdom of Hungary during World War II. These territories had all been under Hungarian rule prior to 1920, and had been transferred to Yugoslavia as part of the post-World War I Treaty of Trianon. They now form part of several states: Yugoslav Bačka is now part of Vojvodina, an autonomous province of Serbia, Yugoslav Baranja and Međimurje are part of modern-day Croatia, and Yugoslav Prekmurje is part of modern-day Slovenia. The occupation began on 11 April 1941 when 80,000 Hungarian troops crossed the Yugoslav border in support of the German-led Axis invasion of Yugoslavia that had commenced five days earlier. There was some resistance to the Hungarian forces from Serb Chetnik irregulars, but the defences of the Royal Yugoslav Army had collapsed by this time. The Hungarian forces were indirectly aided by the local Volksdeutsche, the German minority, which had formed a militia and disarmed around 90,000 Yugoslav troops. Despite only sporadic resistance, Hungarian troops killed many civilians during these initial operations, including some Volksdeutsche. The government of the newly formed Axis puppet state, the Independent State of Croatia, subsequently consented to the Hungarian annexation of the Međimurje area, which dismayed the Croat population of the region.
 W
WOperation Polo was the code name of the Hyderabad "police action" in September 1948, by the then newly independent Dominion of India against Hyderabad State. It was a military operation in which the Indian Armed Forces invaded the Nizam-ruled princely state, annexing it into the Indian Union.
 W
WThe invasion of Kuwait on 2 August 1990 was a two-day operation conducted by Iraq against the neighboring State of Kuwait, which resulted in the seven-month-long Iraqi occupation of the country. This invasion and Iraq's subsequent refusal to withdraw from Kuwait by a deadline mandated by the United Nations led to military intervention by a United Nations-authorized coalition of forces led by the United States. These events came to be known as the first Gulf War and resulted in the expulsion of Iraqi forces from Kuwait and the Iraqis setting 600 Kuwaiti oil wells on fire during their retreat.
 W
WKorea under Japanese Rule or Korea under Japanese Occupation was the period between 1910 and 1945, when Joseon Korea came under the Japanese sphere of influence in the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1876. A complex coalition of the Meiji government, military, and business officials began a process of Korea's political and economic integration into Japan. The Korean Empire became a protectorate of Japan in 1905 in the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1905 and the country was indirectly ruled by the Japanese through the Resident-General of Korea. Japan formally annexed Korea in 1910 in the Japan–Korea Treaty of 1910, without the consent of Gojong, the regent of the Korean Emperor Sunjong. The Japanese Empire had established the Korean Peninsula as a colony of Japan administered by the General Government based in Keijō (Gyeongseong) which governed Korea with near-absolute power.
 W
WThe Kuwait Governorate was the 19th governorate of Iraq established in the aftermath of the invasion of Kuwait by Iraq in 1990. It was preceded by the brief puppet state of the Republic of Kuwait. The Kuwait Governorate consisted of most of the occupied Kuwaiti territory, with the exclusion of the northern areas which became the Saddamiyat al-Mitla' District. Saddam Hussein's relative, Ali Hassan al-Majid became the governor of this province.
 W
WThe Department of the Litoral, commonly known as the Bolivian coast, was the description of the extent of the Pacific coast of the Atacama Desert included in the territory of Bolivia from its inception in 1825 until 1879, when it was lost to Chile.
 W
WThere were many areas annexed by Nazi Germany both immediately before and throughout the course of World War II. Territories that were part of Nazi Germany before the annexations were known as the "Altreich".
 W
WThe Newlands Resolution was a joint resolution passed on July 4, 1898, by the United States Congress to annex the independent Republic of Hawaii. In 1900, Congress created the Territory of Hawaii.
 W
WThe Soviet occupation of the Baltic states covers the period from the Soviet–Baltic mutual assistance pacts in 1939, to their invasion and annexation in 1940, to the mass deportations of 1941.
 W
WThe occupation of the Baltic states involved the military occupation of the three Baltic states—Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania—by the Soviet Union under the auspices of the 1939 Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact in June 1940. They were then annexed into the Soviet Union as constituent republics in August 1940, though most Western powers and nations never recognised their incorporation. On 22 June 1941, Nazi Germany attacked the Soviet Union and within weeks occupied the Baltic territories. In July 1941, the Third Reich incorporated the Baltic territory into its Reichskommissariat Ostland. As a result of the Red Army's Baltic Offensive of 1944, the Soviet Union recaptured most of the Baltic states and trapped the remaining German forces in the Courland pocket until their formal surrender in May 1945. The Soviet "annexation occupation" or occupation sui generis of the Baltic states lasted until August 1991, when the three countries regained their independence.
 W
WThe Recovered Territories are the territories of the former Free City of Danzig and of pre-war Germany that became part of Poland after World War II, at which time their former German inhabitants were forcibly deported.
 W
WThe Rupert's Land Act 1868 was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, authorizing the transfer of Rupert's Land from the control of the Hudson's Bay Company to the Dominion of Canada. Often confused with the Deed of Surrender, the Act is different as it only expressed that the United Kingdom and Canada permitted the transfer but did not settle on the details of exchange with HBC which were outline in the Deed.
 W
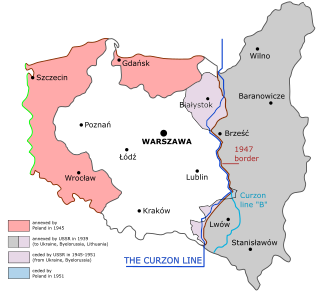
WOn the basis of a secret clause of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, the Soviet Union invaded Poland on September 17, 1939, capturing the eastern provinces of the Second Polish Republic. Lwów, present day Lviv, the capital of the Lwów Voivodeship and the principal city and cultural center of the region of Galicia, was captured and occupied by September 22, 1939 along with other provincial capitals including Tarnopol, Brześć, Stanisławów, Łuck, and Wilno to the north. The eastern provinces of interwar Poland were inhabited by an ethnically mixed population, with ethnic Poles as well as Polish Jews dominant in the cities. These lands now form the backbone of modern Western Ukraine and West Belarus.
 W
WSeventeen days after the German invasion of Poland in 1939, which marked the beginning of the Second World War, the Soviet Union invaded the eastern regions of Poland and annexed territories totaling 201,015 square kilometres (77,612 sq mi) with a population of 13,299,000. Inhabitants besides ethnic Poles included Czechs, Lithuanians, Belarusians, Ukrainians, Jews, and other minority groups.
 W
WThe Texas annexation was the 1845 annexation of the Republic of Texas into the United States of America, which was admitted to the Union as the 28th state on December 29, 1845.