 W
WTropical Cyclone Alibera was the second longest-lasting tropical cyclone on record in the south-west Indian Ocean, with a duration of 22 days. It formed on December 16, 1989, well to the northeast of Madagascar. For several days, it meandered southwestward while gradually intensifying. On December 20, Alibera intensified to tropical cyclone status with 10‑minute maximum sustained winds of 120 km/h (75 mph), or the equivalent of a minimal hurricane. That day, the Météo-France office in Réunion (MFR) estimated 10‑minute winds of 140 km/h (85 mph), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC), an unofficial warning agency for the region, estimated peak 1‑minute winds of 250 km/h (150 mph). After drifting erratically for several days, the storm began a steady southwest motion on December 29 as a greatly weakened system. On January 1, Alibera struck southeastern Madagascar near Mananjary, having re-intensified to just below tropical cyclone status. It weakened over land but again restrengthened upon reaching open waters on January 3. The storm turned to the southeast, then to the southwest, and finally back to the southeast, dissipating on January 5.
 W
WTropical Cyclone Belna was a strong tropical cyclone that made landfall over northwestern Madagascar in December 2019, becoming the first to do so since Hellen in 2014. Belna's precursor—an initially broad trough of low pressure west of Seychelles—was formally designated as a zone of disturbed weather on 2 December during a favourable period for tropical cyclogenesis in the Indian Ocean. The disturbance gradually developed over the course of several days, tracking slowly westward. Météo-France (MFR) upgraded the system to a tropical depression on 5 December and then to a tropical storm later that day. Belna reached tropical cyclone strength on 7 December as it began to turn towards the southwest, peaking with maximum sustained winds of 155 km/h (100 mph) before fluctuating in intensity over the following day as it passed just east of Mayotte. On 9 December, Belna restrengthened and reattained its peak winds upon making landfall near Soalala along the northwestern coast of Madagascar. The cyclone weakened before ultimately dissipating over southern Madagascar on 11 December.
 W
WTropical Cyclone Bingiza was the only named storm to make landfall in the inactive 2010–11 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. The second of three storms, Bingiza developed on February 9 to the northeast of Madagascar. For a few days it meandered generally southwestward, failing to intensify significantly. On February 12, the storm began a steady westward track as environmental conditions became more favorable. In a 24‑hour period, Bingiza developed from a moderate tropical storm into an intense tropical cyclone with a well-defined eye. After attaining peak 10–minute sustained winds of 155 km/h (100 mph), the cyclone moved ashore in northeastern Madagascar on February 14 and quickly weakened as it crossed the country. Bingiza emerged into the Mozambique Channel as a weak tropical disturbance, and it turned southward to move across western Madagascar. Bingiza attained tropical storm status before making its final landfall near Morondava, degenerating into a remnant low on February 17, and dissipating two days later.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Bondo was the first of a series of six tropical cyclones to impact Madagascar during the 2006–07 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Bondo developed on December 15 in the central Indian Ocean, west of Diego Garcia. After strengthening into a moderate tropical storm on December 18, the storm rapidly intensified while moving westward, taking advantage of favorable atmospheric conditions. Within 18 hours of being named, Bondo intensified to tropical cyclone status, or the equivalent of a minimal hurricane. The Météo-France office on Réunion (MFR) estimated peak 10 minute sustained winds of 205 km/h (125 mph), although the American-based Joint Typhoon Warning Center estimated stronger 1 minute winds of 250 km/h (155 mph). While near peak intensity, Bondo passed just south of Agaléga island, before weakening slightly and moving through the Farquhar Group of islands belonging to the Seychelles, becoming the strongest cyclone to affect that island group in decades. Bondo turned southwestward, and after brushing the northern coast of Madagascar, the cyclone made landfall near Mahajanga on December 25. The storm continued southward, and was last tracked by the MFR on December 28.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Bonita in January 1996 struck both Madagascar and Mozambique, causing severe damage. The long-lived storm began developing in the last hours of 1995, and slowly consolidated over the open waters of the South-West Indian Ocean. Tracking generally toward the west-southwest, the disturbance received its name from Météo-France on January 5. Ultimately peaking as an intense tropical cyclone, Bonita bypassed Mauritius and Réunion to the north before striking northeastern Madagascar late on January 10. There, the storm affected up to 150,000 people, flooded wide tracts of croplands, and killed 25 people. In the aftermath, disaster relief came from both the government of Madagascar and the international community, as well as non-governmental organizations (NGOs); the United Nations Department of Humanitarian Affairs assisted in the distribution of about $450,000 in monetary donations.
 W
WSevere Tropical Storm Chedza was a deadly tropical cyclone that struck Madagascar in January 2015. It formed from the intertropical convergence zone and moved over Mozambique, After moving open waters, the system began organizing on January 14, becoming Tropical Storm Chedza two days later. It quickly intensified over the Mozambique Channel due to warm waters and favorable conditions, and the storm attained peak 10 minute sustained winds of 100 km/h (65 mph) on January 16. That day, Chedza moved ashore western Madagascar between Belo sur Mer and Morondava, and it quickly crossed the island while weakening. The storm briefly re-intensified, passing southwest of Réunion before turning to the southeast. Chedza became extratropical on January 19, and was last noted two days later.
 W
WIn early 2000, severe flooding occurred in the African nation of Madagascar after Cyclone Leon–Eline and Severe Tropical Storm Gloria struck the nation within a two-week period. The first storm, Eline, formed on February 1, and took an extended track across the Indian Ocean, eventually making landfall near Mahanoro on February 17. On March 1, Gloria struck northeastern Madagascar, and like Eline, moved southwestward across the country.
 W
WTropical Cyclone Elita was an unusual tropical cyclone that made landfall on Madagascar three times. The fifth named storm of the 2003–04 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Elita developed in the Mozambique Channel on January 24, 2004. It strengthened to tropical cyclone status before striking northwestern Madagascar on January 28; it was the first storm to strike western Madagascar at that intensity since Cyclone Cynthia in 1991. Elita weakened to tropical depression status while crossing the island, and after exiting into the southwest Indian Ocean, it turned to the west and moved ashore in eastern Madagascar on January 31. After once again crossing the island, the cyclone reached the Mozambique Channel and re-intensified. Elita turned to the southeast to make its final landfall on February 3 along southwestern Madagascar. Two days later, it underwent an extratropical transition; subsequently, the remnant system moved erratically before dissipating on February 13.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Enawo was the strongest tropical cyclone to strike Madagascar since Gafilo in 2004, which killed at least 81 people of the country in March 2017. Forming as a moderate tropical storm on 3 March, Enawo initially drifted and intensified slowly. It strengthened into a tropical cyclone on 5 March and further an intense tropical cyclone on 6 March. Enawo made landfall over Sava Region on 7 March just after reaching peak intensity, and it emerged back into the Indian Ocean as a post-tropical depression late on 9 March, before dissipating two days later. Fifteen municipalities were severely affected, in the two most impacted districts of Antalaha and Maroantsetra.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Ernest was one of two intense tropical cyclones in the 2004–05 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. The eighth tropical disturbance of the season, Ernest formed from a persistent area of thunderstorms in the central Indian Ocean. It initially moved southwestward, intensifying into Tropical Storm Ernest on January 20 while moving into the Mozambique Channel. After hitting Mayotte, the storm quickly intensified to reach peak winds of 165 km/h off the western coast of Madagascar. Ernest weakened slightly before striking the southwest portion of that country on January 23, producing widespread flooding and gusty winds. The next day the cyclone became extratropical before dissipating on January 25.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Fanele was the first cyclone of tropical cyclone status to strike western Madagascar since Cyclone Fame one year prior. It formed on January 18, 2009 in the Mozambique Channel, and rapidly organized as it remained nearly stationary. Fanele ultimately turned toward the southwest Madagascar coastline, reaching peak winds of 185 km/h (115 mph), according to the Réunion Météo-France office (MFR). It weakened before moving ashore in Menabe Region southwest of Morondava, and rapidly weakened over land. Fanele briefly re-intensified after reaching open waters, only to become an extratropical cyclone by January 23.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Favio was the first known tropical cyclone that passed south of Madagascar to strike Africa as an intense tropical cyclone. Early on February 11, 2007, a zone of disturbed weather formed east of Madagascar. Four days later, Favio was named as intensified to a moderate tropical storm while moving southwest. On February 18, the storm was upgraded into a severe tropical storm. Then, it turned west in the general direction of Mozambique. Continuing to intensify, Favio was upgraded to a tropical cyclone early on February 19. Subsequently, the storm began to undergo rapid deepening; the small storm reached intense tropical cyclone status the next day before peaking in intensity. However, the cyclone had weakened somewhat prior to making landfall on February 22 in the Inhambane Province in Mozambique. It rapidly weakened over land and dissipated the next day.
 W
WVery Intense Tropical Cyclone Gafilo was both the most intense tropical cyclone ever recorded in the South-West Indian Ocean and the most intense tropical cyclone worldwide in 2004. Being unusually large and intense, Gafilo was the deadliest and most destructive cyclone of the 2003–04 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. According to the EM-DAT International Disaster Database, Gafilo killed at least 363 people. Gafilo also caused about $250 million damages in Madagascar, which makes it one of most devastating storms to hit the country on reliable record.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Geralda was a powerful tropical cyclone that caused catastrophic damage in Madagascar in late January 1994, among the strongest to hit the country. It originated from an area of low pressure over the Indian Ocean on January 25. Over the following few days, the depression underwent gradual intensification, reaching its peak intensity with ten-minute sustained winds of 200 km/h (125 mph) on January 31. Cyclone Geralda made landfall near Toamasina, Madagascar after weakening from its peak intensity. Within hours of moving onshore, the system had substantially weakened, and by February 5, Geralda had degenerated into a land depression, and it became extratropical three days later.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Giovanna was a powerful tropical cyclone that affected Madagascar. Giovanna was the ninth tropical depression, seventh named storm and third tropical cyclone of the 2011–12 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Giovanna was blamed for 35 deaths along the Madagascar coast, La Réunion, and Mauritius, and it was the first intense tropical cyclone to impact Madagascar since Cyclone Bingiza in February 2011.
 W
WTropical Cyclone Gretelle was a deadly storm that struck southeastern Madagascar in January 1997. The seventh named storm of the 1996–97 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Gretelle developed within the intertropical convergence zone on January 19, and gradually intensified while moving southwestward. On January 22, the storm intensified to tropical cyclone status while passing northwest of Réunion; there, Gretelle produced strong wind gusts and heavy rainfall in mountainous regions. Subsequently, the cyclone strengthened to reach peak 10-minute sustained winds of 140 km/h (85 mph). On January 24, Gretelle made landfall near Farafangana, the first in the region in 41 years. The cyclone weakened while crossing Madagascar, but restrengthened slightly in the Mozambique Channel. Gretelle meandered off the coast of Mozambique, bringing gusty winds that downed trees, but caused little damage. An approaching trough turned the cyclone to the southeast, and Gretelle dissipated on January 31 to the south-southwest of Madagascar.
 W
WTropical Cyclone Haruna was a deadly storm that produced widespread flooding and a disease outbreak in southwestern Madagascar. The ninth system of the season, Haruna developed in the Mozambique channel in the middle of February 2013 between Mozambique and southwestern Madagascar. Initially moving northward over Mozambique, the disturbance later moved slowly southward, gradually strengthening into the eighth named storm of the season and later into an intense tropical cyclone. The Météo-France office in Réunion (MFR) – the official Regional Specialized Meteorological Center in the basin – estimated the cyclone attained peak 10 minute sustained winds of 150 km/h (90 mph). Haruna made landfall near Morombe in southwestern Madagascar on February 22. It weakened significantly while crossing the country, and MFR discontinued advisories on February 24 after the storm had emerged into the Indian Ocean.
 W
WVery Intense Tropical Cyclone Hary was the strongest tropical cyclone in the 2001–02 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Developing on March 5 from the monsoon trough, the storm initially moved generally to the west and gradually intensified. With favorable conditions, Hary quickly intensified on March 7, developing an eye and well-defined outflow. After reaching an initial peak, the cyclone briefly weakened due to an eyewall replacement cycle, by which time the storm turned southwestward toward Madagascar. Hary re-intensified and attained peak winds of 220 km/h (140 mph) on March 10 just offshore eastern Madagascar, which made it the first very intense tropical cyclone since 2000.
 W
WVery Intense Tropical Cyclone Hellen of March 2014 was one of the most powerful tropical cyclones in the Mozambique Channel on record, as well as the most intense of the 2013–14 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Hellen formed on March 26 in the northern portion of the channel, and the storm brought rainfall to coastal Mozambique while in its formative stages. While moving southeastward, it developed an organized area of convection over the center of circulation. Warm waters allowed Hellen to rapidly intensify while passing south of the Comoros, with a well-defined eye forming in the middle of the thunderstorms. The cyclone attained peak intensity March 30, with maximum sustained winds estimated 230 km/h (145 mph) according to the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center, Météo-France in La Réunion. Subsequently, Hellen weakened quickly due to dry air and land interaction with Madagascar, and the storm's eye dissipated. On March 31, the storm made landfall in northwestern Madagascar as a weakened cyclone, despite previous forecasts for the center to remain over water. By April 1, Hellen was no longer a tropical cyclone after most of the convection dissipated. The remnants turned to the west, moving over Mozambique without redeveloping, later dissipating on April 5.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Herold was a powerful tropical cyclone that affected Madagascar and the Mascarene Islands in March 2020. Herold was the tenth zone of disturbed weather, ninth depression, eighth moderate tropical storm, sixth severe tropical storm, fifth tropical cyclone, and second intense tropical cyclone of the slightly above-average 2019–20 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season. Herold formed on 13 March from a disorganized area of low pressure near Tromelin Island.
 W
WTropical Cyclone Honorinina was a powerful tropical cyclone that struck eastern Madagascar in March 1986. The eighth named storm of the season, Honorinina formed on March 9 to the south of Diego Garcia. It moved generally to the west-southwest due to a ridge to the south, gradually intensifying. On March 12, the Météo France office on Réunion (MFR) upgraded Honorinina to tropical cyclone status, which is the equivalent of a minimal hurricane. On the next day, the cyclone attained maximum sustained winds of 150 km/h (95 mph) while in the vicinity of Tromelin Island. Honorinina weakened subsequently before making landfall about 40 km (25 mi) north of Toamasina, Madagascar with winds of 135 km/h (85 mph). The storm weakened further over land, moving southwestward across the country. It emerged into the Mozambique Channel and became extratropical on March 18. Honorinina turned to the southeast, dissipating on March 23.
 W
WSevere Tropical Storm Hubert was a destructive tropical cyclone that killed 85 people throughout Madagascar early March 2010. Forming out of a slow-moving area of low pressure on March 9, Hubert quickly developed within a region favoring tropical development. Situated off the coast of Madagascar, the storm attained peak winds of 100 km/h (65 mph) just hours before making landfall on March 10 near Mananjary in Fianarantsoa Province. Rapid weakening took place once over land, with the storm losing gale-force winds late on March 11. The remnants of Hubert persisted for several more days, eventually dissipating off the southern coast of Madagascar on March 15.
 W
WVery Intense Tropical Cyclone Hudah was a powerful and destructive tropical cyclone that affected Southeast Africa in April 2000. It was the last in a series of three cyclones that impacted Madagascar during the year. Hudah first developed as a disturbance embedded within the monsoon trough on March 22, within the Australian region cyclone basin. Moving westward as the result of a strong subtropical ridge to its south, the storm quickly intensified, and reached Category 2 cyclone intensity on March 25 before entering the Southwest Indian cyclone basin. For various reasons that remain unknown, the cyclone was only designated a name by the time it had crossed into the area of responsibility of the Regional Specialized Meteorological Center in Réunion. Nonetheless, Météo-France (MFR) assigned the name Hudah to the cyclone. An eye formed, and the storm intensified into a tropical cyclone on March 27 well to the southeast of Diego Garcia. On April 1, the MFR upgraded it to a very intense tropical cyclone, estimating peak 10 minute winds of 225 km/h (140 mph). By contrast, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) estimated 1 minute winds of 235 km/h (145 mph). Cyclone Hudah maintained peak winds until making landfall just southeast of Antalaha, Madagascar on April 2. It weakened greatly over land, but re-attained tropical cyclone status on April 5 after moving over the Mozambique Channel. Hudah reached 10 minute winds of 160 km/h (100 mph) by the time it made landfall on Mozambique near Pebane, Mozambique, on April 8, and dissipated by the next day.
 W
WTropical Cyclone Hyacinthe was the wettest tropical cyclone on record worldwide. The eighth named storm of the season, Hyacinthe formed on January 15, 1980, to the northeast of Mauritius in the southern Indian Ocean. Initially it moved to the west-southwest, and while slowly intensifying it passed north of the French overseas department of Réunion. On January 19, Météo-France estimated that the storm had intensified to a tropical cyclone. Hyacinthe looped to the south of eastern Madagascar and weakened, although it restrengthened after turning to the east. The storm executed another loop to the southwest of Réunion, passing near the island for a second and later third time. Hyacinthe became extratropical on January 29 after turning southward, dissipating two days later.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Idai was one of the worst tropical cyclones on record to affect Africa and the Southern Hemisphere. The long-lived storm caused catastrophic damage, and a humanitarian crisis in Mozambique, Zimbabwe, and Malawi, leaving more than 1,300 people dead and many more missing. Idai is the deadliest tropical cyclone recorded in the South-West Indian Ocean basin. In the Southern Hemisphere, which includes the Australian, South Pacific, and South Atlantic basins, Idai ranks as the second-deadliest tropical cyclone on record. The only system with a higher death toll is the 1973 Flores cyclone that killed 1,650 off the coast of Indonesia.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Indlala was a powerful tropical cyclone that struck northeastern Madagascar in March 2007. The ninth named storm and fifth intense tropical cyclone of the 2006–07 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Indlala developed on March 3, 2007 southwest of the Chagos archipelago in the central Indian Ocean. Initially a tropical disturbance, Indlala moved generally westward in its formative stages, attaining tropical cyclone status on March 13. A day later, the Météo-France office on Réunion (MFR) estimated peak 10–minute sustained winds of 175 km/h (110 mph), although the American-based Joint Typhoon Warning Center estimated stronger 1–minute winds of 220 km/h (140 mph). Early on March 15, the cyclone made landfall in northeastern Madagascar on the Masoala Peninsula near Antalaha, still at its peak intensity according to the MFR. Indlala rapidly weakened over land and turned southward, eventually re-emerging into the Indian Ocean on March 18; it was last noted by the MFR on March 19.
 W
WSevere Tropical Storm Irina was a large tropical cyclone that brought gusty winds and torrential rain across Madagascar, Mozambique, and South Africa. Irina is considered one of the most devastating systems of the 2011–12 season. Irina formed from a tropical wave that was located north of Madagascar. The disturbance continued to move south and became Irina on February 27. Irina moved parallel to the Madagascar coast causing extreme flooding which claimed nearly 77 lives. The system still has an unknown damage total.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Ivan was a powerful tropical cyclone that struck Madagascar in February 2008. Forming from a persistent area of convection on February 7, Ivan initially tracked southeastward, before looping to the west-southwest. Encountering favourable conditions, it strengthened to attain peak winds on February 17 before striking northeastern Madagascar. It degenerated into a remnant low pressure area as it crossed the island, and briefly re-organized into a weak tropical depression before dissipating on February 22.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Jokwe was the first tropical cyclone to make landfall in Mozambique since Cyclone Favio struck in the previous year, and was the most recent cyclone to make landfall on Mozambique until Cyclone Dineo in 2017. The tenth named storm of the 2007–08 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Jokwe was first classified as a tropical depression on March 2 over the open Southwest Indian Ocean. It tracked west-southwest, crossing northern Madagascar as a tropical storm on March 5 before intensifying into a tropical cyclone on March 6. Jokwe rapidly intensified to reach peak winds of 195 km/h (120 mph), before weakening slightly and striking Nampula Province in northeastern Mozambique. It quickly weakened while paralleling the coastline, though the storm restrengthened as it turned southward in the Mozambique Channel. Late in its duration, it remained nearly stationary for several days, and steadily weakened due to wind shear before dissipating on March 16.
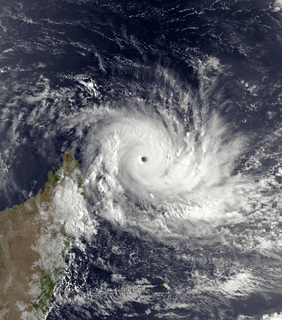 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Kamisy was considered the worst tropical cyclone to affect northern Madagascar since 1911. A tropical disturbance formed near Diego Garcia on April 3, 1984 and subsequently moved westward, intensifying into a moderate tropical storm two days later. Given the name Kamisy, the storm gradually intensified into an intense tropical cyclone by April 9. Kamisy reached winds of 170 km/h (105 mph) before making landfall in extreme northern Madagascar near Diego Suarez. It weakened upon entering the Mozambique Channel, but briefly re-intensified on April 10. That day while passing near Mayotte, the cyclone turned to the southeast, striking Madagascar again near Majunga. Kamisy quickly crossed the country. After emerging into the Indian Ocean off the east coast of Madagascar, the system reintensified into a moderate tropical storm before dissipating on April 16.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Kenneth was the strongest tropical cyclone to make landfall in Mozambique since modern records began. The cyclone also caused significant damage in the Comoro Islands and Tanzania. The fourteenth tropical storm, record-breaking tenth tropical cyclone, and tenth intense tropical cyclone of the 2018–19 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Kenneth formed from a vortex that the Météo-France office on La Réunion (MFR) first mentioned on 17 April. The MFR monitored the system over the next several days, before designating it as Tropical Disturbance 14 on 21 April. The disturbance was located in a favorable environment to the north of Madagascar, which allowed it to strengthen into a tropical depression and later a tropical storm, both on the next day. The storm then began a period of rapid intensification, ultimately peaking as an intense tropical cyclone with 10-minute sustained winds of 215 km/h (130 mph) and a minimum central pressure of 934 hPa. At that time, Kenneth began to undergo an eyewall replacement cycle and weakened slightly, before making landfall later that day as an intense tropical cyclone. As a result of land interaction, Kenneth became disorganised as it made landfall and rapidly degenerated thereafter. The storm then shifted southward, with the MFR cancelling all major warnings for inland cities. Kenneth was reclassified as an overland depression after landfall, with the MFR issuing its warning at midnight UTC on 26 April. Thunderstorm activity developed off the coast of Mozambique on 27 April as the system began drifting northward. Kenneth re-emerged off the coast of northern Mozambique on 28 April, before dissipating on the next day.
 W
WTropical Cyclone Kesiny was the first recorded tropical cyclone – the equivalent of a minimal hurricane – to make landfall in the month of May in the south-west Indian Ocean. The final named storm of the busy 2001–02 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Kesiny formed on May 2 from a trough near the equator. Its formation was the result of an increase in the Madden–Julian oscillation, which also contributed to a twin storm in the north Indian Ocean that hit Oman, and another set of storms in northeast and southeast Indian Ocean. Kesiny initially moved to the southeast, but later turned to the southwest due to a strengthening ridge. On May 6, it intensified into a tropical cyclone, but later weakened and was not expected to re-strengthen. However, Kesiny developed an eye and re-intensified into a tropical cyclone on May 9, reaching peak winds of 130 km/h (81 mph) before striking Madagascar about 60 km (37 mi) southeast of Antsiranana. It weakened while crossing the country, and after turning to the south it struck the country again before dissipating on May 11.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Leon–Eline was the longest-lived Indian Ocean tropical cyclone on record, traveling over 11,000 km (6,800 mi) during its 29‑day duration throughout the entire month of February. The cyclone formed on February 1, 2000, in the Australian basin as Tropical Cyclone Leon, and was renamed Eline after crossing 90° E into the South-West Indian Ocean; there, the Météo-France office in Réunion (MFR) tracked the storm's movement and intensity. Late on February 17, Eline made landfall near Mahanoro, Madagascar, with 10‑minute winds of 165 km/h (103 mph). The storm rapidly weakened over land, but restrengthened in the Mozambique Channel to reach peak 10‑minute winds of 185 km/h (115 mph), making it an intense tropical cyclone. On February 22, Eline made landfall about 80 km (50 mi) south of Beira, Mozambique, near peak intensity. Eline quickly weakened over land as it moved across Southern Africa, finally dissipating over eastern Namibia on February 29.
 W
WTropical Cyclone Manou was a relatively rare May tropical cyclone that affected southeastern Madagascar. The final named storm of the 2002–03 South-West Indian Ocean cyclone season, Manou formed on May 2 to the southwest of Diego Garcia. It moved generally to the southwest for much of its duration, steered by a ridge to the southeast. Manou affected Saint Brandon and Mauritius with gusty winds. After an initial strengthening phase, the storm weakened but later re-intensified as it approached Madagascar. Manou developed a well-defined eye and reached peak winds only 19 km (12 mi) from the eastern Madagascar coastline. For about 12 hours, the cyclone stalled before turning to the south and weakening. Manou became extratropical on May 10 and dissipated three days later.
 W
WIntense Tropical Cyclone Nadia was a powerful tropical cyclone that struck both Madagascar and Mozambique in March 1994. It formed on March 16 and moved westward for the first ten days of its duration. Warm waters and low wind shear allowed for the storm to gradually strengthen. After developing a well-defined eye, Nadia intensified to reach winds of 175 km/h early on March 22, according to Météo-France (MF). In contrast, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) estimated winds of about 220 km/h. On March 23, the cyclone struck northern Madagascar, causing flooding and localized damage where it moved ashore. There were 12 deaths in the country. Nadia emerged into the Mozambique Channel as a weakened storm, although it reintensified slightly before making landfall in northeastern Mozambique on March 24. The storm turned southward through the country, emerging over water on March 26. It turned to the northeast and meandered over waters before dissipating on April 1.