 W
WThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, fiat panis, translates to "let there be bread". It was founded in October 1945.
 W
WThe Agricultural Market Information System (AMIS) is an inter-agency platform to enhance food market transparency and encourage international policy coordination in times of crisis. It was established at the request of the Group of Twenty (G20) in 2011. Countries participating in AMIS encompass the main producing and consuming countries of major food crops covered by the initiative: wheat, maize, rice and soybeans. AMIS is hosted by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) in Rome/Italy and supported by a joint Secretariat, which currently consists of eleven international organizations and entities. Apart from FAO, these are the Group on Earth Observations Global Agricultural Monitoring (GEOGLAM) initiative, the International Fund for Agricultural Development (IFAD), the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), the International Grains Council (IGC), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Food Program (WFP), the World Trade Organization (WTO), the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the United Nations High-Level Task Force on the Global Food Security Crisis (UN-HLTF), and the World Bank.
 W
WAnimal genetic resources for food and agriculture (AnGR) are a subset of genetic resources and a specific element of agricultural biodiversity. The term animal genetic resources refers specifically to the genetic resources of avian and mammalian species, which are used for food and agriculture purposes. Further terms referring to AnGR are "farm animal genetic resources" or "livestock diversity".
 W
WThe Asia-Pacific Fishery Commission (APFIC), originally called the Indo-Pacific Fisheries Council (IPFC) is a Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) Article XIV Regional Fisheries Body which covers fisheries, aquaculture and related aquatic resource issues in the Asia-Pacific region. APFIC functions as a Regional Consultative Forum raising awareness amongst member countries, fisheries organizations and fisheries professionals in the Asia-Pacific region.
 W
WDee Dee Bridgewater is an American jazz singer. She is a three-time Grammy Award-winning singer-songwriter, as well as a Tony Award-winning stage actress. For 23 years, she was the host of National Public Radio's syndicated radio show JazzSet with Dee Dee Bridgewater. She is a United Nations Goodwill Ambassador for the Food and Agriculture Organization.
 W
WThe Codex Alimentarius is a collection of internationally recognized standards, codes of practice, guidelines, and other recommendations relating to foods, food production, and food safety.
 W
WCommunication for Development (C4D) is all the different types of communication that need to take place in societies if sustainable democratic development is to occur.
 W
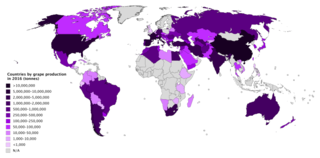
WThis is a list of countries by grape production in 2016 and 2017, based on data from the Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database. The estimated total world production for grapes in 2017 was 74,276,583 metric tonnes, down 1.0% from 74,992,047 tonnes in 2016. China was the largest producer of grapes, accounting for 16.8% of global production. Italy came second at 10.9%, followed by the United States at 9.6%.
 W
WDAD-IS is the acronym of the worldwide Domestic Animal Diversity Information System of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, within the FAO's management of animal genetic resources programme. It includes a searchable database of information about breeds, the Global Databank for Animal Genetic Resources; it also holds tools for management, and contacts for the National and Regional Coordinators for the programme. Data from the Global Databank is used for reporting on the global status and trends of animal genetic resources. The fourth version of the DAD-IS was launched on 21 November 2017.
 W
WThe European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO) is an intergovernmental organisation responsible for European cooperation in plant protection in the European and Mediterranean region. Founded in 1951 and based in Paris, France, EPPO is the Regional Plant Protection Organization (RPPO) for Europe under the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC).
 W
WThe Goodwill Ambassadors Programme of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations has been in place since 1999. The main purpose of the programme is to increase public awareness and to disseminate information on issues related to food security and hunger.
 W
WThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) leads the programme Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS), which helps identify ways to mitigate threats faced by these systems and their people and enhance the benefits derived from these dynamic systems.
 W
WThe International Day of Forests was established on the 21st day of March, by resolution of the United Nations General Assembly on November 28, 2012. Each year, various events celebrate and raise awareness of the importance of all types of forests, and trees outside forests, for the benefit of current and future generations. Countries are encouraged to undertake efforts to organize local, national, and international activities involving forests and trees, such as tree planting campaigns, on International Day of Forests. The Secretariat of the United Nations Forum on Forests, in collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organization, facilitates the implementation of such events in collaboration with governments, the Collaborative Partnership on Forests, and international, regional and subregional organizations. International Day of Forests was observed for the first time on March 21, 2013.
 W
WThe International Tropical Fruits Network (TFNet) is an independent and self-financing global network established under the auspices of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). It is now an intergovernmental and inter-institutional international organization, with the mandate and role to promote sustainable global development of the tropical fruit in relation to production, consumption and trade. It is membership-based, with members acting through one lead agency on inter-country decisions.
 W
WThe year 2011 was declared the International Year of Forests by the United Nations to raise awareness and strengthen the sustainable management, conservation and sustainable development of all types of forests for the benefit of current and future generations.
 W
WThis is a list of countries by papaya production in 2016 and 2017, based on data from the Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database. The estimated total world production for papayas in 2017 was 13,016,281 metric tonnes, down 0.6% from 13,097,219 tonnes in 2016. India was by far the largest producer, accounting for nearly 46% of global production. Dependent territories are shown in italics.
 W
WThis is a list of countries by pear production in 2016 and 2017, based on data from the Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database. The estimated total world production for pears in 2017 was 24,168,309 metric tonnes, an increase of 2.1% from 23,676,110 tonnes in 2016. China was by far the largest producer, accounting for over 67% (two-thirds) of global production.
 W
WThis is a list of countries by pineapple production in 2016 and 2017, based on data from the Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database. The estimated total world production for pineapples in 2017 was 27,402,956 metric tonnes, an increase of 4.6% from 26,195,845 tonnes in 2016. Dependent territories are shown in italics.
 W
WThis is a list of countries by potato production in 2016, based on data from the Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database. The total world production for potatoes in 2016 was 376,826,967 metric tonnes. China was by far the largest producer, accounting for 26.3% of world production. Dependent territories are shown in italics. Total production in 2019 was 423 mln tonnes.
 W
WThis is a list of countries by soybean production in 2018, based on data from the Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database. The total world production for soybeans in 2018 was 348,712,311 metric tonnes. Brazil was the largest producer, accounting for 36% of world production. Many nation have launched government soybean support programs in their countries.
 W
WThis is a list of countries by tomato production in 2016 and 2017, based on data from the Food and Agriculture Organization Corporate Statistical Database. The estimated total world production for tomatoes in 2017 was 182,301,395 metric tonnes, an increase of 1.6% from 179,508,401 tonnes in 2016. China was by far the largest producer, accounting for nearly 33% of global production. Dependent territories are shown in italics.
 W
WMutti - Industria Conserve Alimentari is an Italian company that specializes in preserved food, particularly in the tomato sector, founded in 1899 in Piazza di Basilicanova, a district in Montechiarugolo, in the province of Parma.
 W
WThe North American Plant Protection Organization (NAPPO), is the phytosanitary standard setting organization recognized by the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). It was created in 1976 as a regional organization of the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC) of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations. Previously based in Ottawa, Ontario, it is now headquartered in Raleigh, North Carolina.
 W
WThe Rural Income Generating Activities (RIGA) Project is a collaboration between the Food and Agriculture Organization, the World Bank, and American University that seeks to contribute to the understanding of the income generating activities, both agricultural and non-agricultural, of rural households in developing countries. The RIGA project achieves this by two means. First, through the development of an innovative database of income sources from various developing countries, which is available free of charge to researchers via the project’s website. Second, by producing studies and publications that use the database to analyze pressing economic and policy issues.
 W
WThe State of the World's Animal Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture is a major report on the breeds of farm livestock in the world. It was published by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) in 2007. It covers mammalian and avian domestic livestock breeds, but does not include fish or honey bees and other invertebrates. It is based on information submitted to the FAO, in the form of reports of participating countries, thematic studies prepared by experts and data on individual breeds submitted to DAD-IS. An annex to the report, the List of breeds documented in the Global Databank for Animal Genetic Resources, gives an estimate of conservation status for all breeds for which sufficient data had been received. The report has been translated into Arabic, Chinese, French, Indonesian, Russian and Spanish.
 W
WThe United Nations Programme on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation is a collaborative programme of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), created in 2008 in response to the UNFCCC decisions on the Bali Action Plan and REDD at COP-13. It should not be confused with REDD+, a voluntary climate change mitigation approach that has been developed by Parties to the UNFCCC.
 W
WUnited Nations Water (UN-Water) is an interagency mechanism that coordinates the efforts of United Nations entities and international organizations working on water and sanitation issues.″Over 30 UN organizations carry out water and sanitation programmes, reflecting the fact that water issues run through all of the UN’s main focus areas. UN-Water’s role is to coordinate so that the UN family ‘delivers as one’ in response to water related challenges.″
 W
WWorld Food Day is an international day celebrated every year worldwide on 16 October to commemorate the date of the founding of the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization in 1945. The day is celebrated widely by many other organizations concerned with hunger and food security, including the World Food Programme and the International Fund for Agricultural Development. WFP received the Nobel Prize in Peace for 2020 for their efforts to combat hunger, contribute to peace in conflict areas, and for playing a leading role in stopping the use of hunger in the form of a weapon for war and conflict.
 W
WThe World Summit on Food Security took place in Rome, Italy between 16 and 18 November 2009. The decision to convene the summit was taken by the Council of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) in June 2009, at the proposal of FAO Director-General Dr Jacques Diouf. Sixty Heads of State and Government and 192 ministers, from 182 countries and the European Community, attended the summit, which took place at FAO's headquarters.
 W
W W
W W
W W
W