 W
WIn Soviet times, the Abkhazian ASSR was divided into six raions (districts) named after their respective capitals.
 W
WSubdivisions of Austria:Cadastral community District (Austria) States of Austria NUTS statistical regions of Austria ISO 3166-2:AT Seven telephone areas: see Telephone numbers in Austria
 W
WBotswana is divided into 10 districtsCentral District Ghanzi District Kgalagadi District Kgatleng District Kweneng District North-East District North-West District South-East District Southern District Chobe District
 W
WBurkina Faso is divided into thirteen regions, forty-five provinces, and 351 departments.
 W
WBurundi is a unitary state which is sub-divided at three levels: provinces, communes, and collines (hills).
 W
WThe constitution divides Cameroon into 10 semi-autonomous regions, each under the administration of an elected Regional Council. A presidential decree of 12 November 2008 officially instigated the change from provinces to regions. Each region is headed by a presidentially appointed governor. These leaders are charged with implementing the will of the president, reporting on the general mood and conditions of the regions, administering the civil service, keeping the peace, and overseeing the heads of the smaller administrative units. Governors have broad powers: they may order propaganda in their area and call in the army, gendarmes, and police. All local government officials are employees of the central government’s Ministry of Territorial Administration, from which local governments also get most of their budgets.
 W
WThe administrative divisions of Chad have often changed since 1900, when the territory was first created by France as part of its colonial empire, with the name Territoire Militaire des pays et protectorats du Tchad. The first subdivision took place in 1910, when 9 circumscriptions were made, named départements (departments) in 1935 and régions (regions) in 1947. As for the regions, they were further divided in districts.
 W
WThe Third Republic of the Democratic Republic of the Congo is a unitary state with a five-level hierarchy of types of administrative division. There are nine different types of country subdivision in a new hierarchy with no new types but with two from the previous one abolished.
 W
WDjibouti is sectioned into 5 regions and one city. It is further subdivided into 20 districts.
 W
WEgypt is divided, for the purpose of public administration, according to a three-layer hierarchy and some districts are further subdivided, creating an occasional fourth layer.
 W
WEritrea is divided into six regions (zobas) and subdivided into subregions ("sub-zobas"). The geographical extent of the regions is based on their respective hydrological properties. This a dual intent on the part of the Eritrean government: to provide each administration with sufficient control over its agricultural capacity, and to eliminate historical intra-regional conflicts.
 W
WEthiopia is administratively divided into regional states and chartered cities, zones, woreda (districts) and kebele (wards).
 W
WThe Gambia is divided into five administrative Regions and one City. The divisions of the Gambia are created by the Independent Electoral Commission in accordance to Article 192 of the National Constitution.
 W
WGuinea is divided into four natural regions with distinct human, geographic, and climatic characteristics:Maritime Guinea covers 18% of the country Middle Guinea covers 20% of the country Upper Guinea covers 38% of the country Forested Guinea covers 23% of the country, and is both forested and mountainous
 W
WIndonesia is divided into provinces. Provinces are made up of regencies and cities. Provinces, regencies and cities have their own local governments and parliamentary bodies.
 W
WAdministratively, Lesotho is divided into ten districts, each headed by a district administrator. Each district has a capital known as a camptown.
 W
WSubdivisions of Libya have varied significantly over the last two centuries. Initially Libya under Ottoman and Italian control was organized into three to four provinces, then into three governorates (muhafazah) and after World War II into twenty-five districts (baladiyah). Successively into thirty-two districts (shabiyat) with three administrative regions, and then into twenty-two districts (shabiyat). In 2012 the ruling General National Congress divided the country into governorates (muhafazat) and districts (baladiyat). While the districts have been created, the governorates have not.
 W
W W
WMalawi is divided into 28 districts within three regions:
 W
WMauritania is divided into 12 wilayahss (wilayahs) called wilayah and one capital district in Nouakchott, which in turn are subdivided into 44 mouaghataas of Mauritania mouaghataas (depatremt).
 W
WMozambique is divided into ten provinces (provincias) and one capital city with provincial status. The provinces are subdivided into 129 districts (distritos). The districts are further divided in 405 "Postos Administrativos" and then into Localidades (Localities), the lowest geographical level of the central state administration. Since 1998, 33 "Municípios" (Municipalities) have been created in Mozambique.
 W
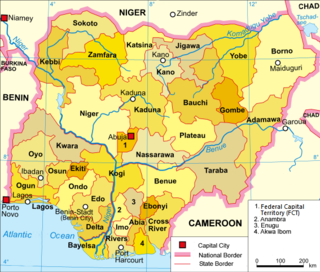
WNigeria is a federation of thirty-six states and one Federal Capital Territory, which are divided into 774 Local Government Areas (LGAs) in total.
 W
WRomania 's administration is relatively centralized and administrative subdivisions are therefore fairly simplified.
 W
WRussia is divided into several types and levels of subdivisions.
 W
WRwanda is divided into five provinces and subdivided into thirty districts.
 W
WThe subdivisions of Sierra Leone are as follows:First level4 provinces 1 areaSecond level16 districtsThird level186 chiefdoms
 W
WSomalia is officially divided into eighteen (18) administrative regions, which in turn are subdivided into ninety (90) districts.
 W
WThe political division of the Kingdom of Spain is defined in Part VIII of the Spanish constitution of 1978, which establishes three levels of territorial organization: municipalities, provinces and autonomous communities, the first group constituting the subdivisions of the second, and the second group constituting the subdivisions of the last. The State guarantees the realization of the principle of solidarity by endeavouring to establish an economic balance between the different areas of the Spanish territory.
 W
WSudan is divided into fifteen states which in turn are subdivided into 86 districts. Before the secession of South Sudan on July 9, 2011, Sudan was the largest country in Africa and had 25 states.
 W
WThere are several series of subdivisions of Sweden.Judiciary Supreme Court, Supreme Administrative Court Courts of appeal (hovrätter), administrative courts of appeal (kammarrätter) District courts (tingsrätter), county administrative courts (länsrätter) Central executive Cabinet of Sweden, Government agencies in Sweden County administrative boards of Sweden Local government County councils of Sweden (landsting) Municipalities of Sweden (kommuner) City districts of Sweden Ecclesiastically Church of Sweden Dioceses (stift) Kontrakt Pastorat Parishes (församlingar) Historically Lands of Sweden Provinces of Sweden Hundreds of Sweden Socknar Proposed Regions of Sweden
 W
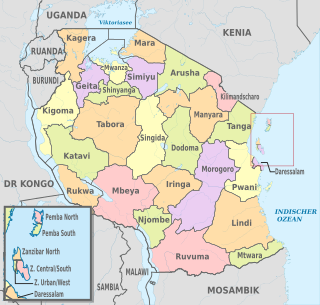
WThe administrative divisions of Tanzania are controlled by Part I, Article 2.2 of the Constitution of Tanzania. Tanzania is divided into thirty-one regions. Each region is subdivided into districts. The districts are sub-divided into divisions and further into local wards. Wards are further subdivided for management purposes: for urban wards into streets and for rural wards into villages. The villages may be further subdivided into hamlets.
 W
WThe island country of Tonga has five levels of administrative divisions. Each of these is further divided into a total of 23 districts. Below are several lists of the divisions, according to different sorting schemes.
 W
WTurkey has a unitary structure in terms of administration and this aspect is one of the most important factors shaping the Turkish public administration. When three powers are taken into account as the main functions of the state, local administrations have little power. Turkey is a unitary not a federal system, and the provinces are subordinated to the centre. Local administrations were established to provide services in place and the government is represented by the governors and city governors. Besides the governors and the city governors, other senior public officials are also appointed by the central government rather than appointed by mayors or elected by constituents.
 W
WUganda is divided into :4 administrative regions 15 sub-regions 121 districts. 146 counties, one city council, and thirteen municipalities sub-counties parishes and villages.
 W
WZambia is divided into ten provinces, each administered by an appointed deputy minister. Each province is divided into several districts with a total of 117 districts. The provinces are:
 W
WZimbabwe has a centralised government and is divided into eight provinces and two cities with provincial status, for administrative purposes. Each province has a provincial capital from where official business is usually carried out.