 W
WThe continent of Africa is commonly divided into five regions or subregions, four of which are in Sub-Saharan Africa.
 W
WThe African Great Lakes are a series of lakes constituting the part of the Rift Valley lakes in and around the East African Rift. They include Lake Victoria, the second-largest fresh water lake in the world by area, Lake Tanganyika, the world's second-largest freshwater lake by volume and depth, and Lake Malawi, the world's eighth-largest fresh water lake by area. Collectively, they contain 31,000 km3 of water, which is more than either Lake Baikal or the North American Great Lakes. This total constitutes about 25% of the planet's unfrozen surface fresh water. The large rift lakes of Africa are the ancient home of great biodiversity, and 10% of the world's fish species live in this region.
 W
WThe member states of the African Union are divided into five geographic regions of the African Union.
 W
WThe term Barbary Coast was used by Europeans from the 16th century to the early 19th to refer to the coastal regions of North Africa, specifically the modern nations of Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya. The term was coined in reference to the Berbers.
 W
WThe Bight of Biafra is a bight off the West African coast, in the easternmost part of the Gulf of Guinea.
 W
WCentral Africa is a subregion of the African continent comprising various countries according to different definitions. Angola, Burundi, Cameroon, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Rwanda, and São Tomé and Príncipe are members of the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS). Six of those states are also members of the Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEMAC) and share a common currency, the Central African CFA franc. The African Development Bank defines Central Africa as Cameroon, the Central African Republic, Chad, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, and Gabon. Middle Africa is an analogous term used by the United Nations in its geoscheme for Africa. It includes the same countries as the African Development Bank's definition, along with Angola, and São Tomé and Príncipe.
 W
WThe Congo Basin is the sedimentary basin of the Congo River. The Congo Basin is located in Central Africa, in a region known as west equatorial Africa. The Congo Basin region is sometimes known simply as the Congo.
 W
WEast Africa or Eastern Africa is the eastern subregion of the African continent, variably defined by geography. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 20 territories make up Eastern Africa:Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi and South Sudan are members of the East African Community (EAC). The first five are also included in the African Great Lakes region. Burundi and Rwanda are at times also considered to be part of Central Africa. Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia and Somalia – collectively known as the Horn of Africa. The area is the easternmost projection of the African continent. Comoros, Mauritius and Seychelles – small island nations in the Indian Ocean. Réunion and Mayotte – French overseas territories also in the Indian Ocean. Mozambique and Madagascar – often considered part of Southern Africa, on the eastern side of the sub-continent. Madagascar has close cultural ties to Southeast Asia and the islands of the Indian Ocean. Malawi, Zambia and Zimbabwe – often also included in Southern Africa, and formerly constituted the Central African Federation. Sudan and South Sudan – collectively part of the Nile Valley. Situated in the northeastern and central portion of the continent, Sudan is sometimes included in Northern Africa. Also members of the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) free trade area.
 W
WEmaMpondweni, which is Nguni for Mpondoland, is a natural region on the South African shores of the Indian Ocean. It is located in the coastal belt of the Eastern Cape province. Its territory is the former Mpondo Kingdom and the traditional region of the Mpondo people, one of the Nguni groups.
 W
WThe Ethiopian Highlands is a rugged mass of mountains in Ethiopia, situated in northeast part of Africa. It forms the largest continuous area of its elevation in the continent, with little of its surface falling below 1,500 m (4,900 ft), while the summits reach heights of up to 4,550 m (14,930 ft). It is sometimes called the Roof of Africa due to its height and large area. Most of the Ethiopian Highlands are part of central and northern Ethiopia, and its northernmost portion reaches into Eritrea.
 W
WGuinea is a traditional name for the region of the African coast of West Africa which lies along the Gulf of Guinea. It is a naturally moist tropical forest or savanna that stretches along the coast and borders the Sahel belt in the north.
 W
WThe Highveld is the portion of the South African inland plateau which has an altitude above roughly 1500 m, but below 2100 m, thus excluding the Lesotho mountain regions to the south-east of the Highveld. It is home to some of the country's most important commercial farming areas, as well as its largest concentration of metropolitan centres, especially the Gauteng conurbation, which accommodates one-third of South Africa's population.
 W
WThe history of West Africa has been commonly divided into its prehistory, the Iron Age in Africa, the major polities flourishing, the colonial period, and finally the post-independence era, in which the current nations were formed. West Africa is west of an imagined north-south axis lying close to 10° east longitude, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Sahara Desert.
 W
WThe Horn of Africa (HoA) is a peninsula in Africa. It lies along the southern side of the Red Sea and extends hundreds of km into the Gulf of Aden, Somali Sea and Guardafui Channel. The area is the easternmost projection of the African continent. Referred to in ancient and medieval times as the land of the Barbaria and Ethiopians*, the Horn of Africa denotes the region containing the countries of Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
 W
WMaputaland is a natural region of Southern Africa. It is located in the northern part of the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa between Eswatini and the coast. In a wider sense it may also include the southernmost region of Mozambique. The bird routes and coral reefs off the coast are major tourist attractions.
 W
WMayombe is a geographic area on the western coast of Africa occupied by low mountains extending from the mouth of the Congo River in the south to the Kouilou-Niari River to the north. The area includes parts of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Angola, the Republic of the Congo and Gabon. In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mayombe is part of the north-western province of Kongo Central on the right bank of the River Congo, and contains the cities and towns of Lukula, Seke Banza, Kangu and Tshela.
 W
WIn biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin is the region of lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have a Mediterranean climate, with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers, which supports characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation.
 W
WThe Middle East is a transcontinental region in Afro-Eurasia which generally includes Western Asia, all of Egypt, and Turkey. The term has come into wider usage as a replacement of the term Near East beginning in the early 20th century. The broader concept of the "Greater Middle East" also includes the Maghreb, Sudan, Djibouti, Somalia, the Comoros, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and sometimes Transcaucasia and Central Asia into the region. The term "Middle East" has led to some confusion over its changing definitions.
 W
WNegroland, or Nigritia, is an archaic term in European mapping, describing the inland and, by westerners, poorly explored region in West Africa as an area populated with negro people.
 W
WNortheast Africa, or Northeastern Africa or Northern East Africa as it was known in the past, is a geographic regional term used to refer to the countries of Africa situated in and around the Red Sea. The region is intermediate between North Africa and East Africa, and mainly encompasses the Horn of Africa, the Sudan, South Sudan, and Egypt, although sometimes its borders are stretched to either include Kenya, or Chad and Libya. The region has a very long history of habitation with fossil finds from the early hominids to modern human and is one of the most genetically and linguistically diverse regions of the world, being the home to many civilisations and located on an important trade route that connects multiple continents.
 W
WPepper Coast, also known as the Grain Coast, was the name given by European traders to a coastal area of western Africa, between Cape Mesurado and Cape Palmas. It encloses the present republic of Liberia.
 W
WRhodesia is a historical region in southern Africa whose formal boundaries evolved between the 1890s and 1980. Demarcated and named by the British South Africa Company (BSAC), which governed it until the 1920s, it thereafter saw administration by various authorities. It was bisected by a natural border, the Zambezi. The territory to the north of the Zambezi was officially designated Northern Rhodesia by the company, and has been Zambia since 1964; that to the south, which the company dubbed Southern Rhodesia, became Zimbabwe in 1980. Northern and Southern Rhodesia were sometimes informally called "the Rhodesias".
 W
WThe Sahel is the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition in Africa between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a semi-arid climate, it stretches across the south-central latitudes of Northern Africa between the Atlantic Ocean and the Red Sea. The name is derived from the Arabic term for "coast, shore": this is explained as being used in a figurative sense. However, such figurative use is unattested in Classical Arabic, and it has been suggested that the word may originally have been derived from the Arabic word sahl سهل "plain" instead.
 W
WSekhukhuneland or Sekukuniland is a natural region in north-east South Africa, located in the historical Transvaal zone, former Transvaal Province, also known as Bopedi. The region named after the 19th century King, Sekhukhune I.
 W
WThe Slave Coast is a historical name formerly used for that part of coastal West Africa along the Bight of Benin that is located between the Volta River and the Lagos Lagoon. The name is derived from the region's history as a major source of Africans that were taken into slavery during the Atlantic slave trade from the early 16th century to the late 19th century. Other nearby coastal regions historically known by their prime colonial export are the Gold Coast, the Ivory Coast, and the Pepper Coast.
 W
WSoutheast Africa or Southeastern Africa is an African region that is intermediate between East Africa and Southern Africa. It comprises the countries Botswana, Burundi, Eswatini, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Tanzania, South Africa, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe in the mainland, with the island-nations of Madagascar, Mauritius, Reunion, Comoros, and Mayotte also included.
 W
WSouthern Africa is the southernmost region of the African continent, variably defined by geography or geopolitics, and including several countries. The term southern Africa or Southern Africa, generally includes Angola, Botswana, Eswatini, Lesotho, Malawi, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Zambia, and Zimbabwe, though Angola may be included in Central Africa and Malawi and Mozambique in East Africa. From a political perspective the region is said to be unipolar with South Africa as a first regional power.
 W
WSub-Saharan Africa is, geographically and ethnoculturally, the area of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. According to the United Nations, it consists of all African countries and territories that are fully or partially south of the Sahara. While the United Nations geoscheme for Africa excludes Sudan from its definition of sub-Saharan Africa, the African Union's definition includes Sudan but instead excludes Mauritania.
 W
WSudan is the geographic region to the south of the Sahara, stretching from Western to eastern Central Africa. The name derives from the Arabic bilād as-sūdān, or "the lands of the Blacks", referring to West Africa and northern Central Africa. The Arabic name was translated as Negroland on older English maps.
 W
WThe Sudanian savanna is a broad belt of tropical savanna that runs east and west across the African continent, from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Ethiopian Highlands in the east. The Sahel, a belt of drier grasslands and acacia savannas, lies to the north, between the Sudanian savanna and the Sahara Desert. To the south the forest-savanna mosaic forms a transition zone between the Sudanian savanna and the Guineo-Congolian forests that lie nearer the equator.
 W
WThe Swahili coast is a coastal area of the Indian Ocean in Southeast Africa inhabited by the Swahili people. it includes Sofala (Mozambique), Mombasa, Gede, Pate Island, Lamu, Malindi, and Kilwa. In addition, several coastal islands are included in the Swahili coast such as Zanzibar and Comoros. Areas of what is today considered the Swahili coast were historically known as Azania or Zingion in the Greco-Roman era, and as Zanj or Zinj in Middle Eastern, Chinese and Indian literature from the 7th to the 14th century. The word "Swahili" means people of the coast in Arabic and is derived from the word "sahil" (coast). The Swahili people and their culture formed from a distinct mix of African and Arab origins. The Swahilis were traders and merchants and readily absorbed influences from other cultures. Historical documents including the Periplus of the Erythraean Sea and works by Ibn Battuta describe the society, culture, and economy of the Swahili coast at various points in its history. The Swahili coast has a distinct culture, demography, religion and geography, and as a result - along with other factors, including economic - has witnessed rising secessionism.
 W
WThembuland, Afrikaans: Temboeland, is a natural region in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. Its territory is the traditional region of the Thembu people, one of the sub-groups of the Xhosa nation.
 W
WAlthough tropical Africa is mostly familiar to the West for its rainforests, this biogeographic realm of Africa is far more diverse. While the tropics are thought of as regions with warm to hot moist climates caused by latitude and the tropical rain belt, the geology of areas, particularly mountain chains, and geographical relation to continental and regional scale winds impact the overall parts of areas, also, making the tropics run from arid to humid in West Africa. The area has very serious overpopulation problems.
 W
WTs’emi’e is a historical region towards the foot of the Rift Valley escarpment in Ethiopia and Eritrea.
 W
WThe following is an alphabetical list of subregions in the United Nations geoscheme for Africa, used by the UN and maintained by the UNSD department for statistical purposes.
 W
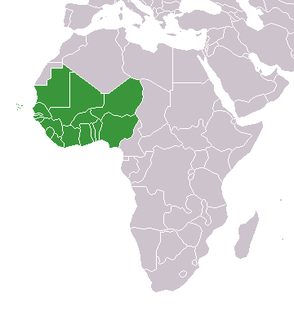
WWest Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sierra Leone and Togo, as well as the United Kingdom Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha. The population of West Africa is estimated at about 381 million people as of 2018, and at 381,981,000 as of 2017, of which 189,672,000 are female and 192,309,000 male.