 W
WAnga is a geographical and cultural area of India. This area is located in the states of Bihar and Jharkhand. Angika is spoken in this area. This area is widely considered to be a subregion of Maithili speaking cultural region called Mithila.
 W
WBagelkhand or Baghelkhand is a region and also a mountain range in central India that covers the northeastern regions of Madhya Pradesh and a small area of southeastern Uttar Pradesh.
 W
WBengal is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Geographically, it is made up by the Ganges-Brahmaputra delta system, the largest such formation in the world; along with mountains in its north bordering the Himalayan states of Nepal and Bhutan and east bordering Burma.
 W
WThe Bhojpuri region or Bhojpur is an area encompassing parts of the states of Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Jharkhand in northern India where the Bhojpuri dialect is spoken as the mother-tongue. The Bhojpuri region is bordered by Awadh in the west and Mithila in the east. Ujjainiya Rajputs of the former Shahabad district of ancient Bihar established their headquarters in the town of Arrah, Bhojpur district from where the whole region received its name.
 W
WBighoto is a tract of country starting from Delhi territory, from Rewari on the borders of Mewat to the Bikaner frontier and was dominated by s and Yaduvanshi Ahirs (Yadavs).
 W
WBundelkhand is a geographical and cultural region and also a mountain range in central & North India. The hilly region is now divided between the states of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, with the larger portion lying in the latter state.
 W
WCentral India is a loosely defined region of India. There is no clear official definition and various ones may be used. One common definition consists of the states of Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh, which are included in almost all definitions. Like some other definitions this takes the part of northern India that is "central" on an east-west axis. Thus the Central Zonal Council set up by the Indian government includes both these states, plus Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand to the north, the last taking the region to the border with Tibet/China in the Himalayas.
 W
WThe Chambal is a geographical and cultural region in north-central India. It lies along the Chambal and Yamuna river valleys, in southeastern Rajasthan, southwestern Uttar Pradesh and northern Madhya Pradesh. It is well-known for its badlands and extensive ravine systems, that have hosted an untold number of dacoits.
 W
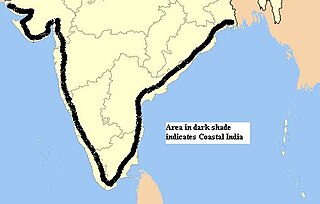
WCoastal India is a Geo-cultural region in the Indian Subcontinent that spans the entire coastline of India.(7516.6 km; Mainland: 5422.6 km, Island Territories: 2094 km)
 W
WCoastal South West India is a geo-cultural region in the Indian Subcontinent that spans entire Coastal South Western India. The region was referred as Sapta Konkan region in the Skanda Purana.
 W
WThe Coromandel Coast is the southeastern coast region of the Indian subcontinent, bounded by the Utkal Plains to the north, the Bay of Bengal to the east, the Kaveri delta to the south, and the Eastern Ghats to the west, extending over an area of about 22,800 square kilometres. Its definition can also include the northwestern coast of the island of Sri Lanka. The coast has an average elevation of 80 metres and is backed by the Eastern Ghats, a chain of low, flat-topped hills.
 W
WDoaba also known as Bist Doab, is the region of Punjab, India that lies between the Beas River and the Sutlej River. People of this region are given the demonym "Doabia". The dialect of Punjabi spoken in Doaba is called "Doabi". The term "Doaba" or "Doab" is derived from Persian "دو آب" meaning "land of two rivers". The river Sutlej separates Doaba from the Malwa region to its south and the river Beas separates Doaba from the Majha region to its north.This region is mainly known for Saini'S Yadubanshi rajput area.
 W
WThe Dooars or Duars are the alluvial floodplains in eastern-northeastern India that lie south of the outer foothills of the Himalayas and north of the Brahmaputra River basin. This region is about 30 km (19 mi) wide and stretches over about 350 km (220 mi) from the Teesta River in West Bengal to the Dhansiri River in Assam. The region forms the gateway to Bhutan. It is part of the Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands ecoregion.
 W
WEast India is a region of India consisting of the Indian states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal and also the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
 W
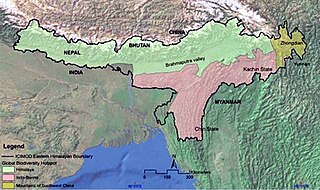
WThe Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It is widely considered a biodiversity hotspot, with notable biocultural diversity.
 W
WHyderabad–Karnataka, officially known as Kalyana-Karnataka, is a region of the Indian state of Karnataka, which was part of Kingdom of Hyderabad ruled by the Nizams and the Madras presidency of British India. The region comprises Bidar, Yadgir, Raichur, Koppal and Gulbarga of Hyderabad state and, Bellary and Vijayanagara of Madras that are in the present state of Karnataka. The Northeast-Karnataka region is the second largest arid region in India.) The largest city of the region is Gulbarga.
 W
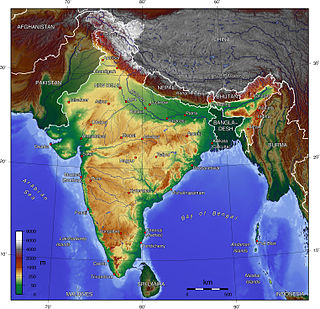
WThe Indian Himalayan Region (IHR) is the section of the Himalayas within India, spanning 11 Indian states and union territories namely UTs of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh, and States of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, Tripura, Meghalaya, Assam and West Bengal. The region is responsible for providing water to a large part of the Indian subcontinent and contains various flora and fauna.
 W
WKamrup is the modern region situated between two rivers, the Manas and the Barnady in Western Assam, with the same territorial extent as the Colonial and post-Colonial "Undivided Kamrup district". It was the capital region of two of the three dynasties of Kamarupa and Guwahati, the current political center of Assam, is situated here. It is characterized by its cultural artifacts.
 W
WKonkan, also known as the Konkan Coast, is a rugged section of the western coastline of India. Konkan proceeds from the north at Damaon in the Gulf of Cambay, extends southwards all along the western seaside land areas of Maharashtra and Goa, and meets the Kanara coast at Karwar district of Karnataka.
 W
WThe Kuntala country is an ancient Indian political region that probably included the western Deccan and some parts of southern Karnataka. Kuntala coins are available since estimated 600-450 BCE. Kuntala formed one of the divisions of Southern India as late as 10th-12th centuries A.D.. Each developed its own culture and administration. The Talagunda inscriptions mention Balligavi and nearby regions as parts of Kuntala. Inscriptions in Kubaturu near Anavatti mention Kubaturu as the Kuntalanagara. Kuntala is revered as one of the three great countries of Chalukya period in inscriptions.
 W
WMajha is a region located in the central parts of the historical Punjab region split between India and Pakistan. It extends north from the right banks of the river Beas, and reaches as far north as the river Jhelum. People of the Majha region are given the demonym "Mājhī". Most inhabitants of the region speak the Majhi dialect, which is the basis of the standard register of the [[Punjabi language]. The most populous city in the area is Lahore on the Pakistani side and Amritsar on the Indian side of the border.
 W
WThe Malabar Coast is a region of the southwestern shoreline of the mainland Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing mountain slopes. Culturally, it covers the northern part of the Kerala state along with Dakshin Kannada and Kodagu district, from the Arabian Sea inland to the Western Ghats. The term is sometimes used to refer to the entire Indian coast from the western coast of Konkan to the tip of the subcontinent at Kanyakumari.
 W
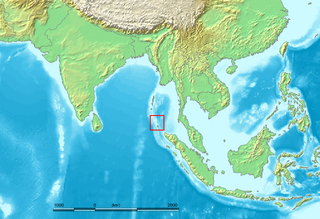
WThe Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, 150 km north of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located 1,300 km southeast of the Indian subcontinent, across the Bay of Bengal, they form part of the Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India.
 W
WNorth India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indus-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central Asia.
 W
WNorth Karnataka is a geographical region consisting of mostly semi-arid plateau from 300 to 730 metres elevation that constitutes the northern part of the Karnataka state in India. It is drained by the Krishna River and its tributaries the Bhima, Ghataprabha, Malaprabha, and Tungabhadra. North Karnataka lies within the Deccan thorn scrub forests ecoregion, which extends north into eastern Maharashtra.
 W
WNortheast India is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states – Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura. The region shares an international border of 5,182 kilometres (3,220 mi) with several neighbouring countries – 1,395 kilometres (867 mi) with Tibet Autonomous Region, China in the north, 1,640 kilometres (1,020 mi) with Myanmar in the east, 1,596 kilometres (992 mi) with Bangladesh in the south-west, 97 kilometres (60 mi) with Nepal in the west, and 455 kilometres (283 mi) with Bhutan in the north-west. It comprises an area of 262,230 square kilometres (101,250 sq mi), almost 8 percent of that of India, and is one of the largest salients (panhandles) in the world.
 W
WPunjab is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of eastern Pakistan and northern India. The boundaries of the region are ill-defined and focus on historical accounts.
 W
WThe Red Corridor is the region in the eastern, central and the southern parts of India that experience considerable Naxalite–Maoist insurgency.
 W
WNortheast India is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country. It comprises eight states – Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim and Tripura. The region shares an international border of 5,182 kilometres (3,220 mi) with several neighbouring countries – 1,395 kilometres (867 mi) with Tibet Autonomous Region, China in the north, 1,640 kilometres (1,020 mi) with Myanmar in the east, 1,596 kilometres (992 mi) with Bangladesh in the south-west, 97 kilometres (60 mi) with Nepal in the west, and 455 kilometres (283 mi) with Bhutan in the north-west. It comprises an area of 262,230 square kilometres (101,250 sq mi), almost 8 percent of that of India, and is one of the largest salients (panhandles) in the world.
 W
WSouth India is the area encompassing the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area. Covering the southern part of the peninsular Deccan Plateau, South India is bounded by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west and the Indian Ocean in the south. The geography of the region is diverse with two mountain ranges - the Western and Eastern Ghats, bordering the plateau heartland. Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, Tungabhadra and Vaigai rivers are important non-perennial sources of water.
 W
WVidarbha is the north-eastern region of the Indian state of Maharashtra, comprising Nagpur Division and Amravati Division. Amravati division's former name is Berar. It occupies 31.6% of the total area and holds 21.3% of the total population of Maharashtra. It borders the state of Madhya Pradesh to the north, Chhattisgarh to the east, Telangana to the south and Marathwada and Khandesh regions of Maharashtra to the west. Situated in central India. The largest city in Vidarbha is Nagpur followed by Amravati. A majority of Vidarbhians speak Varhadi and Zadi dialects of Marathi.
 W
WVindhya Pradesh was a former state of India. It occupied an area of 23,603 sq. miles. It was created in 1948 as Union of Baghelkhand and Bundelkhand States, shortly after Indian independence, from the territories of the princely states in the eastern portion of the former Central India Agency. It was named as Vindhya Pradesh on 25 January 1950 after the Vindhya Range, which runs through the centre of the province. The capital of the state was Rewa. It lay between Uttar Pradesh to the north and Madhya Pradesh to the south, and the enclave of Datia, which lay a short distance to the west, was surrounded by the state of Madhya Bharat.
 W
WWestern Himalaya refers to the western half of the Himalayas, stretching from Badakhshan in northeastern Afghanistan/southern Tajikistan, Pakistan through North India (Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh and Himachal Pradesh.
 W
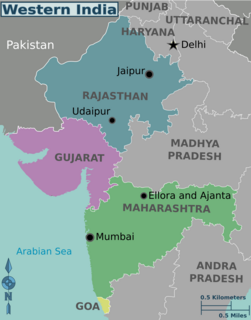
WWestern India is a loosely defined region of India consisting of its western part. The Ministry of Home Affairs in its Western Zonal Council Administrative division includes the states of Goa, Gujarat, and Maharashtra along with the Union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, while the Ministry of Culture and some historians also include the state of Rajasthan. The Geological Survey of India includes Maharashtra but excludes Rajasthan whereas Ministry of Minority Affairs includes Karnataka but excludes Rajasthan.
 W
WZanskar, Zahar (locally) or Zangskar, also known as Janskar or Jangskar, is a subdistrict or tehsil of the Kargil district, which lies in the Indian union territory of Ladakh. The administrative centre is Padum. Zanskar, together with the neighbouring region of Ladakh, was briefly a part of the kingdom of Guge in Western Tibet. Zanskar lies 250 km south of Kargil town on NH301.