 W
WThe Ash Meadows National Wildlife Refuge is a protected wildlife refuge located in the Amargosa Valley of southern Nye County, in southwestern Nevada. It is directly east of Death Valley National Park, and is 90 mi (140 km) west-northwest of Las Vegas.
 W
WThe Bad River is a river flowing to Lake Superior in northern Wisconsin in the United States. It flows for 119.6 kilometres (74.3 mi) in Ashland County, draining an area of 1,061 square miles (2,750 km2) in portions of Ashland, Bayfield and Iron counties. The Bad River sloughs were designated a Ramsar Wetland of International Importance on February 2, 2012.
 W
WBitter Lake National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge located in two separate sections in central Chaves County, New Mexico, United States, a few miles northeast of the city of Roswell. Both sections lie on the banks of the Pecos River. The refuge was established in 1937 to provide habitat for migratory birds such as the sandhill crane and the snow goose, but it is also notable for rare native fish and the over 90 species of dragonflies and damselflies that inhabit the refuge.
 W
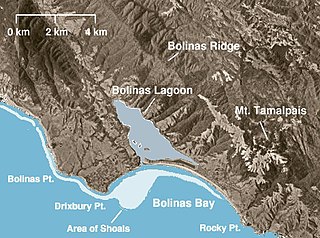
WBolinas Lagoon is a tidal estuary, approximately 1,100 acres (4.5 km2) in area, located in the West Marin region of Marin County, California, United States, adjacent to the town of Bolinas. It is a part of the Greater Farallones National Marine Sanctuary and is considered to be among the possible landing spots of Sir Francis Drake on the west coast of North America in 1579.
 W
WBottomless Lakes State Park is a state park in the U.S. state of New Mexico, located along the Pecos River, about 15 miles (24 km) southeast of Roswell. Established in 1933, it was the first state park in New Mexico. It takes its name from nine small, deep lakes located along the eastern escarpment of the Pecos River valley. The escarpment is an ancient limestone reef, similar to the limestone mountains around Carlsbad Caverns, 80 miles (130 km) to the south. Caves formed within the limestone, and as the Pecos River eroded the escarpment, the caves eventually collapsed, leaving behind several deep, almost circular lakes known as cenotes.
 W
WThe Cache River is a tributary of the White River, 213 mi (343 km) long, in northeastern Arkansas in the United States. Its headwaters also drain a small portion of southeastern Missouri. Via the White River, the Cache is part of the Mississippi River watershed, placing the river and surrounding watershed in the Arkansas Delta.
 W
WThe Cache River is a 92-mile-long (148 km) waterway in southernmost Illinois, in a region sometimes called Little Egypt. The basin spans 737 square miles (1,910 km2) and six counties: Alexander, Johnson, Massac, Pope, Pulaski and Union. Located at the convergence of four major physiographic regions, the river is part of the largest complex of wetlands in Illinois. The Cache River Wetlands — America's northernmost cypress/tupelo swamp — harbors 91 percent of the state's high quality swamp and wetland communities. It provides habitat for more than 100 threatened and endangered species in Illinois. In 1996, the Cache was designated a Wetland of International Importance by the Ramsar Convention.
 W
WThe Cache River National Wildlife Refuge is a 68,993 acre (223 km2) (2014) wildlife refuge in the state of Arkansas managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS). The refuge is one of the Ramsar wetlands of international importance under the Ramsar Convention signed in 1971. It is one of the most important wintering area for ducks and the largest remaining tract of contiguous bottomland hardwood forest on the North American continent. In 2005, a possible sighting of the ivory-billed woodpecker, thought to be extinct, brought attention to the refuge.
 W
WCaddo Lake is a 25,400-acre (10,300 ha) lake and bayou (wetland) on the border between Texas and Louisiana, in northern Harrison County and southern Marion County in Texas and western Caddo Parish in Louisiana. The lake is named after the Southeastern culture of Native Americans called Caddoans or Caddo, who lived in the area until their expulsion in the 19th century. It is an internationally protected wetland under the Ramsar Convention and includes one of the largest flooded cypress forests in the United States. Caddo is one of Texas's few non-oxbow natural lakes and is the second-largest in the South; however, it was artificially altered by the addition of a dam in the 1900s.
 W
WThe Cape May National Wildlife Refuge is a protected area on the Cape May Peninsula in Cape May County, New Jersey. It is part of the National Wildlife Refuge System and managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Established in January 1989 with 90 acres (0.36 km2) acquired from the Nature Conservancy, it has since grown to more than 11,000 acres (45 km2) in size, and plans call for its further expansion to more than 21,200 acres (86 km2). It comprises three distinct and non-contiguous units: the Delaware Bay Division, the Great Cedar Swamp Division and the Two Mile Beach Unit. Located in the Middle Atlantic coastal forests ecoregion, the cape provides habitat for large numbers of migratory birds.
 W
WCatahoula Lake is a large freshwater lake located in La Salle Parish and Rapides Parish of central Louisiana, United States.
 W
WThe Chesapeake Bay is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula with its mouth of the Bay at the south end located between Cape Henry and Cape Charles. With its northern portion in Maryland and the southern part in Virginia, the Chesapeake Bay is a very important feature for the ecology and economy of those two states, as well as others surrounding within its watershed. More than 150 major rivers and streams flow into the Bay's 64,299-square-mile (166,534 km2) drainage basin, which covers parts of six states and all of Washington, D.C. / District of Columbia.
 W
WCheyenne Bottoms is a wetland in the central Great Plains of North America. Occupying approximately 41,000 acres in central Kansas, it is the largest wetland in the interior United States. The Bottoms is a critical stopping point on the Central Flyway for millions of birds which migrate through the region annually.
 W
WChiwaukee Prairie is a 485-acre (1.96 km2) prairie in Pleasant Prairie, Wisconsin managed by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources. It is located along Lake Michigan just north of Illinois and includes grassy wetlands, wooded areas, and the Kenosha Sand Dunes at its northern tip. it is home to an abundance of wildlife. It was designated a Wisconsin State Natural Area in 1967 and a National Natural Landmark in 1973. Together with surrounding areas, and south to Illinois Beach State Park, it constitutes an internationally recognized wetland of importance under the Ramsar Convention, called the Chiwaukee Illinois Beach Lake Plain.
 W
WCongaree National Park is a 26,276-acre American national park in central South Carolina. The park received its official designation in 2003 as the culmination of a grassroots campaign that began in 1969. The park preserves the largest tract of old growth bottomland hardwood forest left in the United States. The lush trees growing in its floodplain forest are some of the tallest in the eastern United States, forming one of the highest temperate deciduous forest canopies remaining in the world. The Congaree River flows through the park. About 15,000 acres are designated as a wilderness area.
 W
WThe Connecticut River is the longest river in the New England region of the United States, flowing roughly southward for 406 miles (653 km) through four states. It rises at the U.S. border with Quebec, Canada, and discharges at Long Island Sound. Its watershed encompasses 11,260 square miles (29,200 km2), covering parts of five U.S. states and one Canadian province, via 148 tributaries, 38 of which are major rivers. It produces 70% of Long Island Sound's fresh water, discharging at 18,400 cubic feet (520 m3) per second.
 W
WCorkscrew Swamp Sanctuary is a National Audubon Society sanctuary located in southwest Florida, north of Naples, Florida and east of Bonita Springs, in the United States. The sanctuary was established to protect one of the largest remaining stands of bald cypress and pond cypress in North America from extensive logging that was ongoing throughout the 1940s and 1950s.
 W
WThe Cypress Creek National Wildlife Refuge is located in the Cache River watershed in southernmost Illinois, largely in Pulaski County, but with extensions into Union, Alexander, and Johnson counties. The refuge was established in 1990 under the authority of the Emergency Wetlands Resources Act of 1986. The refuge protects over 16,000 acres (65 km2) of the Cache River wetlands, and has a purchase boundary of 36,000 acres (146 km²) contiguous.
 W
WDelaware Bay is the estuary outlet of the Delaware River on the northeast seaboard of the United States. Approximately 782 square miles (2,030 km2) in area, the bay's fresh water mixes for many miles with the salt water of the Atlantic Ocean.
The Door Peninsula is a peninsula in eastern Wisconsin, separating the southern part of the Green Bay from Lake Michigan. The peninsula includes northern Brown and Kewaunee counties and all of Door County. It is the western portion of the Niagara Escarpment. Well known for its cherry and apple orchards, the Door Peninsula is a popular tourism destination. With the 1881 completion of the Sturgeon Bay Ship Canal, the northern half of the peninsula became an island.
 W
WElkhorn Slough is a 7-mile-long (11 km) tidal slough and estuary on Monterey Bay in Monterey County, California. The community of Moss Landing and the Moss Landing Power Plant are located at the mouth of the slough on the bay.
 W
WThe Emiquon National Wildlife Refuge is a 11,122-acre (45.01 km2) wetland wildlife refuge located in Waterford Township in Fulton County, Illinois across the Illinois River from the town of Havana. Only 3,000 acres (12 km2) are currently managed by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service as part of the Illinois River National Wildlife and Fish Refuges Complex. It is in the Central forest-grasslands transition ecoregion.
 W
WEverglades National Park is an American national park that protects the southern twenty percent of the original Everglades in Florida. The park is the largest tropical wilderness in the United States, and the largest wilderness of any kind east of the Mississippi River. An average of one million people visit the park each year. Everglades is the third-largest national park in the contiguous United States after Death Valley and Yellowstone. UNESCO declared the Everglades & Dry Tortugas Biosphere Reserve in 1976, and listed the park as a World Heritage Site in 1979, while the Ramsar Convention included the park on its list of Wetlands of International Importance in 1987. Everglades is one of only three locations in the world to appear on all three lists.
 W
WThe Edwin B. Forsythe National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge located in southern New Jersey along the Atlantic coast north of Atlantic City, in Atlantic and Ocean counties. The refuge was created in 1984 out of two existing refuge parcels created to protect tidal wetland and shallow bay habitat for migratory water birds. The Barnegat Division is located in Ocean County on the inland side of Barnegat Bay. The Brigantine Division is located approximately 10 miles (16 km) north of Atlantic City along the south bank of the mouth of the Mullica River. The two divisions are separated by approximately 20 miles (32 km). The refuge is located along most active flight paths of the Atlantic Flyway, making it an important link in the network of national wildlife refuges administered nationwide by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Forsythe Refuge is a part of the Hudson River/New York Bight Ecosystem and The New Jersey Coastal Heritage Trail Route. The refuge is named for Edwin B. Forsythe, conservationist Congressman from New Jersey.
 W
WThe Francis Beidler Forest is an Audubon wildlife sanctuary in Four Holes Swamp, a blackwater creek system in South Carolina, United States. It consists of over 16,000 acres (65 km²) of mainly bald cypress and tupelo gum hardwood forest and swamp with approximately 1,800 acres (7 km2) of old-growth forest. It is the largest virgin stand of these trees in the world, with some trees over 1,000 years old. It is a favorite haunt of birdwatchers and is used for biological research projects by area schools.
 W
WHeron Pond – Little Black Slough Nature Preserve is a parcel of protected wetland property located approximately 5 miles (8 km) southwest of Vienna in Johnson County, Illinois. It was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1972. As part of the Cache River basin, it is classified as a wetland of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
 W
WHoricon Marsh is a marsh located in northern Dodge and southern Fond du Lac counties of Wisconsin. It is the site of both a national and a state wildlife refuge. The silted-up glacial lake is the largest freshwater cattail marsh in the United States.
 W
WAdeline Jay Geo-Karis Illinois Beach State Park is part of the Illinois state park system and is located along Lake Michigan in Winthrop Harbor, Zion, Beach Park and unincorporated Benton Township in northeast Illinois. Together with lands to the north, including Chiwaukee Prairie, it forms the Chiwaukee Prairie Illinois Beach Lake Plain, an internationally recognized wet-land of importance under the Ramsar Convention. The park is broken into two units that encompass an area of 4,160 acres (1,683 ha) and contains over six miles of Lake Michigan shoreline.
 W
WThe Izembek National Wildlife Refuge is the smallest of the National Wildlife Refuges located in the U.S. state of Alaska. It lies on the northwest coastal side of central Aleutians East Borough. Almost all of the refuge was designated as wilderness in 1980 under the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act. The refuge is administered from offices in Cold Bay.
 W
WKakagon Sloughs is a lake in Ashland County, Wisconsin. Species of fish found in the lake include the northern pike, the walleye, panfish, the largemouth bass and the smallmouth bass. It is owned by the Bad River Band of the Lake Superior Tribe of Chippewa Indians. The lake was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1973. On February 2, 2012 it was designated a Ramsar Wetland of International Importance.
 W
WKawai Nui Marsh is, at over 800 acres (3.2 km2), the largest wetlands in the Hawaiian Islands. The marsh is located near Kailua on the windward side of O'ahu and is owned by the State of Hawaii and the City & County of Honolulu. 250 acres (1.0 km2) of the land is from a 1968 sale to the City and County of Honolulu by Kaneohe Ranch. Kawai Nui marsh is a Ramsar Convention wetland site, established in February 2005.
 W
WThe Laguna de Santa Rosa is a 22-mile-long (35 km) wetland complex that drains a 254-square-mile (660 km2) watershed encompassing most of the Santa Rosa Plain in Sonoma County, California, United States.
 W
WMissisquoi National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge located in the eastern shore of Lake Champlain in the U.S. state of Vermont. The refuge is in Franklin County in the northwest corner of the state near the International Boundary with Canada. It is the only National Wildlife Refuge located entirely in Vermont, and is administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service.
 W
WThe Niagara River is a river that flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. There are differing theories as to the origin of the river's name. According to Iroquoian scholar Bruce Trigger, Niagara is derived from the name given to a branch of the locally residing native Neutral Confederacy, who are described as being called the Niagagarega people on several late-17th-century French maps of the area. According to George R. Stewart, it comes from the name of an Iroquois town called Ongniaahra, meaning "point of land cut in two".
 W
WThe Okefenokee National Wildlife Refuge is a 402,000‑acre (1,627 km2) National Wildlife Refuge located in Charlton, Ware, and Clinch Counties of Georgia, and Baker County in Florida, United States. The refuge is administered from offices in Folkston, Georgia. The refuge was established in 1937 to protect a majority of the 438,000 acre (1,772 km2) Okefenokee Swamp. The name "Okefenokee" is a Native American word meaning "trembling earth."
 W
WPalmyra Atoll, also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Northern Line Islands. It is located almost due south of the Hawaiian Islands, roughly one-third of the way between Hawaii and American Samoa. The nearest continent is almost 3,355 miles to the northeast. The atoll is 4.6 sq mi (12 km2), lying in the equatorial Northern Pacific Ocean. Its 9 miles of coastline has one anchorage known as West Lagoon.
 W
WPelican Island National Wildlife Refuge is a United States National Wildlife Refuge (NWR), and part of the Everglades Headwaters NWR complex, located just off the western coast of Orchid Island in the Indian River Lagoon east of Sebastian, Florida. The refuge consists of a 3-acre (12,000 m2) island that includes an additional 2.5 acres (10,000 m2) of surrounding water and is located off the east coast of Florida of the Indian River Lagoon. Established by an executive order of President Theodore Roosevelt on March 14, 1903, Pelican Island was the first National wildlife refuge in the United States. It was created to protect egrets and other birds from extinction through plume hunting.
 W
WQuivira National Wildlife Refuge is located in south central Kansas near the town of Stafford. It lies mostly in northeastern Stafford County, but small parts extend into southwestern Rice and northwestern Reno Counties. Its proximity to the Central Flyway migration route and the salt marshes on the refuge combine to endow the refuge with a large variety of birds. Many of these birds are uncommon in other parts of Kansas or even the central part of the continent.
 W
WSan Francisco Bay is a shallow estuary in the US state of California. It is surrounded by a contiguous region known as the San Francisco Bay Area, and is dominated by the large cities of San Jose, San Francisco and Oakland.
 W
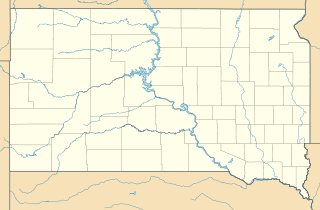
WSand Lake National Wildlife Refuge is located in the northeastern part of the U.S. state of South Dakota and is administered by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Created in 1935, it is a wetlands of international importance and a Globally Important Bird Area. Over 260 bird species are found in the refuge, including many migratory bird species and the world's largest breeding colony of Franklin's gulls.
 W
WTijuana River National Estuarine Research Reserve is a natural reserve in Imperial Beach, California and San Ysidro, San Diego. It encompasses the Tijuana River Estuary, located on the Mexico–United States border. It is divided into two parts: the Tijuana Slough National Wildlife Refuge on the north, and Border Field State Park in the south.
 W
WTomales Bay is a long, narrow inlet of the Pacific Ocean in Marin County in northern California in the United States. It is approximately 15 mi (24 km) long and averages nearly 1.0 mi (1.6 km) wide, effectively separating the Point Reyes Peninsula from the mainland of Marin County. It is located approximately 30 mi (48 km) northwest of San Francisco. The bay forms the eastern boundary of Point Reyes National Seashore. Tomales Bay is recognized for protection by the California Bays and Estuaries Policy. On its northern end, it opens out onto Bodega Bay, which shelters it from the direct current of the Pacific. The bay is formed along a submerged portion of the San Andreas Fault.
 W
WThe Upper Mississippi River National Wildlife and Fish Refuge is a 240,000-acre (970 km2), 261-mile long (420 km) National Wildlife Refuge located in and along the Upper Mississippi River. It runs from Wabasha, Minnesota in the north to Rock Island, Illinois in the south.
 W
WVernon Lake is a man-made lake in Vernon Parish, Louisiana. In 1963, Vernon Lake was created by the impounding of Anacoco Creek, creating a 4,200 acres (1,700 ha) lake for the purpose of water supply and recreation. The lake is five miles west of Leesville, and eight miles north of Anacoco Lake.
 W
WThe White River National Wildlife Refuge is a 160,756 acres (650.56 km2) wildlife refuge located in Desha, Monroe, Phillips, and Arkansas counties in the U.S. state of Arkansas. The refuge is managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service. White River NWR borders on Cache River National Wildlife Refuge at its northern boundary. In 1974, the White River Sugarberry Natural Area was designated as a National Natural Landmark by the National Park Service.
 W
WThe Wisconsin River is a tributary of the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Wisconsin. At approximately 430 miles (692 km) long, it is the state's longest river. The river's name, first recorded in 1673 by Jacques Marquette as "Meskousing", is rooted in the Algonquian languages used by the area's American Indian tribes, but its original meaning is obscure. French explorers who followed in the wake of Marquette later modified the name to "Ouisconsin", and so it appears on Guillaume de L'Isle's map. This was simplified to "Wisconsin" in the early 19th century before being applied to Wisconsin Territory and finally the state of Wisconsin.