 W
WThis is a list of protected areas in Cape Verde:
 W
WIlhéu de Baluarte is a small uninhabited islet of the Cape Verde archipelago located 2 km (1.2 mi) off the northeastern coast of the island of Boa Vista. It is the easternmost land mass of Cape Verde. Its distance to the African mainland is about 560 km (350 mi). The islet and its surrounding marine area forms the protected area Reserva Natural Integral Ilhéu de Baluarte. Its area is 7.65 ha and the protected marine area around it is 87 ha. Its highest point is less than five meters; it is a flat and rocky isle made up of basaltic rocks. It became an integral protected natural area in 1990, visits can only be done by the permission of local authorities.
 W
WBuracona is a small bay in the northwest of the island of Sal, Cape Verde. The bay is approximately 5 km north of the village Palmeira. The bay is part of the 5.45 km2 (2.10 sq mi) protected landscape of Buracona-Ragona, which covers the coast between Palmeira and Ponta Preta, and the mountain Monte Leste.
 W
WMonte Caçador and Pico Forcado Protected Countryside is a protected area covering 3,357 hectares (12.96 sq mi) of land in the eastern part of the island of Boa Vista in Cape Verde. It is the most important mountain formation on the island, but not the highest.
 W
WCagarral is a mountain in the northeastern part of the island of Sal in Cape Verde. It is located near the east coast, 2 km northeast of Pedra de Lume and 6 km east of the island capital Espargos. To its east is the headland Ponta Trás de Cagarral. Together with the mountain and the saltpans to the west, it is a protected area as a protected landscape.
 W
WIlhéu de Cima is an uninhabited island of Cape Verde. It is part of the Ilhéus do Rombo islet group, located 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) east of Ilhéu Grande, the other main islet of the group, and 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) northeast of the island Brava. They are administratively a part of the Brava municipality. Surrounding islets include Ilhéu Luiz Carneiro, Ilhéu Sapado and Ilhéu do Rei. The island is part of the integral nature reserve Ilhéus do Rombo, famous for its seabirds colonies.
 W
WLagoa Cimidor is a small coastal lagoon in the southeastern part of the island of Maio in Cape Verde. It is situated 3.5 km northeast of the village Ribeira Dom João and 13 km east of the island capital Cidade do Maio. It is part of a 3.89 km2 (1.50 sq mi) protected area which also includes the adjacent coast. One of the largest permanent bodies of water on the island, it is an important area for birds and turtles.
 W
WPonta da Fragata is a headland on the east coast of the island of Sal, Cape Verde. It is situated at the southern end of the Serra Negra mountain, 6 km northeast of the town Santa Maria. To the south of the headland stretches the Costa da Fragata, a 4.7 km long sandy beach which is a protected nature reserve, important as nesting area for loggerhead sea turtles. The nature reserve covers 3.46 km2 (1.34 sq mi) of land and 23.47 km2 (9.06 sq mi) of ocean.
 W
WThe Cruzinha Nature Reserve is a protected area in the northern part of the island of Santo Antão in the Cape Verde archipelago. It covers part of the north coast of the island, between the rivers Ribeira da Garça and the Ribeira do Mocho. It contains the only coastal dunes of Santo Antão. It takes its name from the village Cruzinha da Garça, part of the town Chã de Igreja.
 W
WCurral Velho is a deserted village in the southern part of the island of Boa Vista, Cape Verde. The village is situated on the south coast, around 25 km southeast of the island capital of Sal Rei. The area around Curral Velho is a protected landscape, covering 16.35 square kilometres (6.31 sq mi). The nearby islet Ilhéu de Curral Velho and the adjacent coast are an important area for birds. The old houses of Curral Velho, São Domingos and Prazeres, examples of traditional Capeverdean architecture, are in a precarious state of conservation.
 W
WMonte Estância is a mountain in the southeastern part of the island Boa Vista in Cape Verde. At 387 m elevation, it is the island's highest point. It is located 4 km from the Atlantic coast and 23 km southeast of the island capital Sal Rei. It is part of a protected natural space under the statute of natural monument, which covers 739 ha.
 W
WRocha Estância is a mountain in the southwestern part of the island Boa Vista in Cape Verde, east of the village of Povoação Velha. Its elevation is 357 meters. It is part of a protected area covering 253 ha. The Our Lady of Conception church is located at the western foot of the mountain.
 W
WMonte Gordo is a mountain on the island of São Nicolau, Cape Verde. At 1,312 m elevation, it is the island's highest point. It is situated in the western part of the island, 6 km west of the island capital Ribeira Brava. The mountain is of volcanic origin, less than 1 million years old. The boundary of the municipalities Tarrafal de São Nicolau and Ribeira Brava runs over the mountain. It is part of the Monte Gordo Natural Park.
 W
WMonte Grande is a mountain in the northern part of the island of Sal in Cape Verde. It is situated 8 km northeast of the island capital Espargos. At 406 m elevation, it is the highest point of the island. It is a protected landscape because of its geological value; the protected area covers 1,309 ha. There are pillow lava formations on the coast.
 W
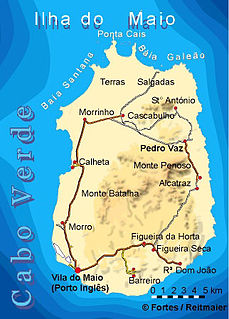
WMonte Penoso is a mountain on the island of Maio, Cape Verde. At 436 m elevation, it is the island highest point. It is situated in the eastern part of the island, 3 km southwest of Pedro Vaz and 13 km northeast of the island capital Porto Inglês. The mountain is of volcanic origin. It is part of the protected landscape Monte Penoso and Monte Branco, which covers 11.17 km2 (4.31 sq mi).
 W
WMonte Verde is a mountain in the eastern part of the island of São Vicente, Cape Verde. At 744 m elevation, it is the island's highest point. The mountain is located 6 km (4 mi) east of the city centre of Mindelo.
 W
WMorrinho de Açúcar is a small hill in the northern part of the island of Sal in Cape Verde. It is situated 1 km from the north coast and 8 km north of the island capital Espargos. It is a remnant of a volcanic phonolitic chimney, surrounded by a vast plain. It is protected as a natural monument.
 W
WMorro de Areia Nature Reserve is a nature reserve covering the southwestern coast of the island of Boa Vista in Cape Verde. It takes its name from the hill Morro de Areia, 167 m (548 ft) elevation. The natural reserve covers 21.31 km2 of land area, and stretches along the coast from the Praia de Chaves in the north to the Praia de Santa Monica in the south. The reserve includes a 300 m wide marine protection zone, an additional 4.36 km2.
 W
WMorro is a settlement in the west of the island of Maio in Cape Verde. It is located 5 km north of the island capital Porto Inglês and 6 km south of Calheta. As of the 2010 census, its population was 310. The beach north of the village, Praia do Morro, is a 6.66 km2 nature reserve.
 W
WBaía da Murdeira is a wide crescent shaped bay on the southwest coast of the island of Sal in Cape Verde. It takes its name from the village Murdeira, which lies at its shore. At its northwestern end lie the steep cliff of Rabo de Junco and the islet Ilhéu Rabo de Junco. The bay is protected as a marine nature reserve, which covers 182 hectares of land and 5,925 hectares of sea, including the Ilhéu Rabo de Junco. It is a nesting area for sea turtles and seabirds.
 W
WIlhéu dos Pásaros is a small uninhabited islet in the Cape Verde archipelago. It lies about 700 m (2,300 ft) off the northeastern coast of the island of Boa Vista, near the beach Praia das Gatas. The area of the islet is 0.82 ha ; with 38 ha of surrounding marine area it forms a protected area. It is a low, flat islet, covered with sedimentary material and sand. It is connected with the main island by a chain of reefs and volcanic rocks. It is an important nesting site for white-faced storm petrel and band-rumped storm petrel.
 W
WPedra de Lume is a village in the northeastern part of the island of Sal, Cape Verde. The village is situated on the east coast, about 5 km east of the island capital Espargos. It has a small port and a lighthouse, Farol de Pedra de Lume.
 W
WPonta do Sol is a headland located in the northwest of the island of Boa Vista. Cape Verde. It is the island's northernmost point. The town Sal Rei is approximately 6 km (3.7 mi) to the south, and the hill Vigia is 2 km (1.2 mi) to the south.
 W
WRabo de Junco is a hill on the west coast of the island of Sal in Cape Verde. It is situated at the northern end of the Baía da Murdeira, 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) southwest of the island capital Espargos. Its steep eroded south face towards the bay is an important nesting area for birds. Rabo de Junco and the surrounding 154 hectares are protected as a nature reserve. It was mentioned as Rabadyunk in the 1747 map by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin. To its west lies the uninhabited islet Ilhéu Rabo de Junco.
 W
WIlhéu de Sal Rei is an uninhabited islet near the coast of Boa Vista Island, Cape Verde. It is located 1 km southwest of the island capital Sal Rei. Its area is 89 ha (0.34 sq mi) and its highest point is 27 m (88.6 ft).
 W
WSalinas of the English Port is a saline wetland in the southwestern part of the island of Maio, Cape Verde, northwest of the city Porto Inglês. It is a 5.34 km2 (2.06 sq mi) protected area and a Ramsar site. It encompasses ecological, landscape, historical and cultural values. The site is frequented by species of birds of conservation interest, some of them protected by national laws and international conventions, and some endemic to the archipelago.
 W
WSanta Luzia is an island of the Barlavento archipelago in Cape Verde located between São Nicolau and São Vicente, the channel of Santa Luzia separates the island of São Vicente and is 8 km wide. The area is 34.2 km². Like all Cape Verdean islands, it is of volcanic origin. The highest point is Topona. Santa Luzia is 12.4 km long and 5.3 km wide.
 W
WThe salt ponds of Santa Maria are a complex of salt evaporation ponds north of the city Santa Maria in the southernmost part of the island of Sal, Cape Verde. It is one of two on the island, the other is near Pedra de Lume. The salt ponds are a protected area as a protected landscape, covering 69 hectares.
 W
WMonte Santo António is a mountain in the southwestern part of the island Boa Vista in Cape Verde. At 379 m (1,243 ft) elevation, it is the island's second highest point. Like Rocha Estância and Monte Estância, it rises steeply from the surrounding plains. It is part of a protected natural area under the statute of natural monument, covering 459 hectares.
 W
WSerra Malagueta is a mountain range located in the northern part of the island of Santiago, Cape Verde. At 1064 m elevation, it is highest point of northern Santiago. The mountain range is protected as the Serra Malagueta Natural Park, that was established on February 24, 2005 and covers 774 hectares. The natural park is situated in the municipalities Tarrafal, São Miguel and Santa Catarina. The summit is in São Miguel, south of the Ribeira Principal valley. The Serra Malagueta formation is of volcanic origin, and was formed between 2.9 and 2.4 million years ago.
 W
WThe Serra do Pico de Antónia is a mountain range in the centre of the island of Santiago in the Cape Verde archipelago. It contains the Pico de Antónia, at 1,392 m (4,567 ft) the highest point of the island. It is protected as a natural park,, covering 28.73 km2 (11.09 sq mi). The natural park covers the connected mountain ranges of Serra do Pico de Antónia and of Rui Vaz.
 W
WSerra Negra is a hill in the southeastern part of the island of Sal in Cape Verde. Its maximum elevation is 104 m, the highest point in southern Sal. It stretches for about 2.5 km along the east coast of the island, between the headland Ponta da Fragata in the south and the Ponta do Morrinho Vermelho in the north. The nearest settlement is Murdeira, to the west. The mountain forms part of a protected area as a nature reserve, important as nesting area for seabirds and turtles. The nature reserve covers 3.31 km2 (1.28 sq mi) of land and 22.96 km2 (8.86 sq mi) of ocean.
 W
WPonta do Sinó is the southernmost point of the island of Sal in Cape Verde. It lies 2 km southwest of Santa Maria city centre. The area north of the headland is a protected area: nature reserve Ponta do Sinó, at the edge of a large tourism development zone. There is a lighthouse on the headland, Farol da Ponta do Sinó, built in 1892.
 W
WMorro Negro is a hill located near the east coast of the island of Boa Vista, Cape Verde. Its elevation is 156 m. The nearest village is Cabeça dos Tarrafes, 5.5 km to the northwest.
 W
WTerras Salgadas is a vast natural area covering the northwestern part of the island of Maio, Cape Verde. It is part of the protected area Parque Natural do Norte da Ilha do Maio. It is the largest saline ecosystem of the whole archipelago, characterized by imposing sand dunes. The area is rich in endemic species of sea birds, fish and sea turtles. The nearest settlements are Morrinho, Cascabulho and Santo António. As "saline" (French) and "zoutpan" (Dutch) it was mentioned in the 1747 map by Jacques-Nicolas Bellin.
 W
WTope de Coroa is a mountain on the island of Santo Antão's, Cape Verde. At 1,979 m elevation, it is the highest point of the island. It is in the western part of the island, 25 km west of the island capital Porto Novo. The mountain is entirely of volcanic origin. The area is the source of several streams including Ribeira de Monte Trigo which flows westward to Monte Trigo.
 W
WMonte Velha is a peak in the northeastern part of the island of Fogo in Cape Verde. Its elevation is 1,482 m. It is a subpeak of the Pico do Fogo volcano, located at the northeastern end of the crater rim. It lies within the municipality of Mosteiros, 4 km southwest of the city centre. Its forest is a protected area, part of the larger Fogo Natural Park.