 W
WAlbania has a variety of climate systems. With its coastline facing the Adriatic and Ionian seas in the Mediterranean sea, its highlands backed upon the elevated Balkan landmass, and the entire country lying at a latitude subject to a variety of weather patterns during the winter and summer seasons, however it has a high number of climatic regions for such a small area. The coastal lowlands have typically mediterranean climate while the highlands have a continental climate. In both the lowlands and the interior, the weather varies markedly from north to south.
 W
WThe climate of Argentina is a vastly complex subject, as the vast size of the country and wide variation in altitude make for a wide range of climate types. Summers are the warmest and wettest season in most of the country except in most of Patagonia where it is the driest season. Winters are normally mild in the north, cool in the center and cold in the southern parts experiencing frequent frost and snow. Because southern parts of the country are moderated by the surrounding oceans, the cold is less intense and prolonged than areas at similar latitudes in the northern hemisphere. Spring and autumn are transition seasons that generally feature mild weather.
 W
WArmenia's different varieties of climates depend on the absolute height of the land. They vary from cold desert on the lower parts of the Ararat plain, to tundra on mountain peaks. The following six basic types can be distinguished. Another type of climate is the dry continental type. It prevails along the middle reaches of the Arax up to an elevation of 1,300 m. It differs from the dry subtropical climate by its cold winters.
 W
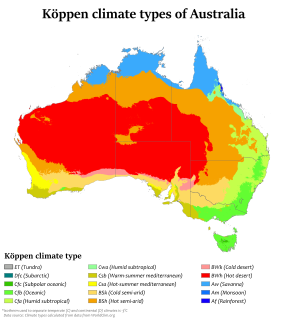
WAustralia's climate is governed mostly by its size and by the hot, sinking air of the subtropical high pressure belt. This moves north-west and north-east with the seasons. The climate is variable, with frequent droughts lasting several seasons, thought to be caused in part by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation. Australia has a wide variety of climates due to its large geographical size. The largest part of Australia is desert or semi-arid. Only the south-east and south-west corners have a temperate climate and moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the country has a tropical climate, varying between grasslands and desert. Australia holds many heat-related records: the continent has the hottest extended region year-round, the areas with the hottest summer climate, and the highest sunshine duration.
 W
WThe climate of Azerbaijan is very diverse. Nine out of eleven existing climate zones are present in Azerbaijan.
 W
WThe climate in Brazil varies considerably from mostly tropical north to temperate zones south of the Tropic of Capricorn.
 W
WThe climate of Chile comprises a wide range of weather conditions across a large geographic scale, extending across 38 degrees in latitude, making generalizations difficult. According to the Köppen system, Chile within its borders hosts at least seven major climatic subtypes, ranging from low desert in the north, to alpine tundra and glaciers in the east and southeast, tropical rainforest in Easter Island, Oceanic in the south and Mediterranean climate in central Chile. There are four seasons in most of the country: summer, autumn, winter, and spring.
 W
WThe Climate of Colombia is characterized for being tropical and isothermal as a result of its geographical location near the Equator presenting variations within five natural regions and depending on the altitude, temperature, humidity, winds and rainfall. Each region maintains an average temperature throughout the year only presenting variables determined by precipitation during a rainy season caused by the Intertropical Convergence Zone.
 W
WCyprus has a subtropical climate - Mediterranean and semi-arid type - according to Köppen climate classification signes Csa and BSh, with very mild winters and warm to hot summers. Snow is possible only in the Troodos mountains in the central part of the island. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry.
 W
WThe climate of Ecuador is tropical and varies with altitude and region, due to differences in elevation and, to a degree, in proximity to the equator.
 W
WEgypt essentially has a hot desert climate. The climate is generally extremely dry all over the country except on the northern Mediterranean coast which receives rainfall in winter. In addition to rarity of rain, extreme heat during summer months is also a general climate feature of Egypt although daytime temperatures are more moderated along the northern coast.
 W
WThe average annual temperature in Estonia is 5.2 °C (41.4 °F). The average temperature in February, the coldest month of the year, is −5.7 °C (21.7 °F). The average temperature in July, which is considered the warmest month of the year, is 16.4 °C (61.5 °F). The climate is also influenced by the Atlantic Ocean, the North-Atlantic Stream and the Icelandic Minimum, which is an area known for the formation of cyclones and where the average air pressure is lower than in neighbouring areas. Estonia is located in a humid zone in which the amount of precipitation is greater than total evaporation. The average precipitation in 1961–1990 ranged from 535 to 727 millimeters per year and was heaviest in late summer. There were between 102 and 127 rainy days a year, and average precipitation was most plentiful on the western slopes of the Sakala and Haanja Uplands. Snow cover, which is deepest in the south-eastern part of Estonia, usually lasts from mid-December to late March.
 W
WThe climate of the Falkland Islands is cool and temperate, regulated by the large oceans which surround it. The Falkland Islands are located over 480 kilometres (298 mi) from South America, to the north of the Antarctic convergence, where cooler waters from the south mix with warmer waters from the north.
 W
WThe climate of Finland is influenced most by its latitude: Finland is located between 60 and 70 N. Because of Finland's northern location, winter is the longest season. Only on the south coast and the southwest is summer as long as winter. On average, winter lasts from early January to late February in the outermost islands in the archipelago and the warmest locations along the southwestern coast – notably in Hanko, and from early October to mid May in the most elevated locations, such as northwestern Lapland and the lowest valleys in northeastern Lapland. This means that southern portions of the country are snow-covered about three to four months of the year, and the northern for about seven months. The long winter causes about half of the annual 500 to 600 millimetres precipitation in the north to fall as snow. Precipitation in the south amounts to about 600 to 700 millimetres annually. Like that of the north, it occurs all through the year, though not so much of it is snow.
 W
WIntroduction
 W
WThe climate in Greece is predominantly Mediterranean. However, due to the country's unique geography, Greece has a remarkable range of micro-climates and local variations. The Greek mainland is extremely mountainous, making Greece one of the most mountainous countries in Europe. To the west of the Pindus mountain range, the climate is generally wetter and has some maritime features. The east of the Pindus mountain range is generally drier and windier in summer. The highest peak is Mount Olympus, 2,918 metres (9,573 ft). The north areas of Greece have a transitional climate between the continental and the Mediterranean climate. There are mountainous areas that have an alpine climate.
 W
WThe climate of Hungary is characterised by its position. Hungary is in the eastern part of Central Europe, roughly equidistant from the Equator and the North Pole, more than 1,000 kilometres (600 mi) from either and about 1,000 kilometres from the Atlantic Ocean.
 W
WThe climate of Iceland is subpolar oceanic near the southern coastal area and tundra inland in the highlands. The island lies in the path of the North Atlantic Current, which makes its climate more temperate than would be expected for its latitude just south of the Arctic Circle. This effect is aided by the Irminger Current, which also helps to moderate the island's temperature. The weather in Iceland is notoriously variable.
 W
WThe climate of India comprises a wide range of weather conditions across a vast geographic scale and varied topography, making generalizations difficult. Climate in north India is generally hotter than south India whereas the South India gets more humid due to nearby coasts. Most parts of the nation don't experience temperatures below 10 °C (50 °F) in winter, and the temperature usually tends to exceed 40 °C (104 °F) during summer. Based on the Köppen system, India hosts six major climatic sub types, ranging from arid deserts in the west, alpine tundra and glaciers in the north, and humid tropical regions supporting rain forests in the southwest and the island territories. Many regions have starkly different microclimates, making it one of the most climatically diverse countries in the world. The country's meteorological department follows the international standard of four seasons with some local adjustments: winter, summer, monsoon (rainy) season, and a post-monsoon period.
 W
WThe climate of Indonesia is almost entirely tropical. The uniformly warm waters that make up 81% of Indonesia's area ensure that temperatures on land remain fairly constant, with the coastal plains averaging 28 °C (82 °F), the inland and mountain areas averaging 26 °C (79 °F), and the higher mountain regions, 23 °C (73 °F). Temperature varies little from season to season, and Indonesia experiences relatively little change in the length of daylight hours from one season to the next; the difference between the longest day and the shortest day of the year is only forty-eight minutes. This allows crops to be grown all year round.
 W
WThe climate of Ireland is mild, humid and changeable with abundant rainfall and a lack of temperature extremes. Ireland's climate is defined as a temperate oceanic climate, or Cfb on the Köppen climate classification system, a classification it shares with most of northwest Europe. The country receives generally warm summers and cool winters.
 W
WItaly has a variety of climate systems. The inland northern areas of Italy have a relatively cool, mid-latitude version of the Humid subtropical climate, while the coastal areas of Liguria and the peninsula south of Florence generally fit the Mediterranean climate profile.
 W
WKosovo is a relatively small territory. Because of the climatic position and complicated structure of the relief it has a variety of climate systems.
 W
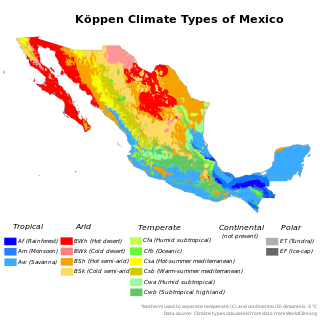
WThe climate of Mexico is very varied. The Tropic of Cancer effectively divides the country into temperate and tropical zones. Land that is north of the twenty-fourth parallel experiences lower temperatures during the winter months. South of the twenty-fourth parallel, temperatures are fairly consistent all year round and vary solely as a function of elevation. The north of the country usually receives less precipitation than the south.
 W
WThe climate of New Zealand is varied due to the country's diverse landscape. Most regions of New Zealand belong to the temperate zone with a maritime climate characterised by four distinct seasons. The main contributing factors are the Pacific Ocean and latitude, although the mountain ranges can cause significant climate variations in locations barely tens of kilometres from each other. Conditions vary from extremely wet on the West Coast of the South Island to almost semi-arid in Central Otago and subtropical in Northland.
 W
WPakistan's climate is a continental type of climate, characterized by extreme variations in temperature, both seasonally and daily, because it is located on a great landmass north of the Tropic of Cancer.
 W
WThe climate of Paraguay consists of a subtropical climate in the Paranaense region and a tropical climate in the Chaco. The Paranaense region has a humid climate, with abundant precipitation throughout the year and only moderate seasonal changes in temperature.
 W
WClimate of Peru describes the diverse climates of this large South American country with an area of 1,285,216 km2 (496,225 sq mi). Peru is located entirely in the tropics but features desert and mountain climates as well as tropical rain forests. Elevations above sea level in the country range from −37 metres (−121 ft) to 6,788 metres (22,270 ft) and precipitation ranges from less than 20 millimetres (0.79 in) annually to more than 8,000 millimetres (310 in). There are three main climatic regions: the Pacific Ocean coast is one of the driest deserts in the world but with some unique features; the high Andes mountains have a variety of microclimates depending on elevation and exposure and with temperatures and precipitation from temperate to polar and wet to dry; and the Amazon Basin has tropical climates, mostly with abundant precipitation, along with sub-tropical climates in elevations above 1,550 metres (5,090 ft).
 W
WThe climate of Puerto Rico in the Köppen climate classification is predominately tropical rainforest. Temperatures throughout the year are warm to hot, averaging near 85 °F (29 °C) in lower elevations and 70 °F (21 °C) in the mountains. Easterly trade winds pass across the island year round while the rainy season stretches from April into November. The relatively cool trade winds are blocked by the mountains of the Cordillera Central which causes rain shadows and sharp variations in the temperature and wind speed over short distances. About a quarter of the average annual rainfall for Puerto Rico occurs during tropical cyclones, which are more frequent during La Niña years.
 W
WThe climate of Romania is temperate continental transitioning into an oceanic climate on the eastern coast, influenced by Scandinavian-Baltic weather, the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. Thus, in the south, there are some influences of a mediterranean climate, characterized by mild winters and stronger rainfalls in the cooler months. In the south-east, the Black Sea induces rare heavy strong rains. In eastern regions the continental character is less pronounced. In the north of the country, the effect of the Scandinavian-Baltic climate is felt, effecting a wetter and colder climate with cold winters. The west of the country has a more pronounced influence of low pressure systems generated over the Atlantic, causing moderate temperatures and stronger precipitation. Climate nuances are demonstrated on the steps of the altitude, the mountain ranges of the Carpathian arc have a cool mountain climate with high humidity throughout the year.
 W
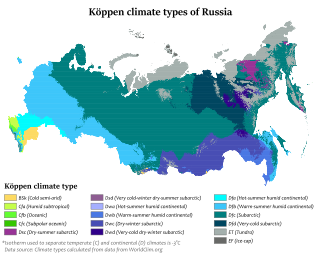
WThe climate of Russia is formed under the European peninsula. The enormous size of the country and the remoteness of many areas from the sea result in the dominance of the continental climate, which is prevalent in European and Asian Russia except for the tundra and the best extreme southwest. Mountains in the south obstructing the flow of cold air masses from the Arctic Ocean and the plain of the south and north makes the country open to Pacific and Atlantic influences.
 W
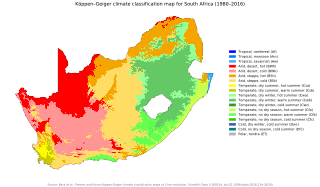
WThe climate of South Africa is determined by South Africa's situation between 22°S and 35°S, in the Southern Hemisphere's subtropical zone, and its location between two oceans, Atlantic and the Indian.
 W
WThe climate in Spain varies across continental Spain. Spain is the most climatically diverse country in Europe with 13 different Köppen climates, excluding the Canary Islands, and is within the 10 most climatically diverse countries in the world. Five main climatic zones can be distinguished, according to the country's Köppen-Geiger climate classification and orographic conditions:The hot-summer Mediterranean climate (Csa) which is also characterized by dry and warm/hot summers and cool to mild and wet winters. According to the Köppen climate classification, this climate is dominant on the Iberian Peninsula, particularly the variety with summer droughts, covering all but the far northern part of the country where the Oceanic climate predominates. The hot-summer Mediterranean climate is further divided into the "Standard Mediterranean" of lowland regions and "Continentalized Mediterranean" of the interior, according to altitude and the mildness or harshness of the winter season. The Standard Mediterranean covers coastal areas the Guadalquivir river basin and the lower reaches of the Tagus and Guadiana basins to the west of the country. The Continentalized Mediterranean climate predominates in Spain's vast table lands, Meseta Central, of the interior. The warm-summer Mediterranean climate (Csb) which predominates in parts of northwestern Spain and mostly inland in central-northern Spain at altitudes above 900-1000 masl. The oceanic climate (Cfb) is located in the northern part of the country, especially in the regions of Galicia, Basque Country, Asturias, Cantabria, and Navarre. This region has regular snowfall in the winter months. The semiarid climate is predominant in the south eastern part of the country and in the middle reaches of the Ebro valley to the north east, reaching as far west as southern Navarre. It is also present in large areas of the central table lands and some of the driest areas of Extremadura. In contrast to the Mediterranean climate, the dry season continues beyond the end of summer and the vegetation is less dense. The warm-summer continental climate (Dfb) which can be found in many areas in north-eastern Spain, in areas starting with altitudes above 1000-1100 masl. It can be found also in some areas in the Cantabrian Mountains and the highest areas of the Sistema Ibérico mountain range in central-eastern Spain.
 W
WSvalbard is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. The climate of Svalbard is principally a result of its latitude, which is between 74° and 81° north. Climate is defined by the World Meteorological Organization as the average weather over a 30-year period. The North Atlantic Current moderates Svalbard's temperatures, particularly during winter, giving it up to 20 °C (36 °F) higher winter temperature than similar latitudes in continental Russia and Canada. This keeps the surrounding waters open and navigable most of the year. The interior fjord areas and valleys, sheltered by the mountains, have fewer temperature differences than the coast, with about 2 °C lower summer temperatures and 3 °C higher winter temperatures. On the south of the largest island, Spitsbergen, the temperature is slightly higher than further north and west. During winter, the temperature difference between south and north is typically 5 °C, and about 3 °C in summer. Bear Island (Bjørnøya) has average temperatures even higher than the rest of the archipelago.
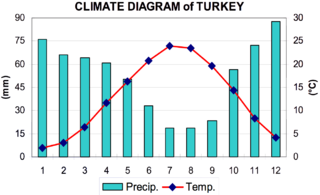 W
WThe coastal areas of Turkey bordering the Aegean Sea and the Mediterranean Sea have a hot-summer Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry summers and mild to cool, wet winters. The coastal areas of Turkey bordering the Black Sea have a temperate Oceanic climate with warm, wet summers and cool to cold, wet winters. The Turkish Black Sea coast receives the greatest amount of precipitation and is the only region of Turkey that receives high precipitation throughout the year. The eastern part of that coast averages 2,500 millimeters annually which is the highest precipitation in the country.
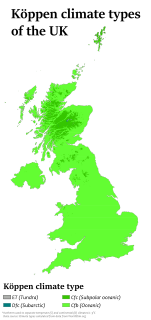 W
WThe United Kingdom straddles the higher mid-latitudes between 49° and 61° N on the western seaboard of Europe. Since the UK is always in or close to the path of the polar front jet stream, frequent changes in pressure and unsettled weather are typical. Many types of weather can be experienced in a single day. In general the climate of the UK is cool and often cloudy and rainy, and high temperatures are infrequent.
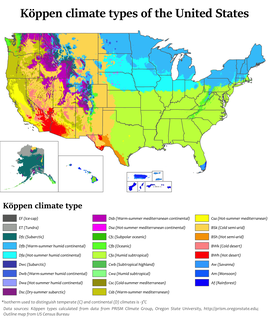 W
WThe climate of the United States varies due to changes in latitude, and a range of geographic features, including mountains and deserts. Generally, on the mainland, the climate of the U.S. becomes warmer the further south one travels, and drier the further west, until one reaches the West Coast.
 W
WThe Climate of Venezuela is characterized for being tropical and isothermal as a result of its geographical location near the Equator, but because of the topography and the dominant wind direction, several climatic types occur which can be the same as found in temperate latitudes, and even polar regions. Latitude exerts little influence on the Venezuelan climate, but the altitude changes it dramatically, particularly the temperature, reaching values very different according to The weather.
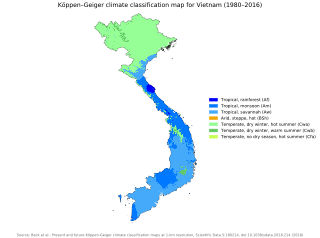 W
WVietnam's climate, because it's in the tropics and strongly influenced by the South China Sea, has a monsoon-influenced tropical climate typical of that of mainland Southeast Asia. In the north, the climate is monsoonal with four distinct seasons while in the south, the climate is tropical monsoon with two seasons. In addition, a temperate climate exists in mountainous areas, which are found in Sa Pa and Da Lat, while a more continental climate exists in Lai Chau Province and Son La Province.
 W
WThe climate of Zambia in Central and Southern Africa is definitely tropical modified by altitude (elevation). In the Köppen climate classification, most of the country is classified as humid subtropical or tropical wet and dry, with small patches of semi-arid steppe climate in the south-west.