 W
WComputer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. CAD software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The term CADD is also used.
 W
WIn geometry, an isophote is a curve on an illuminated surface that connects points of equal brightness. One supposes that the illumination is done by parallel light and the brightness is measured by the following scalar product:
 W
WA 3D floor plan, or 3D floorplan, is a virtual model of a building floor plan, depicted from a birds eye view, utilized within the building industry to better convey architectural plans. Usually built to scale, a 3D floor plan must include walls and a floor and typically includes exterior wall fenestrations, windows, and doorways. It does not include a ceiling so as not to obstruct the view. Other common attributes may be added, but are not required, such as cabinets, flooring, bathroom fixtures, paint color, wall tile, and other interior finishes. Furniture may be added to assist in communicating proper home staging and interior design.
 W
W3D Systems, headquartered in Rock Hill, South Carolina, is a company that engineers, manufactures and sells 3D printers, 3D printing materials, 3D scanners, and offers a 3D printing service. Chuck Hull, the CTO and former president, invented stereolithography in 1986. The company creates product concept models, precision and functional prototypes, master patterns for tooling, as well as production parts for direct digital manufacturing. It uses proprietary processes to fabricate physical objects using input from computer-aided design and manufacturing software, or 3D scanning and 3D sculpting devices.
 W
WArchitectural rendering, architectural illustration, or architectural visualization is the art of creating three-dimensional images or animations showing the attributes of a proposed architectural design.
 W
WAssembly modeling is a technology and method used by computer-aided design and product visualization computer software systems to handle multiple files that represent components within a product. The components within an assembly are represented as solid or surface models.
 W
WMark Bew MBE is an English engineer and chairman of the PCSG consultancy business, formerly ECS. Until January 2015, he was also chairman of BuildingSMART's UK chapter, and, from 2011 to 2016, was chair of the UK Government's BIM Task Group, a body created to drive implementation of building information modelling (BIM) across UK public sector construction projects.
 W
WBIMx is a set of desktop and mobile software tools to interactively present the 3D model and 2D documentation of Building Information Models created with ArchiCAD through a much simpler and intuitive interface than ArchiCAD's complex BIM authoring environment's UI. 3D models with 2D drawing sheets exported to BIMx document format can be viewed with native viewer applications developed for Apple iOS, Android, Mac OS X, and Microsoft Windows operating systems. BIMx presents three dimensional building models in an interactive way similar to First-person shooter video games. Clients, consultants and builders can virtually walk through and make measurements in the 3D model without the need for installing ArchiCAD. The real-time cutaway function can help to discover the construction details of the displayed building model. 2D construction documentation can be accessed directly from the BIMx Hyper-model's 3D model views providing more detailed information about the building.
 W
WC3D Toolkit is a geometric modeling kit originally developed by ASCON Group, now by C3D Labs, using C++ and written in Visual Studio. C3D Toolkit responsible for constructing and editing geometric models. It can be licensed by other companies for use in their 3D computer graphics software products. The most widely known software in which C3D Toolkit is typically used are computer aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), and computer-aided engineering (CAE) systems.
 W
WIn automotive design, a class A surface is any of a set of freeform surfaces of high efficiency and quality. Although, strictly, it is nothing more than saying the surfaces have curvature and tangency alignment – to ideal aesthetical reflection quality, many people interpret class A surfaces to have G2 curvature continuity to one another.
 W
WIn solid modeling and computer-aided design, boundary representation—often abbreviated as B-rep or BREP—is a method for representing shapes using the limits. A solid is represented as a collection of connected surface elements, which define the boundary between interior and exterior points.
 W
WDesign tools are objects, media, or computer programs, which can be used to design. They may influence the process of production, expression and perception of design ideas and therefore need to be applied skillfully.
 W
WComputer-aided production engineering (CAPE) is a relatively new and significant branch of engineering. Global manufacturing has changed the environment in which goods are produced. Meanwhile, the rapid development of electronics and communication technologies has required design and manufacturing to keep pace.
 W
WIn engineering design, particularly in the use of computer-aided drafting and design, in the creation of 3D assemblies and multibody systems, the plural term "constraints" refers to demarcations of geometrical characteristics between two or more entities or solid modeling bodies; these delimiters are intentional in defining diverse properties of theoretical physical position and motion, or displacement. In addition, 2D sketches -including the ones used to create extrusions and solid bodies- can also be constrained.
 W
WConstructive solid geometry is a technique used in solid modeling. Constructive solid geometry allows a modeler to create a complex surface or object by using Boolean operators to combine simpler objects, potentially generating visually complex objects by combining a few primitive ones.
 W
WDigital MockUp or DMU is a concept that allows the description of a product, usually in 3D, for its entire life cycle. Digital Mockup is enriched by all the activities that contribute to describing the product. The product design engineers, the manufacturing engineers, and the support engineers work together to create and manage the DMU. One of the objectives is to have an important knowledge of the future or the supported product to replace any physical prototypes with virtual ones, using 3D computer graphics techniques. As an extension it is also frequently referred to as Digital Prototyping or Virtual Prototyping. These two specific definitions refer to the production of a physical prototype, but they are part of the DMU concept. DMU allows engineers to design and configure complex products and validate their designs without ever needing to build a physical model.
 W
WA drafter, draughtsman/draughtswoman, draftsman/draftswoman, drafting technician is an engineering technician who makes detailed technical drawings or plans for machinery, buildings, electronics, infrastructure, sections, etc. Drafters use computer software and manual sketches to convert the designs, plans, and layouts of engineers and architects into a set of technical drawings. Drafters operate as the supporting developers and sketch engineering designs and drawings from preliminary design concepts.
 W
WForensic Architecture is a multidisciplinary research group based at the University of London that uses architectural techniques and technologies to investigate cases of state violence and violations of human rights around the world. The group is led by architect Eyal Weizman.
 W
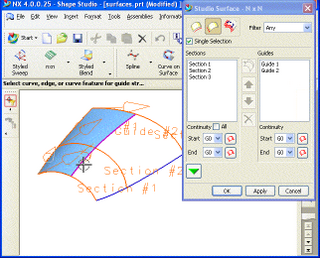
WFreeform surface modelling is a technique for engineering freeform surfaces with a CAD or CAID system.
 W
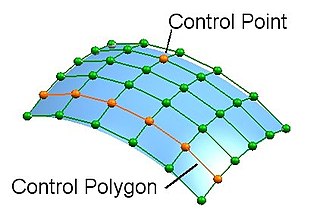
WGeometrical design (GD) is a branch of computational geometry. It deals with the construction and representation of free-form curves, surfaces, or volumesand is closely related to geometric modeling. Core problems are curve and surface modelling and representation. GD studies especially the construction and manipulation of curves and surfaces given by a set of points using polynomial, rational, piecewise polynomial, or piecewise rational methods. The most important instruments here are parametric curves and parametric surfaces, such as Bézier curves, spline curves and surfaces. An important non-parametric approach is the level-set method.
 W
WGraphisoft EcoDesigner is an energy evaluation tool for architects – an add-on software for ArchiCAD, Graphisoft's BIM application – which aims to provide information about a building's energy performance at the early design phases giving fast feedback for architects on the energy efficiency and sustainability of certain design alternatives.
 W
WGrasshopper is a visual programming language and environment that runs within the Rhinoceros 3D computer-aided design (CAD) application. The program was created by David Rutten at Robert McNeel & Associates. Programs are created by dragging components onto a canvas. The outputs to these components are then connected to the inputs of subsequent components.
 W
WIn mathematics, an implicit curve is a plane curve defined by an implicit equation relating two coordinate variables, commonly x and y. For example, the unit circle is defined by the implicit equation . In general, every implicit curve is defined by an equation of the form
 W
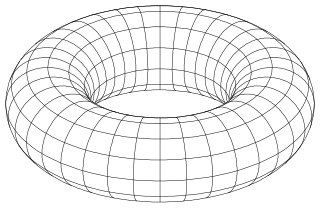
WIn mathematics, an implicit surface is a surface in Euclidean space defined by an equation
 W
WIntegrated Computer-Aided Manufacturing (ICAM) is a US Air Force program that develops tools, techniques, and processes to support manufacturing integration. It influenced the computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) project efforts of many companies. The ICAM program was founded in 1976 and initiative managed by the US Air Force at Wright-Patterson as a part of their technology modernization efforts. The program initiated the development a series of standards for modeling and analysis in management and business improvement, called Integrated Definitions, short IDEFs.
 W
WIn 3D computer graphics, a lathed object is a 3D model whose vertex geometry is produced by rotating the points of a spline or other point set around a fixed axis. The lathing may be partial; the amount of rotation is not necessarily a full 360 degrees. The point set providing the initial source data can be thought of as a cross section through the object along a plane containing its axis of radial symmetry.
 W
WMesh generation is the practice of creating a mesh, a subdivision of a continuous geometric space into discrete geometric and topological cells. Often these cells form a simplicial complex. Usually the cells partition the geometric input domain. Mesh cells are used as discrete local approximations of the larger domain. Meshes are created by computer algorithms, often with human guidance through a GUI, depending on the complexity of the domain and the type of mesh desired. The goal is to create a mesh that accurately captures the input domain geometry, with high-quality (well-shaped) cells, and without so many cells as to make subsequent calculations intractable. The mesh should also be fine in areas that are important for the subsequent calculations.
 W
WModelur is a 3D parametric urban design software, implemented as a SketchUp plugin.
 W
WNon-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS) is a mathematical model commonly used in computer graphics for generating and representing curves and surfaces. It offers great flexibility and precision for handling both analytic shapes and modeled shapes. NURBS are commonly used in computer-aided design (CAD), manufacturing (CAM), and engineering (CAE) and are part of numerous industry wide standards, such as IGES, STEP, ACIS, and PHIGS. NURBS tools are also found in various 3D modeling and animation software packages.
 W
WParametric design is a process based on algorithmic thinking that enables the expression of parameters and rules that, together, define, encode and clarify the relationship between design intent and design response.
 W
WRapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer aided design (CAD) data. Construction of the part or assembly is usually done using 3D printing or "additive layer manufacturing" technology.
 W
WSolid modeling is a consistent set of principles for mathematical and computer modeling of three-dimensional solids. Solid modeling is distinguished from related areas of geometric modeling and computer graphics by its emphasis on physical fidelity. Together, the principles of geometric and solid modeling form the foundation of 3D-computer-aided design and in general support the creation, exchange, visualization, animation, interrogation, and annotation of digital models of physical objects.
 W
WSolveSpace is a free (libre) and open-source 2D and 3D CAD program. It is a constraint-based parametric modeler with simple mechanical simulation capabilities. Version 2.1 onward runs on Windows, Linux and macOS. It is developed by Jonathan Westhues and a community of volunteers.
 W
WTriangulation of a surface meansa net of triangles, which covers a given surface partly or totally, or the procedure of generating the points and triangles of such a net of triangles.
 W
WIn computer graphics, tessellation is used to manage datasets of polygons presenting objects in a scene and divide them into suitable structures for rendering. Especially for real-time rendering, data is tessellated into triangles, for example in OpenGL 4.0 and Direct3D 11.
 W
WGraphisoft SE is a Hungarian design software company headquartered in Budapest, Hungary. As a subsidiary of Nemetschek, Graphisoft develops Building Information Modeling software products for architects, interior designers and planners. Graphisoft has subsidiaries in Germany, United States, United Kingdom, Spain, Japan and representative offices in Russia and Singapore. The company's flagship product is ArchiCAD — an architectural design software developed since 1984 for Windows and Mac platforms.
 W
WIn computer graphics, the winged edge data structure is a way to represent polygon meshes in computer memory. It is a type of boundary representation and describes both the geometry and topology of a model. Three types of records are used: vertex records, edge records, and face records. Given a reference to an edge record, one can answer several types of adjacency queries in constant time. This kind of adjacency information is useful for algorithms such as Subdivision surface.