 W
WRichard Andree was a German geographer and cartographer, noted for devoting himself especially to ethnographic studies. He wrote numerous books on this subject, dealing notably with the races of his own country, while an important general work was Ethnographische Parallelen und Vergleiche.
 W
WPhilipp Apian was a German mathematician and medic. The son of Petrus Apianus (1495–1552), he is also known as the cartographer of Bavaria.
 W
WMartin Behaim, also known as Martin von Behaim and by various forms of Martin of Bohemia, was a German textile merchant and cartographer. He served John II of Portugal as an adviser in matters of navigation and participated in a voyage to West Africa. He is now best known for his Erdapfel, the world's oldest surviving globe, which he produced for the Imperial City of Nuremberg in 1492.
 W
WWalter Emmerich Behrmann was a German geographer. He is remembered for introducing a cylindrical map projection known as the "Behrmann projection".
 W
WHeinrich Karl Wilhelm Berghaus was a German geographer and cartographer who conducted trigonometric surveys in Prussia and taught geodesy at the Bauakademie in Berlin. He taught cartography and produced a pioneering and influential thematic atlas which provided maps of flora, fauna, climate, geology, diseases and a range of other information. He was a friend of Alexander von Humboldt and produced some of the maps used in his publications. A nephew Hermann Berghaus also worked in cartography.
 W
WHermann Berghaus was a German cartographer.
 W
WGeorg Braun was a topo-geographer. From 1572 to 1617 he edited the Civitates orbis terrarum, which contains 546 prospects, bird's-eye views and maps of cities from all around the world. He was the principal editor of the work, he acquired the tables, hired the artists, and wrote the texts. He died as an octogenarian in 1622, as the only survivor of the original team to witness the publication of volume VI in 1617.
 W
WConrad Buno, was a German copperplate engraver, cartographer and publisher at the court of Wolfenbüttel (Guelpherbytum) and brother of Johann Buno (1617–1697), the theologian and pedagogue from Lüneburg.
 W
WHeinrich Bünting was a Protestant pastor and theologian. He is best known for his book of woodcut maps titled Itinerarium Sacrae Scripturae first published in 1581.
 W
WCarl Diercke was a German cartographer.
 W
WMax Eckert was a German geographer.
 W
WJohann Friedrich Endersch was a German cartographer and mathematician. Endersch also held the title of Royal Mathematician to King Augustus III of Poland.
 W
WErhard Etzlaub, was an astronomer, geodesist, cartographer, instrument maker and physician.
 W
WJoseph Fischer, S.J. was a German clergyman and cartographer. Fischer had an eminently successful career as a cartographer, publishing old maps. In 1901, while he was investigating the Vikings' discovery of America, he accidentally discovered the long-lost map of Martin Waldseemüller, dated 1507. This map, which claims to update Ptolemy with the voyages of Amerigo Vespucci, is the first known to display the word America. The map was purchased from its owner by the United States Library of Congress in 2001 for ten million dollars.
 W
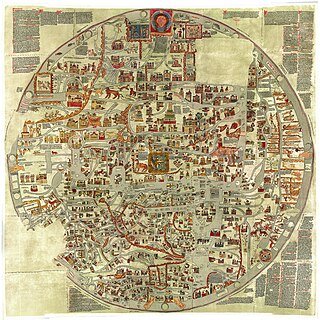
WGervase of Ebstorf is best known as the author of the Ebstorf Map, a medieval mappa mundi created in around 1234.
 W
WFryderyk Getkant or Frederick Getkant (1600–1666) was a Prussian military engineer of Lithuanian descent, artillery lieutenant and cartographer,. He is also known as a first who had written down Lithuanian folk song with melody in 1634.
 W
WFranz Ludwig Güssefeld was a German cartographer. He is noted for his highly accurate maps which were mostly published by Homannsche Erben in Nuremberg.
 W
WBruno Hassenstein was a German cartographer born in Ruhla, Thuringia.
 W
WMartin Helwig was a German cartographer of and from Silesia and pedagogue. He was born in Neisse and died in Breslau, Holy Roman Empire.
 W
WCaspar Hennenberger was a German Lutheran pastor, historian and cartographer.
 W
WAugustin Hirschvogel was a German artist, mathematician, and cartographer known primarily for his etchings. His thirty-five small landscape etchings, made between 1545 and 1549, assured him a place in the Danube School, a circle of artists in sixteenth-century Bavaria and Austria.
 W
WJohann Baptist Homann was a German geographer and cartographer, who also made maps of the Americas.
 W
WJohannes Honter was a Transylvanian Saxon, renaissance humanist, Protestant reformer, and theologian. Honter is best known for his geographic and cartographic publishing activity, as well as for implementing the Lutheran reform in Transylvania and founding the Evangelical Church of Augustan Confession in Romania.
 W
WRichard Kiepert was a German cartographer born in Weimar. He was the son of famed geographer Heinrich Kiepert.
 W
WKarl Julius Heinrich Lange was a German cartographer.
 W
WEilhard Lubinus was a German Lutheran theologian and philosopher, also known as a classical scholar, mathematician and cartographer. He was an influence on Comenius.
 W
WHenricus Martellus Germanus is the latinized name of Heinrich Hammer, a geographer and cartographer from Nuremberg who lived and worked in Florence from 1480 to 1496.
 W
WCount Ludwig August Mellin was a Baltic German politician, cartographer, writer and publicist. He is best known for creating the first professional atlas visualizing Livonia, the Atlas von Liefland, oder von den beyden Gouvernementern u. Herzogthümern Lief- und Ehstland, und der Provinz Oesel in 1798.
 W
WFriedrich Karl Ferdinand Freiherr von Müffling, called Weiss was a Prussian Generalfeldmarschall and military theorist. He served as Blücher's liaison officer in Wellington's headquarters during the Battle of Waterloo and was one of the organizers of the final victory over Napoleon. After the wars he served a diplomatic role at the Congress of Aix-la-Chappelle and was a major contributor to the development of the Prussian General Staff as Chief. Müffling also specialized in military topography and cartography.
 W
WSebastian Münster was a German cartographer, cosmographer, and a Christian Hebraist scholar. His work, the Cosmographia from 1544, was the earliest German description of the world.
 W
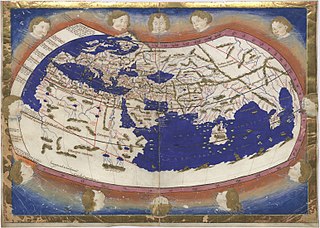
WNicolaus Germanus was a German cartographer who published an edition of Jacopo d'Angelo's Latin translation of Ptolemy's Geography. He also created two globes depicting earth and sky in 1477, predating Martin Behaim's Erdapfel.
 W
WCarsten Niebuhr, or Karsten Niebuhr, was a German mathematician, cartographer, and explorer in the service of Denmark. He is renowned for his participation in the Royal Danish Arabia Expedition (1761-1767). He was the father of the Danish-German statesman and historian Barthold Georg Niebuhr, who published an account of his father's life in 1817.
 W
WCarl Ludwig von Oesfeld was the Royal Prussian Privy Councillor and a German cartographer.
 W
WDietrich Heinrich Ludwig von Ompteda was a Hanoverian jurist and government minister.
 W
WAugustus Heinrich Petermann was a German cartographer.
 W
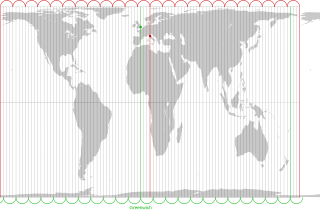
WArno Peters was a German historian who developed the Peters world map, based on the Gall–Peters projection.
 W
WFriedrich Wilhelm Putzger was a German teacher and cartographer.
 W
WCarl August Rathjens was a German geographer whose primary interests were in South Arabian historiography, geology and ethnography. He made several visits to Yemen, in the years 1927, 1931, 1934 and 1938. He is considered the greatest scholar of Yemeni research in the 20th century. He contributed more than any other in conducting scientific and ethnographic research, resulting in a wide range of findings, and he has left over 2500 ethnographical items and some 4000 positive and negative photographs from South Arabia.
 W
WChristian Gottlieb Reichard was a German cartographer born in Schleiz, Thuringia. He studied law in Leipzig and subsequently became a city official in Bad Lobenstein.
 W
WMatthias Ringmann (1482–1511), also known as Philesius Vogesigena, was an Alsatian German humanist scholar, cosmographer, and poet. Along with cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, he is credited with the first documented usage of the word America, on the 1507 map Universalis Cosmographia in honour of the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci.
 W
WHermann von Rosenberg was a German naturalist born in Darmstadt. He published a few books and several articles concerning his work in the East Indies. In these he describes the geography, zoology, linguistics and ethnography of the islands.
 W
WHartmann Schedel was a German historian, physician, humanist, and one of the first cartographers to use the printing press. He was born and died in Nuremberg. Matheolus Perusinus served as his tutor.
 W
WJohannes Schöner was a renowned and respected German polymath. It is best to refer to him using the usual 16th-century Latin term "mathematicus", as the areas of study to which he devoted his life were very different from those now considered to be the domain of the mathematician. He was a priest, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, cosmographer, cartographer, mathematician, globe and scientific instrument maker and editor and publisher of scientific tests. In his own time he enjoyed a European wide reputation as an innovative and influential globe maker and cosmographer and as one of the continent's leading and most authoritative astrologers. Today he is remembered as an influential pioneer in the history of globe making and as a man who played a significant role in the events that led up to the publishing of Copernicus' "De revolutionibus" in Nürnberg in 1543.
 W
WMatthäus Seutter was one of the most important and prolific German map publishers of the 18th century.
 W
WKarl Spruner von Merz, or Karl von Spruner as he preferred to be known, was a German cartographer and scholar.
 W
WAdolf Stieler was a German cartographer and lawyer who worked most of his life in the Justus Perthes Geographical Institute in Gotha. Although he studied law and would serve in government for his entire career, he maintained an interest in cartography and published many famous works. His Handatlas was the leading German world atlas until the middle of the 20th century.
 W
WEmil von Sydow was a German geographer and cartographer born in Freiberg, Saxony.
 W
WGeorg Tannstetter, also called Georgius Collimitius, was a humanist teaching at the University of Vienna. He was a medical doctor, mathematician, astronomer, cartographer, and the personal physician of the emperors Maximilian I and Ferdinand I. He also wrote under the pseudonym of "Lycoripensis". His Latin name "Collimitius" is derived from limes meaning "border" and is a reference to his birth town: "Rain" is a German word for border or boundary.
 W
WGeorg Heinrich Tischbein was a German engraver, etcher, cartographer and engineer from the Tischbein family of artists.
 W
WCaspar Vopel (1511–1561) was a German cartographer and instrument maker. Born in Medebach, he studied mathematics and medicine at the University of Cologne in 1526–1529. He taught mathematics at the Gymnasium of Cologne and in the early 1530s established a workshop to produce celestial and terrestrial globes, armillary spheres, sundials, quadrants and astrolabes. An exemplar of Vopel’s 1536 globe is held at Tenri University Library, Nara. In 1545 he began to prepare maps and atlases. His mappemonde of 1545 is titled NOVA ET INTEGRA VNIVERSALISQVE ORBIS TOTIVS IVXTA GERMANVM NEOTERICORVM TRADITIONEM DESCRIPTIO . Vopel is sometimes credited with the promotion of the ancient asterism Coma Berenices to constellation status.
 W
WHermann Wagner was a German geographer and cartographer who was a native of Erlangen. He was the son of anatomist Rudolf Wagner (1805–1864) and brother to economist Adolph Wagner (1835–1917).
 W
WMartin Waldseemüller was a German cartographer and humanist scholar. Sometimes known by the Latinized form of his name, Hylacomylus, his work was influential among contemporary cartographers. He and his collaborator, Matthias Ringmann, are credited with the first recorded usage of the word America to name a portion of the New World in honour of the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci. Waldseemüller was also the first to map South America as a continent separate from Asia; the first to produce a printed globe and the first to create a printed wall map of Europe. A set of his maps printed as an appendix to the 1513 edition of Ptolemy's Geography is considered to be the first example of a modern atlas.
 W
WAndreas Walsperger was a German cartographer of the 15th century. The son of a carpenter, he became a Benedictine monk at St. Peter's in Salzburg in 1434. He left the monastery in 1442. Little more is known about him except that in 1448/9 he created his map in Konstanz.
 W
WJohann(es) Werner was a German mathematician. He was born in Nuremberg, Germany, where he became a parish priest. His primary work was in astronomy, mathematics, and geography, although he was also considered a skilled instrument maker.
 W
W