 W
WDarian Dam was constructed on the Sirwan River between 2009 and 2015. The Dam is located in the Hawrāmān region of Kurdistan and Kermanshah. The Darian Dam Archeological Salvage Program (DDASP) was planned by Iranian Center for Archaeological Research before flooding the reservoir.
 W
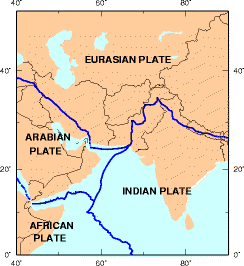
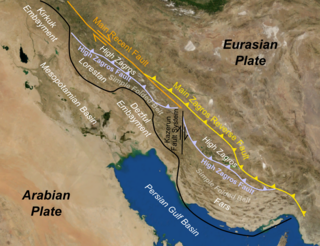
WThe Zagros Mountains are a long mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq and southeastern Turkey. This mountain range has a total length of 1,600 km (990 mi). The Zagros mountain range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border, while covering much of southeastern Turkey and northeastern Iraq. From this border region, the range roughly follows Iran's coast on the Persian Gulf. It spans the whole length of the western and southwestern Iranian plateau, ending at the Strait of Hormuz. The highest point is Mount Dena, at 4,409 metres (14,465 ft).
 W
WThe 2005 Qeshm earthquake occurred on November 27 at 13:52 IRST on the sparsely populated Qeshm Island off Southern Iran, killing 13 people and devastating 13 villages. It was Iran's second major earthquake of 2005, following that at Zarand in February. The epicenter was about 1,500 kilometers (930 mi) south of Tehran, close to Iran's southern borders. Initial measurements showed that the earthquake registered about 6.0 on the moment magnitude scale, although that was reduced to 5.8 after further analysis. More than 400 minor aftershocks followed the main quake, 36 of which were greater than magnitude 2.5. The earthquake occurred in a remote area during the middle of the day, limiting the number of fatalities. Iranian relief efforts were effective and largely adequate, leading the country to decline offers of support from other nations and UNICEF.
 W
WAbidar is a mountain to the West of Sanandaj, Kurdistan Province, Iran. With an elevation of 2550 metres, Mount Abidar is made of Upper Cretaceous rocks and is located in the Sanandaj-Sirjan geological and structural zone. This mountain is the place where the residents of Sanandaj go hiking and has many beautiful sub parks like "Amirieh" Jungle Park. Abidar main Jungle Park was designed and renewed in 1995 by the mayor of the time, Ardavan Nosoudi. He built and designed new roads to the highest places of the mount to increase the accessibility even for older people, without destroying the original view.
 W
WThe Alwand or Halwan River is a river in eastern Iraq and western Iran. It rises in the Zagros Mountains in Iran.
 W
WAtashkadeh is a mountain located in Paveh County, Kermanshah Province, Iran. Atashkadeh, meaning the firewall is a mountain range isolated from Shahu, including the Zagros mountain range, located south of the Paveh city and in the village of Khanahaha. This mountain starts from the village of sword and leads to the river Siervan. The peak of the sanctuary, as the highest peak of the southern shaho, has views of the wide area near Kermanshah, Ravansar, Vujvanrood, and Salas Babakhani, and the Heldjah and Shahrsar areas of Kurdistan and Marivan. For this reason, at the time of the Zoroastrians, there was a place to light the fire, by which they announced their message of religion. The fire temple of Paveh (fire) lasted for about 750 to 800 years. The fire temple, from ancient times, was the place of pilgrimage and fire of Zoroastrians, and it was burned for 800 years., Iran.
 W
WDasht-e Kâhou is a mountaintop plain above Taq-e Bostan Mount located in north of Kermanshah city in west of Iran.
 W
WDena is the name for a sub-range within the Zagros Mountains. Mount Dena, with 80 km (50 mi) length and 15 km (49,000 ft) average width, is situated on the boundary of the Isfahan, Kohgiluyeh and Boyer-Ahmad and Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Provinces of Iran.
 W
WThe Diyala River, is a river and tributary of the Tigris. It is formed by the confluence of Sirwan river and Tanjero river in Darbandikhan Dam in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate of Northern Iraq. It covers a total distance of 445 km (277 mi).
 W
WGarrin Mountain, or Kuh-e Garin, is a vast high-elevated mountain of the Zagros Mountains, located in Hamedan Province and Lorestan Province of western Iran.
 W
WHajji Firuz Tepe is an archaeological site located in West Azarbaijan province in north-western Iran and lies in the north-western part of the Zagros Mountains. The site was excavated between 1958 and 1968 by archaeologists from the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. The excavations revealed a Neolithic village that was occupied in the second half of the sixth millennium BC where some of the oldest archaeological evidence of grape-based wine was discovered in the form of organic residue in a pottery jar.
 W
WThe Hamrin Mountains are a small mountain ridge in northeast Iraq. The westernmost ripple of the greater Zagros mountains, the Hamrin mountains extend from the Diyala Governorate bordering Iran, northwest to the Tigris river, crossing northern Saladin Governorate and southern Kirkuk Governorate.
 W
WThe Iranian Plate is a small tectonic plate thought to underlie Iran and Afghanistan, and parts of Iraq and Pakistan.
 W
WThe Kārun is Iran's most effluent and only navigable river. It is 950 km (590 mi) long. It rises in the Zard Kuh mountains of the Bakhtiari district in the Zagros Range, receiving many tributaries, such as the Dez and the Kuhrang, before passing through the capital of the Khuzestan Province of Iran, the city of Ahvaz before emptying to its mouth into Arvand Rud.
 W
WKuhe Haji Ebrahim is a mountain of the Qandil Mountains, a subrange of the Zagros Mountains. The peak is located in western Iran and eastern Iraq, in western Asia.
 W
WLake Urmia is an endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is located between the provinces of East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan in Iran, and west of the southern portion of the Caspian Sea. At its greatest extent, it was the largest lake in the Middle East and the sixth-largest saltwater lake on Earth, with a surface area of approximately 5,200 km2 (2,000 sq mi), a length of 140 km (87 mi), a width of 55 km (34 mi), and a maximum depth of 16 m (52 ft). By late 2017, the lake had shrunk to 10% of its former size due to persistent general drought in Iran, but also the damming of the local rivers that flow into it, and the pumping of groundwater from the surrounding area. This dry spell was broken in 2019 and the lake is now filling up once again. The recovery of the lake has continued in 2020 due to above average precipitation and the actions of the Lake Urmia Restoration Program.
 W
WThe Laylan River is an endorheic river in western Iran.
 W
WLorestan Province is a province of western Iran in the Zagros Mountains. The population of Lorestan was 1,760,649 people in 2016, according to the last conducted census. In 2014 it was placed in Region 4.
 W
WMount Arbaba is a mountain of the Zagros Mountains range, near the city of Baneh in Kurdistan Province of western Iran.
 W
WMount Bisotoun is a mountain of the Zagros Mountains range, located in Kermanshah Province of western Iran. It is located 525 kilometers (326 mi) west of Tehran.
 W
WButin or Botin located on the Pendro terrain in Kurdistan Region. The mountain lies 4 km (2 mi) to the northeast of Pendro and some 100 km (62 mi) from Erbil. Hunting in Butin is prohibited and it is home to a large population of Wild Goat and other wildlife. Butin has a lot of valuable trees and mountain herbs, the most extensive growths on the Butin slopes.
 W
WMount Judi, also known as Qardū, is Noah's apobaterion or "Place of Descent", the location where the Ark came to rest after the Great Flood, according to very Early Christian and Islamic tradition.
 W
WMeywala is a mountain of the Zagros Mountains, located in western Iran, north of the city of Kermanshah.
 W
WParâw is a mount located in north east of Kermanshah city in west of Iran. Parâw With an approximate length of 80 km and an area of 880 square kilometers is part of the Zagros Mountains. Paraw is one of the 1515 Ultra-prominent peak of world.
 W
WOshtorankuh is a mountain that is located in city of Azna, extended to Aligoudarz and about 15 kilometres south of the city of Dorud in Lorestan Province in Iran. With an elevation of 4050 metres, the Oshtorankuh is the highest mountain in Lorestan Province. Stretched in a northwest-southeast direction, the Oshtorankuh is situated in the Zagros Mountains and is among the high mountains of this range. The ِDez Dam start in the Zagros mountains near the Oshtorankuh.
 W
WPomegranate valley is a location 50 km east of Khorramabad, Lorestan province, Iran.
 W
WThe Qandil Mountains, are a mountainous area of Iraqi Kurdistan near the Iraq-Iran border. The region belongs to the Zagros mountain range and is difficult to access, with extremely rugged terrain. The highest peaks reach over 3,000m.
 W
WQizil Üzan is a river flowing in northwestern and northern Iran.
 W
WSalavatabad is a mountain range in the west part of Sanandaj city, Kurdistan Province, western Iran.
 W
WThe Shahar River, also known as Shahar Chay or Barde Sur is a river in the Zagros Mountains of northwestern Iran.
 W
WShaho is a mountain of the central Zagros Mountains range. It is located between cities of Kamyaran, Sarv Abad, Marivan, Nodeshe, Nawsoud, Pave, Javanroud, Rawansar in the district of Kurdistan and Kermanshah Provinces, western Iran. The highest peak of this mountain is called Havi Khani, located at the height of 3390 meters. Some of the other highest peaks are Zavoli 3205 meters, Pir Kheder 3090 meters, Nour 3110 meters highest from the sea level. The Shaho mountain is close to the Sirvan River.
 W
WStatue of Hercules is located in Mount Behistun, Iran. It was discovered in 1958. The statue was sculpted in 148 BC for a governor of the Seleucid Empire or the Parthian Empire. Hercules is lying on a 2 m long platform and holds a bowl in his left hand. He has put his right hand on his foot. The statue is 1.47 m long and is attached to the mountain. The head of the statue was stolen twice, but discovered again in 1996. However, the current head is a double and the actual head is in Cultural Heritage, Handcrafts and Tourism Organization. At the time it was discovered, he had a penis, but after the Islamic Revolution (1979) it was broken down by locals.
 W
WYafteh is an Upper Paleolithic cave located at the foot of Yafteh Mountain in the Zagros Mountains range, located northwest of Khoramabad in western Zagros, Lorestan Province of western Iran.
 W
WThe Zagros fold and thrust belt is an approximately 1,800-kilometre (1,100 mi) long zone of deformed crustal rocks, formed in the foreland of the collision between the Arabian Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is host to one of the world's largest petroleum provinces, containing about 49% of the established hydrocarbon reserves in fold and thrust belts (FTBs) and about 7% of all reserves globally.
 W
WThe Zagros Mountains forest steppe is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in western Asia. The ecoregion extends along the Zagros Mountains, stretching from eastern Turkey and northern Iraq to southern Iran.
 W
WZagros Paleolithic Museum is a museum in Kermanshah, Iran, established in 2008. The museum contains a large collection of stone tools and animal fossil bones from various Paleolithic sites in Iran. In Iran, it is the only museum of its kind.
 W
WZard-Kuh is a sub-range in the central Zagros Range, Iran.
 W
WZayanderud, also spelled as Zayandeh-Rood or Zayanderood, is the largest river of the Iranian Plateau in central Iran.
 W
WLake Zrebar, also known as Zeribar or Zrewar, , is a lake in the Zagros Mountains, within Kurdistan Province of western Iran.