 W
WThe Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is a country situated in Southwest Asia, the largest country of Arabia, by the Arabian Peninsula, bordering the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea, north of Yemen. Its extensive coastlines on the Persian Gulf and Red Sea provide great leverage on shipping through the Persian Gulf and the Suez Canal. The kingdom occupies 80% of the Arabian Peninsula. Most of the country's boundaries with the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Oman, and the Republic of Yemen are undefined, so the exact size of the country remains unknown. The Saudi government estimate is at 2,217,949 square kilometres, while other reputable estimates vary between 2,149,690 and 2,240,000 sq. kilometres. Less than 1% of the total area is suitable for cultivation, and in the early 1960s, population distribution varied greatly among the towns of the eastern and western coastal areas, the densely populated interior oases, and the vast, almost empty deserts.
 W
WAbqaiq is a Saudi Aramco gated community and oil-processing facilities located in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia, located in the desert 60 km southwest of the Dhahran-Dammam-Khobar metropolitan area, and north of the Rub' al-Khali, the second largest sand desert in the world also known as the "Empty Quarter". The community was built in the 1940s by Aramco. The Abqaiq community had a population of approximately 1,500 in 2012, though the inclusion of the population outside the Saudi Aramco community brings this number closer to 30,000.
 W
WAl Lith is a city in the Tihamah region on the coast of the Red Sea south west of the holy city of Mecca. It is the fifth largest city in population in Makkah Province, and it is one of the large sea ports of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia on the Red Sea, and Miqat Yalamlam is located north of it. The estimated population of Al Lith is over 72,000 people.
 W
WAl-Awjam is a small city located in the Eastern Province of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia on the coast of the Persian Gulf. The village lies in far north-eastern corner of the Eastern Province, in a petroleum-rich region near the Ghawar and Qatif oilfields. It has a population of 11,460.
 W
WAl Ma'abiyat is a large archeological site in Wadi al-'Ula, Saudi Arabia.
 W
WAl-Magar was a prehistoric culture of the Neolithic whose epicenter lied in modern-day southwestern Najd in Saudi Arabia. Al-Magar is possibly one of the first cultures in the world where widespread domestication of animals occurred, particularly the horse, during the Neolithic period.
 W
WAl-Yamamah is an ancient historical region lying in the Najd region of modern-day Saudi Arabia, or sometimes more specifically, the now-extinct ancient village of Jaww Al-Yamamah, near Al-Kharj, after which the rest of the region was named. Only a handful of centralized states ever arose in Yamamah, but it figured prominently in early Islamic history due to it becoming a central theater in the Ridda Wars immediately following Muhammad's death. Despite being incorporated into the Najd region, the term 'Al-Yamamah' remains in use as a traditional and historical term to reference or emphasize the region's ancient past. The current headquarters of the Saudi government in Riyadh, for example, is known as the Palace of Yamamah.
 W
WDammam is the sixth-most populous city in Saudi Arabia and the capital of the Eastern Province. The judicial and administrative bodies of the province, in addition to the administrative offices of other minor governmental departments functioning within the province, are located in the city. The word itself is generally used to refer to the city, but may also refer to its eponymous governorate.
 W
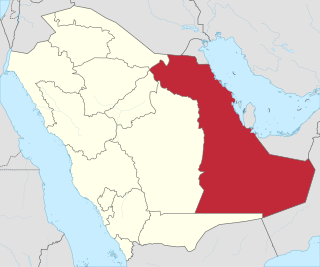
WThe Eastern Province, also known as the Eastern Region, and officially the Emirate of the Eastern Province, is the easternmost of the 13 provinces of Saudi Arabia. It is the largest province by area and the third most populous after the Riyadh Province and the Makkah Province. In 2017, the population was 4,900,325. Of these, 3,140,362 were Saudi citizens and 1,759,963 were foreign nationals The province accounts for 15.05% of the entire population of Saudi Arabia and is named for its geographical location relative to the rest of the kingdom.
 W
WEin Heet Cave is a natural cave which is located 30 kilometers southeast of Riyadh city, near Alkharj, Saudia Arabia.
 W
WHafar al-Batin, also frequently spelled Hafr al-Batin, is a Saudi Arabian city in the Eastern Province. It is located 430 km north of Riyadh, 94.2 km from the Kuwait border, and about 74.3 from the Iraq border. The city lies in the dry valley of the Wadi al-Batin, which is part of the longer valley of the river Wadi al-Rummah, which leads inland toward Medina and formerly emptied into the Persian Gulf.
 W
WThe Hejaz is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. The name of the region is derived from the Arabic root Ḥ-J-Z, meaning "to separate," and it is so called as it separates the land of the Najd in the east from the land of Tihāmah in the west. It is also known as the "Western Province." It is bordered in the west by the Red Sea, in the north by Jordan, in the east by the Najd, and in the south by the 'Asir Region. Its largest city is Jeddah, the second largest city in Saudi Arabia, with Mecca and Medina being the fourth and fifth largest cities respectively in Saudi Arabia.
 W
WIrqah is a town in the western part of Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
 W
WJalamid(Arabic: حزم الجلاميد) is a town and crossroads in Saudi Arabia near the Iraqi border.
 W
WThe Mahd Al Thahab, is a small gold area in the Arabian Peninsula. It is located in the Province of Al-Madinah, in the Hejazi region of Saudi Arabia.
 W
WMina, also transliterated as Muna, and commonly known as the City of Tents is a valley and neighborhood located in the Masha'er district of Mecca in the Makkah Province of Saudi Arabia, 8 kilometres southeast of Mecca, covering an area of approximately 20 km2 (7.7 sq mi). Mina incorporates the tents, the Jamarat area, and the slaughterhouses just outside the tent city.
 W
WNajd or Nejd is a geographical central region of Saudi Arabia that accounts for about a third of the population of the country. Najd consists of the modern administrative regions of Riyadh, Sudair, Al-Qassim, and Ha'il.
 W
WWādī Nakhlah is an area in the Hejazi region of Saudi Arabia between the cities of Mecca and Ta'if, which serves as a boundary for the Islamic Ḥaram of Mecca.
 W
WAl-Qurh, is a village and archaeological site of Al-Ula governorate, north of Medina Saudi Arabia. The name القرح name translates as ulcers
 W
WRabigh is a city and governorate in the Makkah Province of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, situated on the coast of the Red Sea, around 208 km (129 mi) northwest of Mecca in the historic Hejaz region. The city had an estimated population of 180,352 in 2014 and is situated at an elevation of 13 m (43 ft) above sea level, close to the border with the Madinah Province. The city dates back to Pre-Islamic Arabia and up to the 17th century, was known as al-Juhfah, or al-Johfah.
 W
WRas Tanura is a city in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia located on a peninsula extending into the Persian Gulf. The name Ras Tanura applies both to a gated Saudi Aramco employee compound and to an industrial area further out on the peninsula that serves as a major oil port and oil operations center for Saudi Aramco, the largest oil company in the world. Today, the compound has about 3,200 residents, with a few Americans and British expats.
 W
WSakākā is a city in northwestern Saudi Arabia which is the capital of Al Jawf Province. It is located just to the north of the An Nafud desert. Sakakah had a population of 242,813 at the 2010 census.
 W
WShaybah is a settlement dominated by a major crude oil production oil site, the Shaybah oil field, in Saudi Arabia, located approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) from the northern edge of the Rub' Al-Khali desert. It is about 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) south of the border to Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, which is a straight line drawn in the desert. It is 40 kilometres (25 mi) south of the eastern part of Abu Dhabi's Liwa Oasis.
 W
WShaybah Oil Field is a super-giant disputed oil field under the control of Saudi Arabia and is located in the northern edge of the Rub' Al-Khali/Empty Quarter desert. It is located about 10 km south of the border to Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, which is a straight line drawn in the desert. It is 40 km south of the eastern part of Liwa Oasis of Abu Dhabi.
 W
WTārūt Island is an island in the Persian Gulf belonging to the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia, connected by two causeways to Qatif. It is six kilometers from the coast, and is the longest island in the Persian Gulf after Qeshm Island, extending from Ra’s Tannurah in the north to Qatif in the west. The island has an area of 70 square kilometers, and a population (2010) of 77,757. It contains a number of towns and villages, including Tārūt itself, Deyrah, and Darīn.
 W
WTihamah or Tihama refers to the Red Sea coastal plain of the Arabian Peninsula from the Gulf of Aqaba to the Bab el Mandeb.
 W
WJabal Tuwaiq is a narrow escarpment that cuts through the plateau of Najd in central Arabia, running approximately 800 km (500 mi) from the southern border of Al-Qasim in the north, to the northern edge of the Empty Quarter desert near Wadi ad-Dawasir in the south. It is 600 m (2,000 ft) high and also has a Middle Jurassic stratigraphic section. The eastern side slopes downwards gradually, while the western side ends in an abrupt manner. The escarpment can be thought of as a narrow plateau, though the locals refer to it as a jebel ("mount"). Marshall Cavendish used the name "Tuwayr Mountains" to describe mountains of central Arabia, distinct from the Shammar in the north, the Dhofar in the south, and the Hajar to the east.
 W
WUqair (Arabic:عقير) is an ancient fort of Islamic origin, located in the Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. It is the first seaport in the Persian Gulf. It is alternatively spelled Al-'Uqair, Uqayr, and Ogair, all Latin transliterations of the same Arabic word. It has been linked by some to the ancient city of Gerrha mentioned in Greek and Roman sources. The site was also the location of the conference at which the Uqair Protocol of 1922 was issued, which helped to establish the borders of modern Saudi Arabia.
 W
WWadi al-'Ula is a wadi in western Saudi Arabia. Wadi Al Ula is a tributary of the Wadi Jizal.
 W
WWadi Al-Batin is an intermittent river in Saudi Arabia and Kuwait. It is the lowest and final section of Wadi al-Rummah. It runs 45 miles (75 km) in a northeast-southwest direction through the Al-Dibdibah plain and has been recognized since 1913 as the border between Kuwait and Iraq.
 W
WWadi Al-Rummah or ar-Rummah is one of the Arabian Peninsula's longest river valleys, at a length of almost 600 km (370 mi). Now mostly dry and partly blocked by encroaching sand dunes, the wadi arises near Medina at Jibāl al Abyaḑ. It heads towards the north-east, connecting to several smaller wadis, like Mohalla Wadi and Murghala Wadi to the north and Jifn Wadi and Jarir Wadi to the south. It ends at Thuayrat Dunes of the ad-Dahna Desert in Al-Qassim Province near Buraidah.
 W
WWadi Arar also known as Wadi `Ar`ar and Wādī `Ar`ar is a wadi in the central part of the Northern Borders Region of Saudi Arabia. Wadi Arar starts about 125 km from Arar city, flows southwest to the northeast, past Arar city and merges with many Wadis and Sha’ibs, before crossing the Iraqi border.
 W
WThe miqat is the principal boundary at which Muslim pilgrims intending to perform the Ḥajj or Umrah pilgrimages must be enter the state of iḥrām , a state of consecration in which certain permitted activities are made prohibited.