 W
WThe France–Italy border is the international boundary between France and Italy.
 W
WAiguille de Leschaux is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif on the border of Haute-Savoie, France and Aosta Valley, Italy.
 W
WThe Aiguille de Rochefort is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif in France and Italy. The peak lies on the Rochefort arête between the Dent du Géant and the Grandes Jorasses and is usually climbed during a traverse of the ridge.
 W
WAiguille de Scolette or Pierre Menue is a mountain of Savoie (F) and of the province of Turin (I). It lies in the Cottian Alps and has an elevation of 3,506 metres above sea level.
 W
WThe Aiguille de Triolet is a mountain on the eastern part the Mont Blanc massif, on the border between France and Italy.
 W
WThe Aiguille des Glaciers is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif of the Graian Alps. It lies on the borders of Savoie and Haute-Savoie in France and Aosta Valley in Italy.
 W
WMont d'Ambin or Rocca d'Ambin is a mountain on the border of Savoie, France and of the Province of Turin, Italy. It lies in the Ambin group of the Cottian Alps. On the Italian side, it commands the view of the Val di Susa. It has an elevation of 3,378 metres (11,083 ft) above sea level.
 W
WRocca Bernauda, in French Roche Bernaude, is a mountain of the Alps of 3,222 metres (10,571 ft). It is the most western point of Italy after the cession of Valle Stretta with the Paris Peace Treaties of 1947.
 W
WMonte Bertrand (Italian) or Mont Bertrand (French) is a mountain located on the French-Italian border between Piemonte and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur.
 W
WMont Blanc is the highest mountain in the Alps and Western Europe, rising 4,808 m (15,774 ft) above sea level. It is the second-highest and second most prominent mountain in Europe, after Mount Elbrus, and it is the eleventh most prominent mountain summit in the world. The mountain stands between the regions of Aosta Valley, Italy, and Savoie and Haute-Savoie, France. It gives its name to the Mont Blanc massif, which itself forms part of a larger range referred to as the Graian Alps. The location of the summit of Mont Blanc is on the watershed line between the valleys of Ferret and Veny in Italy and the valleys of Montjoie, and Arve in France, on the border between the two countries. Ownership of the summit area has long been a subject of historical dispute between the two countries.
 W
WBrec de Chambeyron (3,389) is a mountain of the Cottian Alps on the border between France and Italy. It is the second highest summit of the Chambeyron Massif, after Aiguille de Chambeyron and its sharp, rocky peak dominates the Upper Ubaye Valley. The word "Brec" or "Bric" in French is used for a mountain resembling a rocky tooth. It was first climbed in 1878 by Paul Agnel and Joseph Risoul.
 W
WCime de l'Agnel is a mountain. It is one of the main peaks of the Mercantour-Argentera, upstream of Upper Boréon in the Vésubie, at the border between the Alpes-Maritimes and Piedmont.
 W
WCime du Gélas is a 3,143 m high mountain on the boundary between France and Italy. It is part of the Maritime Alps.
 W
WMonte Clapier is a mountain in the Maritime Alps, on the boundary between the province of Cuneo and the French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte-d'Azur.
 W
WThe Croce Rossa or Croix Rousse is a mountain of the Graian Alps, on the border between Piedmont, Italy and Savoie, France.
 W
WThe Dent du Géant is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif in France and Italy.
 W
WThe Dôme de Rochefort is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif in Haute-Savoie, France and of Aosta Valley, Italy.
 W
WThe Dôme du Goûter is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif. It is a shoulder of Mont Blanc, whose summit lies two kilometres to the south-east. The Dôme is traversed on ascents of Mont Blanc via the Bosses route.
 W
WEnciastraia is a mountain in the Maritime Alps, on the boundary between the province of Cuneo and the French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte-d'Azur.
 W
WMonte Grammondo is a mountain in Liguria, northern Italy, part of the Alps.
 W
WThe Gran Queyron or Grand Queyron is a 3,060 metres high mountain of the Cottian Alps.
 W
WThe Grande Aiguille Rousse is a mountain peak of the Graian Alps in Savoie, France, situated between the Maurienne and Tarentaise valleys near the Italian border. Reaching an altitude of 3,482 meters, it exceeds its junior to the west, the Petite Aiguille Rousse, by just 50 m (160 ft). Not far from Levanna, the Grande Aiguille Rousse overlooks Serrù Lake and the Gran Paradiso National Park in Italy.
 W
WThe Grandes Jorasses is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif, on the boundary between Haute-Savoie in France and Aosta Valley in Italy.
 W
WLancebranlette is a mountain of Savoie, France and of Aosta Valley, Italy. It lies in the Mont Blanc Massif range. It has an elevation of 2,936 metres above sea level.
 W
WThe Levanne is a group of mountains of Savoie, France and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, Italy. It lies in the Graian Alps range. The three main peaks are:Levanna Orientale - 3.555 m Levanna Centrale - 3.619 m Levanna Occidentale - 3.593 m
 W
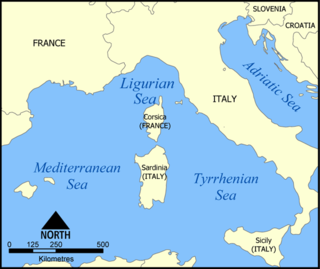
WThe Ligurian Sea is an arm of the Mediterranean Sea, between the Italian Riviera (Liguria) and the island of Corsica. The sea is theorized to be named after the ancient Ligures people.
 W
WThe Punta Marguareis (It) or Pointe Marguareis (Fr) is a mountain in the Ligurian Alps, on the boundary between Italy and France; It is the highest peak of the Ligurian Alps.
 W
WMont Maudit is a mountain in the Mont Blanc massif in France and Italy. The French name literally means "Cursed Mountain". Until the end of the 18th century, Mont Blanc and its satellite peaks were collectively known in French as the Montagne Maudite.
 W
WThe Cima Mongioia or simply Mongioia or Bric de Rubren is a 3,340 metres high mountain of the Cottian Alps.
 W
WThe Punta Nera is a mountain of Savoie (France) and of the Province of Turin (Italy). It lies in the Cottian Alps range. It has an elevation of 3,047 metres above sea level.
 W
WCima di Pertegà (Italian) or Cime de la Pertègue (French) is a mountain located on the French-Italian border between Piemonte and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur.
 W
WPointe de Paumont or Cima del Vallone is a mountain of Savoie, France and of the Province of Turin, Italy. It lies in the Cottian Alps range. It has an elevation of 3,171 metres above sea level.
 W
WPunta Bagnà or Cime du Grand Vallon is a mountain of Savoie, France and of the Province of Turin, Italy. It lies in the Cottian Alps range. It has an elevation of 3,129 metres above sea level.
 W
WThe Punta Merciantaira or Grand Glaiza is a 3,293 metres high mountain of the Cottian Alps.
 W
WThe Punta Ramiere or Bric Froid is a mountain in the Cottian Alps belonging to the department of Hautes-Alpes (FR) and the province of Turin (IT). It's the highest peak of the long stretch of the Po/Rhone water divide starting from the Aiguille de Scolette (north) and ending with the Monviso group (south).
 W
WRognosa d'Etiache or Rognosa d'Étache is a mountain in the Cottian Alps on the border of Turin, Italy, and Savoie, France. It has an elevation of 3,382 metres above sea level.
 W
WMonte Saccarello (Italian) or Mont Saccarel (French) is a mountain located on the French-Italian border between Liguria, Piedmont and Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur.
 W
WPunta Sommeiller or Pointe Sommeiller is a mountain of the Province of Turin, Italy and of Savoie, France. It lies in the Cottian Alps range. It has an elevation of 3,333 metres (10,935 ft) above sea level.
 W
WThe Strait of Bonifacio is the strait between Corsica and Sardinia, named after the Corsican town Bonifacio. It is 11 km (6.8 mi) wide and divides the Tyrrhenian Sea from the western Mediterranean Sea. The strait is notorious among sailors for its weather, currents, shoals, and other obstacles.
 W
WMonte Tanarello (Italian) or Mont Tanarel (French) is a 2094 metres high mountain located on the French-Italian border.
 W
WRocca dei Tre Vescovi is a mountain in the Maritime Alps, on the boundary between the province of Cuneo and the French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte-d'Azur.
 W
WTsanteleina (3,601m) is a mountain of the Graian Alps located on the border between Savoie, France and Aosta Valley, Italy. It lies at the head of the Val di Rhèmes, although the summit itself is hidden from view in the valley. The eastern side of the mountain lies within the Gran Paradiso National Park. The normal route to the summit is from the north as the paths on the other side of the mountain have been neglected due to the poor quality of the rock. The north face is also popular with ski mountaineers.