 W
WA landscape is the visible features of an area of land, its landforms, and how they integrate with natural or man-made features. A landscape includes the physical elements of geophysically defined landforms such as (ice-capped) mountains, hills, water bodies such as rivers, lakes, ponds and the sea, living elements of land cover including indigenous vegetation, human elements including different forms of land use, buildings, and structures, and transitory elements such as lighting and weather conditions. Combining both their physical origins and the cultural overlay of human presence, often created over millennia, landscapes reflect a living synthesis of people and place that is vital to local and national identity.
 W
WAccona desert refers to a hilly area in the Siena province of Italy, within the municipality of Asciano [43°14'4.30"N; 11°33'37.48"E] often enlarged to include the biancana site of Le Fiorentine - Leonina [ 43°17'32.95”N; 11°26'54.07"E]. The term desert is inappropriate from a physical and climatic point of view, rather the climate is Mediterranean with a hot dry summer and almost 800 mm/y of rain. A real desert has never existed here, unless “desert” was a way of describing severely eroded areas, more properly called “badlands”, even if temporary ones.
 W
WIn agriculture, gardening, and landscaping, barkdust is a form of mulch produced out of chipped or shredded tree bark. Coarser forms of barkdust may be known as bark nuggets. Trees typically used in the production of barkdust include the Douglas fir and the Western hemlock.
 W
WThe terms barrier ridge, a term of art in the Earth Sciences, especially Geology and sometimes barrier range describing the existence of gross landforms describing long ridgelines which are particularly difficult to pass, especially in the context of being on foot or dependent upon other forms of animal powered transportation systems, in mountainous and sometimes hilly terrains.
 W
WThe terms barrier ridge, a term of art in the Earth Sciences, especially Geology and sometimes barrier range describing the existence of gross landforms describing long ridgelines which are particularly difficult to pass, especially in the context of being on foot or dependent upon other forms of animal powered transportation systems, in mountainous and sometimes hilly terrains.
 W
WBioswales are channels designed to concentrate and convey stormwater runoff while removing debris and pollution. Bioswales can also be beneficial in recharging groundwater.
 W
WThe Botanical garden of Upper Brittany is a private estate, open to the public, with an area of 25 hectares, located in the Ille-et-Vilaine department of Brittany, near the medieval city of Fougères. The park is part of the estate of "La Foltière", where stands the "Château de la Foltière", built in 1847.
 W
WSchönburg Castle is in the municipality of Schönburg 4.5 kilometers east of Naumburg at the heart of Federal Republic of Germany in the State of Saxony-Anhalt. It has been proposed by Germany for inscription in the List of World Heritage.
 W
WA check dam is a small, sometimes temporary, dam constructed across a swale, drainage ditch, or waterway to counteract erosion by reducing water flow velocity. Check dams themselves are not a type of new technology; rather, they are an ancient technique dating from the second century A.D. Check dams are typically, though not always, implemented in a system of several dams situated at regular intervals across the area of interest.
 W
WIn the visual arts a cityscape is an artistic representation, such as a painting, drawing, print or photograph, of the physical aspects of a city or urban area. It is the urban equivalent of a landscape. Townscape is roughly synonymous with cityscape, though it implies the same difference in urban size and density implicit in the difference between the words city and town. In urban design the terms refer to the configuration of built forms and interstitial space.
 W
WThe cottage garden is a distinct style that uses informal design, traditional materials, dense plantings, and a mixture of ornamental and edible plants. English in origin, it depends on grace and charm rather than grandeur and formal structure. Homely and functional gardens connected to working-class cottages go back centuries, but their stylized reinvention occurred in 1870s England, as a reaction to the more structured, rigorously maintained estate gardens with their formal designs and mass plantings of greenhouse annuals.
 W
WThe European green infrastructure is an important part of the new (post-2010) EU strategy for biodiversity and biodiversity policy.
 W
WThe Fab Tree Hab is a hypothetical ecological home design developed at MIT by Mitchell Joachim, Javier Arbona and Lara Greden. With the idea of easing the burden humanity places on the environment with conventional housing by growing "living, breathing" tree homes.
 W
WA garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the display, cultivation, or enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature, as an ideal setting for social or solitary human life. The single feature identifying even the wildest wild garden is control. The garden can incorporate both natural and man-made materials.
 W
WGarden design is the art and process of designing and creating plans for layout and planting of gardens and landscapes. Garden design may be done by the garden owner themselves, or by professionals of varying levels of experience and expertise. Most professional garden designers have some training in horticulture and the principles of design. Some are also landscape architects, a more formal level of training that usually requires an advanced degree and often a state license. Amateur gardeners may also attain a high level of experience from extensive hours working in their own gardens, through casual study, serious study in Master Gardener Programs, or by joining gardening clubs.
 W
WA garden / flora festival or exposition is a festival and exposition held to celebrate the arts of gardening, garden design, landscaping and landscape architecture. There are local garden festivals, regional garden festivals, national garden festivals and international garden festivals. The idea probably originated with Germany's Bundesgartenschau. The UK held five garden festivals in the period 1984–1992.
 W
WGoseck, a monastery built on the foundations of a castle, as well as the vineyard of Dechantenberg is located in the municipality of Goseck of Saxony-Anhalt in Germany. It has been proposed by Germany for inscription in the List of World Heritage. The World Heritage nomination Naumburg Cathedral and the High Medieval Cultural Landscape of the Rivers Saale and Unstrut is representative for the processes that shaped the continent during the High Middle Ages between 1000 and 1300: Christianization, the so-called “Landesausbau” and the dynamics of cultural exchange and transfer characteristic for this very period.
 W
WA grassed waterway is a 2-metre (6.6 ft) to 48-metre-wide native grassland strip of green belt. It is generally installed in the thalweg, the deepest continuous line along a valley or watercourse, of a cultivated dry valley in order to control erosion. A study carried out on a grassed waterway during 8 years in Bavaria showed that it can lead to several other types of positive impacts, e.g. on biodiversity.
 W
WGreen infrastructure or blue-green infrastructure is a network providing the “ingredients” for solving urban and climatic challenges by building with nature. The main components of this approach include stormwater management, climate adaptation, less heat stress, more biodiversity, food production, better air quality, sustainable energy production, clean water and healthy soils, as well as the more anthropocentric functions such as increased quality of life through recreation and providing shade and shelter in and around towns and cities. Green infrastructure also serves to provide an ecological framework for social, economic and environmental health of the surroundings.
 W
WGroenendaal park lies at the center of Heemstede, Netherlands. The park includes the grounds of old Heemstede country estates Bosbeek, and Meer en Berg. Along its western borders are the old Heemstede country estates Hartekamp, Huis te Manpad, and Iepenrode. On the eastern boundary is the city cemetery.
 W
WThe villages of Großwilsdorf and the Rödel Plateau are situated in Saxony-Anhalt in the middle of Germany. It has been proposed by Germany for inscription in the List of World Heritage. The World Heritage nomination Naumburg Cathedral and the High Medieval Cultural Landscape of the Rivers Saale and Unstrut is representative for the processes that shaped the continent during the High Middle Ages between 1000 and 1300: Christianization, the so-called Landesausbau and the dynamics of cultural exchange and transfer characteristic for this very period.
 W
WSlieve Gullion is a mountain in the south of County Armagh, Northern Ireland. The mountain is the heart of the Ring of Gullion and is the highest point in the county, with an elevation of 573 metres (1,880 ft). At the summit is a small lake and two ancient burial cairns, one of which is the highest surviving passage grave in Ireland. Slieve Gullion appears in Irish mythology, where it is associated with the Cailleach and the heroes Fionn mac Cumhaill and Cú Chulainn. It dominates the countryside around it, offering views as far away as Antrim, Dublin Bay and Wicklow on a clear day. Slieve Gullion Forest Park is on its eastern slope.
 W
WHardscape refers to hard landscape materials in the built environment structures that are incorporated into a landscape. This can include paved areas, driveways, retaining walls, sleeper walls, stairs, walkways, and any other landscaping made up of hard wearing materials such as wood, stone, and concrete, as opposed to softscape, the horticultural elements of a landscape.
 W
WThe discussion of the history of landscape architecture is a complex endeavor as it shares much of its history with that of landscape gardening and architecture, spanning the entirety of man's existence. However, it was not until relatively recent history that the term "landscape architecture" or even "landscape architect" came into common use.
 W
WHügelkultur is a horticultural technique where a mound constructed from decaying wood debris and other compostable biomass plant materials is later planted as a raised bed. Adopted by permaculture advocates, it is suggested the technique helps to improve soil fertility, water retention, and soil warming, thus benefiting plants grown on or near such mounds.
 W
WHydroelectricity is electricity produced from hydropower. In 2015, hydropower generated 16.6% of the world's total electricity and 70% of all renewable electricity, and was expected to increase by about 3.1% each year for the next 25 years.
 W
WKleinjena is situated 4 kilometres north of Naumburg on a long spur at the foot of the Finne mountain range above the village of Kleinjena, at the heart of Federal Republic of Germany in the State of Saxony-Anhalt. It has been proposed by Germany for inscription in the List of World Heritage. The World Heritage nomination is representative for the processes that shaped the continent during the High Middle Ages between 1000 and 1300: Christianization, the so-called "Landesausbau" and the dynamics of cultural exchange and transfer characteristic for this very period.
 W
WLand rehabilitation as a part of environmental remediation is the process of returning the land in a given area to some degree of its former state, after some process has resulted in its damage. Many projects and developments will result in the land becoming degraded, for example mining, farming and forestry.
 W
WA landform is a natural or artificial feature of the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Typical landforms include hills, mountains, plateaus, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins.
 W
WLandscape contracting is: "a profession that involves the art and technology of landscape and garden project planning, construction and landscape management, and maintenance and gardening; for garden aesthetics, human enjoyment and safety, and ecosystem-plant community sustainability."
 W
WLandscape detailing describes the process of integrating soft and hard landscape materials to create a landscape design. It requires knowledge of:landscape architecture landscape engineering landscape products
 W
WLandscape ecology is the science of studying and improving relationships between ecological processes in the environment and particular ecosystems. This is done within a variety of landscape scales, development spatial patterns, and organizational levels of research and policy. Concisely, landscape ecology can be described as the science of landscape diversity as the synergetic result of biodiversity and geodiversity.
 W
WThe Landscape Institute (LI) is a UK based professional body for the landscape profession. Its membership includes landscape architects, urban designers, landscape planners, landscape scientists and landscape managers. The LI also has a category for academic members.
 W
WLandscaping refers to any activity that modifies the visible features of an area of land, including:Living elements, such as flora or fauna; or what is commonly called gardening, the art and craft of growing plants with a goal of creating a beauty within the landscape. Natural elements such as landforms, terrain shape and elevation, or bodies of water; and Abstract elements such as the weather and lighting conditions.
 W
WLow-impact development (LID) is a term used in Canada and the United States to describe a land planning and engineering design approach to manage stormwater runoff as part of green infrastructure. LID emphasizes conservation and use of on-site natural features to protect water quality. This approach implements engineered small-scale hydrologic controls to replicate the pre-development hydrologic regime of watersheds through infiltrating, filtering, storing, evaporating, and detaining runoff close to its source. Green infrastructure investments are one approach that often yields multiple benefits and builds city resilience.
 W
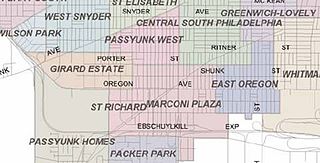
WMarconi Plaza is an urban park square located in South Philadelphia, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The plaza was named to recognize the 20th-century cultural identity in Philadelphia of the surrounding Italian-American enclave neighborhood and became the designation location of the annual Columbus Day Parade.
 W
WNational Conservation Lands, formally known as the National Landscape Conservation System, is a 35-million-acre (140,000 km2) collection of lands in 873 federally recognized areas considered to be the crown jewels of the American West. These lands represent 10% of the 258 million acres (1,040,000 km2) managed by the Bureau of Land Management (BLM). The BLM is the largest federal public land manager and is responsible for over 40% of all the federal public land in the nation. The other major federal public land managers include the US Forest Service (USFS), National Park Service (NPS), and the US Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS).
 W
WA natural landscape is the original landscape that exists before it is acted upon by human culture. The natural landscape and the cultural landscape are separate parts of the landscape. However, in the 21st century, landscapes that are totally untouched by human activity no longer exist, so that reference is sometimes now made to degrees of naturalness within a landscape.
 W
WThe Naumburg Cathedral and the High Medieval Cultural Landscape of the Rivers Saale and Unstrut is situated at the heart of the Federal Republic of Germany in the State of Saxony-Anhalt. Naumburg Cathedral and the landscpae has been proposed by Germany for inscription in the List of World Heritage. On July 1, 2018, only Naumburg Cathedral was listed as a UNESCO World Heritage site.
 W
WAn observation deck, observation platform, or viewing platform is an elevated sightseeing platform usually situated upon a tall architectural structure, such as a skyscraper or observation tower. Observation decks are sometimes enclosed from weather, and a few may include coin-operated telescopes for viewing distant features.
 W
WThe Olmsted Brothers company was an influential landscape architectural firm in the United States, established in 1898 by brothers John Charles Olmsted (1852–1920) and Frederick Law Olmsted Jr. (1870–1957), sons of the eminent landscape architect Frederick Law Olmsted.
 W
WA park is an area of natural, semi-natural or planted space set aside for human enjoyment and recreation or for the protection of wildlife or natural habitats. Urban parks are green spaces set aside for recreation inside towns and cities. National parks and country parks are green spaces used for recreation in the countryside. State parks and provincial parks are administered by sub-national government states and agencies. Parks may consist of grassy areas, rocks, soil and trees, but may also contain buildings and other artifacts such as monuments, fountains or playground structures. Many parks have fields for playing sports such as baseball and football, and paved areas for games such as basketball. Many parks have trails for walking, biking and other activities. Some parks are built adjacent to bodies of water or watercourses and may comprise a beach or boat dock area. Urban parks often have benches for sitting and may contain picnic tables and barbecue grills.
 W
WA parkway is a landscaped thoroughfare. The term is particularly used for a roadway in a park or connecting to a park from which trucks and other heavy vehicles are excluded.
 W
WPermeable paving is a method of paving vehicle and pedestrian pathways to enable infiltration of stormwater runoff. Permeable pavement surfaces typically include pervious concrete, porous asphalt, paving stones and interlocking pavers. Unlike traditional impervious paving materials, permeable paving systems allow stormwater to percolate and infiltrate through the pavement and into the aggregate layers and/or soil below. In addition to reducing surface runoff, permeable paving systems can trap suspended solids, thereby filtering pollutants from stormwater. The goal is to control stormwater at the source, reduce runoff and improve water quality by filtering pollutants in the subsurface layers.
 W
WA public open space is defined as an open piece of land both green space or hard space to which there is public access.
 W
WSchleberoda is a village and a former municipality in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Since 1 July 2009, it is part of the town Freyburg.
 W
WA seascape is a photograph, painting, or other work of art which depicts the sea, in other words an example of marine art. The word originated as a formation from landscape, which was first used of images of land in art. By a similar development, "seascape" has also come to mean actual views of the sea itself, and to be applied in planning contexts to geographical locations possessing a good view of the sea.
 W
WA shade tree is a large tree whose primary role is to provide shade in the surrounding environment due to its spreading canopy and crown, where it may give shelter from sunlight in the heat of the summer for people who seek recreational needs in urban parks and house yards, and thus, also protecting them from the sun's harmful UV rays and sunburns. Therefore, some shade trees may be grown specifically for the comfort of the population due to their convenient shelter.
 W
WA stile is a structure or opening that provides people passage over or through a boundary via steps, ladders, or narrow gaps. Stiles are often built in rural areas along footpaths, fences, walls, or hedges that enclose animals, allowing people to move freely.
 W
WSustainable cities, urban sustainability, or eco-city is a city designed with consideration for social, economic, environmental impact, and resilient habitat for existing populations, without compromising the ability of future generations to experience the same. The UN Sustainable Development Goal 11 defines sustainable cities as those that are dedicated to achieving green sustainability, social sustainability and economic sustainability. They are committed to doing so by enabling opportunities for all through a design focused on inclusivity as well as maintaining a sustainable economic growth. The focus also includes minimizing required inputs of energy, water, and food, and drastically reducing waste, output of heat, air pollution – CO2, methane, and water pollution. Richard Register first coined the term "ecocity" in his 1987 book Ecocity Berkeley: Building Cities for a Healthy Future, where he offers innovative city planning solutions that would work anywhere. Other leading figures who envisioned sustainable cities are architect Paul F Downton, who later founded the company Ecopolis Pty Ltd, as well as authors Timothy Beatley and Steffen Lehmann, who have written extensively on the subject. The field of industrial ecology is sometimes used in planning these cities.
 W
WA swale is a shady spot, or a sunken or marshy place. In particular, in US usage, it is a shallow channel with gently sloping sides. Such a swale may be either natural or man-made. Artificial swales are often infiltration basins, designed to manage water runoff, filter pollutants, and increase rainwater infiltration.
 W
WUrban design is the process of designing and shaping the physical features of cities, towns, and villages and planning for the provision of municipal services to residents and visitors. Although it deals with issues of a larger scale than architecture, it cannot be understood as a wholly separated field of research and design, since the quality of one depends on the quality of the other. In fact, it is this very interdependency, which has been termed relational design by Barcelona-based architect Enric Massip-Bosch, which makes urban design and architecture inextricably linked in many university education programs, especially in Europe. This tendency towards reintegration in architectural studies is also gaining momentum in the USA.
 W
WA village green is a common open area within a village or other settlement. Historically, a village green was common grassland with a pond for watering cattle and other stock, often at the edge of a rural settlement, used for gathering cattle to bring them later on to a common land for grazing. Later, planned greens were built into the centres of villages.
 W
WA water bar or interceptor dyke is a road construction feature that is used to prevent erosion on sloping roads, cleared paths through woodland, or other accessways by reducing flow length. It is a diagonal channel across the road that diverts surface water off the road and into a stable drain way. By constructing a series of water bars at intervals along a road, the volume of water flowing down the road is reduced. Without water bars, flooding, washouts, and accelerated road degradation can occur.