 W
WInterbasin transfer or transbasin diversion are terms used to describe man-made conveyance schemes which move water from one river basin where it is available, to another basin where water is less available or could be utilized better for human development. The purpose of such designed schemes can be to alleviate water shortages in the receiving basin, to generate electricity, or both. Rarely, as in the case of the Glory River which diverted water from the Tigris to Euphrates River in modern Iraq, interbasin transfers have been undertaken for political purposes. While ancient water supply examples exist, the first modern developments were undertaken in the 19th century in Australia, India and the United States; large cities such as Denver and Los Angeles would not exist as we know them today without these diversion transfers. Since the 20th century many more similar projects have followed in other countries, including Israel, Canada and China. Utilized alternatively, the Green Revolution in India and hydropower development in Canada could not have been accomplished without such man-made transfers.
 W
WThe All-American Canal is an 80-mile (130 km) long aqueduct, located in southeastern California. It conveys water from the Colorado River into the Imperial Valley and to nine cities. It is the Imperial Valley's only water source, and replaced the Alamo Canal, which was located mostly in Mexico. The Imperial Dam, about 30 miles (48 km) northeast of Yuma, Arizona on the Colorado River, diverts water into the All-American Canal, which runs to just west of Calexico, California before its last branch heads mostly north into the Imperial Valley. Five smaller canals branching off the All American Canal move water into the Imperial Valley. These canal systems irrigate up to 630,000 acres (250,000 ha) of crop land and have made possible a greatly increased crop yield in this area, originally one of the driest on earth. It is the largest irrigation canal in the world, carrying a maximum of 26,155 cubic feet per second (740.6 m3/s). Agricultural runoff from the All American Canal drains into the Salton Sea.
 W
WThe Governor Edmund G. Brown California Aqueduct is a system of canals, tunnels, and pipelines that conveys water collected from the Sierra Nevada Mountains and valleys of Northern and Central California to Southern California. Named after California Governor Edmund Gerald "Pat" Brown Sr., the over 400-mile (640 km) aqueduct is the principal feature of the California State Water Project.
 W
WThe California State Water Project, commonly known as the SWP, is a state water management project in the U.S. state of California under the supervision of the California Department of Water Resources. The SWP is one of the largest public water and power utilities in the world, providing drinking water for more than 23 million people and generating an average of 6,500 GWh of hydroelectricity annually. However, as it is the largest single consumer of power in the state itself, it has a net usage of 5,100 GWh.
 W
WThe Catskill Aqueduct, part of the New York City water supply system, brings water from the Catskill Mountains to Yonkers where it connects to other parts of the system.
 W
WThe Central Arizona Project (CAP) is a 336 mi (541 km) diversion canal in Arizona in the southern United States.
 W
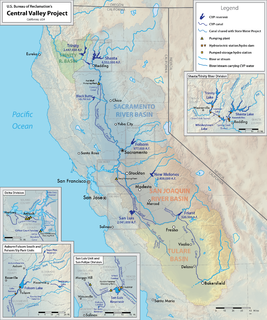
WThe Central Valley Project (CVP) is a federal power and water management project in the U.S. state of California under the supervision of the United States Bureau of Reclamation (USBR). It was devised in 1933 in order to provide irrigation and municipal water to much of California's Central Valley—by regulating and storing water in reservoirs in the northern half of the state, and transporting it to the water-poor San Joaquin Valley and its surroundings by means of a series of canals, aqueducts and pump plants, some shared with the California State Water Project (SWP). Many CVP water users are represented by the Central Valley Project Water Association.
 W
WThe Chicago Sanitary and Ship Canal, historically known as the Chicago Drainage Canal, is a 28-mile-long (45 km) canal system that connects the Chicago River to the Des Plaines River. It reverses the direction of the Main Stem and the South Branch of the Chicago River, which now flows out of Lake Michigan rather than into it. The related Calumet-Saganashkee Channel does the same for the Calumet River a short distance to the south, joining the Chicago canal about halfway along its route to the Des Plaines. The two provide the only navigation for ships between the Great Lakes Waterway and the Mississippi River system.
 W
WThe Coachella Canal is a 122-mile (196 km) aqueduct that conveys Colorado River water for irrigation northwest from the All-American Canal to the Coachella Valley north of the Salton Sea in Riverside County, California.
 W
WThe Colorado River Aqueduct, or CRA, is a 242 mi (389 km) water conveyance in Southern California in the United States, operated by the Metropolitan Water District of Southern California (MWD). The aqueduct impounds water from the Colorado River, at Lake Havasu on the California-Arizona border, west across the Mojave and Colorado deserts to the east side of the Santa Ana Mountains. It is one of the primary sources of drinking water for Southern California.
 W
WThe Colorado-Big Thompson Project is a federal water diversion project in Colorado designed to collect West Slope mountain water from the headwaters of the Colorado River and divert it to Colorado's Front Range and plains. In Colorado, approximately 80% of the state's precipitation falls on the West Slope, in the Rocky Mountains, while around 80% of the state's growing population lives along the East Slope, between the cities of Fort Collins and Pueblo.
 W
WThe Croton Aqueduct or Old Croton Aqueduct was a large and complex water distribution system constructed for New York City between 1837 and 1842. The great aqueducts, which were among the first in the United States, carried water by gravity 41 miles (66 km) from the Croton River in Westchester County to reservoirs in Manhattan. It was built because local water resources had become polluted and inadequate for the growing population of the city. Although the aqueduct was largely superseded by the New Croton Aqueduct, which was built in 1890, the Old Croton Aqueduct remained in service until 1955.
 W
WThe Daryan Dam, also spelled Darian, is an embankment dam constructed on the Sirvan River just north of Daryan in Paveh County, Kermanshah Province, Iran. The primary purpose of the dam is to supply up to 1,378,000,000 m3 (1,117,000 acre⋅ft) of water annually to the 48 km (30 mi) long Nosoud Water Conveyance Tunnel where it will irrigate areas of Southwestern Iran. The dam also has a 210 MW hydroelectric power station. Construction on the dam began in 2009 and the dam began to fill its reservoir in late November 2015. The Darian Dam Archaeological Salvage Program (DDASP) was planned by Iranian Center for Archaeological Research before flooding the reservoir. As a result a number of important archaeological sites were discovered and some were excavated. The power station was commissioned in 2018. The dam's diversion tunnel was completed in June 2011. The dam was designed by Stucky of France and consultation was provided by Mahab Ghodss, International Consulting Engineering Co. In August 2010 Farab Co. won the contract to build the power station. In 2011, workers on the project held a protest against unpaid wages. The dam is also the subject of protest due to the forced relocations and ecological/cultural impact its reservoir will have.
 W
WThe Delaware Aqueduct is an aqueduct in the New York City water supply system. It takes water from the Rondout, Cannonsville, Neversink, and Pepacton reservoirs on the west bank of the Hudson River through the Chelsea Pump Station, then into the West Branch, Kensico, and Hillview reservoirs on the east bank, ending in at Hillview in Yonkers, New York.
 W
WDillon Reservoir, sometimes referred to as Lake Dillon, is a large fresh water reservoir located in Summit County, Colorado, United States, south of I-70 and bordered by the towns of Frisco, Silverthorne, and Dillon. It is a reservoir for the city of Denver, and its waters are under the control of Denver Water. Popular ski areas are close to the reservoir, including Copper Mountain, Keystone, Arapahoe Basin, and Breckenridge.
 W
WThe Friant-Kern Canal is a 152 mi (245 km) aqueduct managed by the United States Bureau of Reclamation in Central California to convey water to augment irrigation capacity in Fresno, Tulare, and Kern counties. A part of the Central Valley Project, canal construction began in 1949 and was completed in 1951 at a cost of $60.8 million.
 W
WThe Fryingpan-Arkansas Project, or "Fry-Ark," is a water diversion, storage and delivery project serving southeastern Colorado. The multi-purpose project was authorized in 1962 by President Kennedy to serve municipal, industrial, and hydroelectric power generation, and to enhance recreation, fish and wildlife interests. Construction began in 1964 and was completed in 1981. The project includes five dams and reservoirs, one federal hydroelectric power plant, and 22 tunnels and conduits totaling 87 miles (140 km) in length. The Bureau of Reclamation, under the Department of the Interior built and manages the project.
 W
WThe Goldfields Water Supply Scheme is a pipeline and dam project that delivers potable water from Mundaring Weir in Perth to communities in Western Australia's Eastern Goldfields, particularly Coolgardie and Kalgoorlie. The project was commissioned in 1896 and completed in 1903.
 W
WThe Grand Ditch, also known as the Grand River Ditch and originally known as the North Grand River Ditch, is a water diversion project in the Never Summer Mountains, in northern Colorado. It is 14.3 miles (23.0 km) long, 20 feet (6.1 m) wide, and 3 feet (0.91 m) deep on average. Streams and creeks that flow from the highest peaks of the Never Summer Mountains are diverted into the ditch, which flows over the Continental Divide at La Poudre Pass at 10,175 feet (3,101 m), delivering the water into Long Draw Reservoir and the Cache La Poudre River for eastern plains farmers. The water would otherwise have gone into the Colorado River that flows west towards the Pacific; instead, the Cache La Poudre River goes East and through the Mississippi River discharges into the Gulf of Mexico.
 W
WThe Grand Prairie Area Demonstration Project is an interbasin transfer project to provide water to eastern Arkansas for the purposes of agricultural water supply, aquifer recharge, prairie and wetland restoration, water conservation and waterfowl management. The project, conceived by the US Army Corps of Engineers' Memphis District and approved by US Congress in 1950, generally involves the pumping of water from the White River near DeValls Bluff into pipelines and canals throughout Arkansas's Grand Prairie, specifically to farmers in Arkansas, Lonoke and Prairie counties. The new water source is intended to relieve groundwater pumping from the Alluvial and Sparta aquifers that underlie the Prairie.
 W
WThe Gunnison Tunnel is an irrigation tunnel constructed between 1905 and 1909 by the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation in Montrose County, Colorado. The 5.8 mile long tunnel diverts water from the Gunnison River to the arid Uncompahgre Valley around Montrose, Colorado.
 W
WHetch Hetchy is the name of a valley, a reservoir and a water system in California in the United States. The glacial Hetch Hetchy Valley lies in the northwestern part of Yosemite National Park and is drained by the Tuolumne River. For thousands of years before the arrival of settlers from the United States in the 1850s, the valley was inhabited by Native Americans who practiced subsistence hunting-gathering. During the late 19th century, the valley was renowned for its natural beauty – often compared to that of Yosemite Valley – but also targeted for the development of water supply for irrigation and municipal interests.
 W
WThe Indira Gandhi Canal is the longest canal of India. It starts from the Harike Barrage at Harike, a few kilometers below the confluence of the Satluj and Beas rivers in the Indian state of Punjab and terminates in irrigation facilities in the Thar Desert in the north west of Rajasthan state. Previously known as the Rajasthan Canal, it was renamed the Indira Gandhi Canal on 2 November 1984 following the assassination of Prime Minister Indira Gandhi.
 W
WThe Karakum Canal in Turkmenistan is one of the largest irrigation and water supply canals in the world. Started in 1954, and completed in 1988, it is navigable over much of its 1,375-kilometre (854 mi) length, and carries 13 cubic kilometres (3.1 cu mi) of water annually from the Amu-Darya River across the Karakum Desert in Turkmenistan. The canal opened up huge new tracts of land to agriculture, especially to cotton monoculture heavily promoted by the Soviet Union, and supplying Ashgabat with a major source of water. The canal is also a major factor leading to the Aral Sea environmental disaster.
 W
WThe Klamath Project is a water-management project developed by the United States Bureau of Reclamation to supply farmers with irrigation water and farmland in the Klamath Basin. The project also supplies water to the Tule Lake National Wildlife Refuge, and the Lower Klamath National Wildlife Refuge. The project was one of the first to be developed by the Reclamation Service, which later became the Bureau of Reclamation.
 W
WThe Klamath Project is a water-management project developed by the United States Bureau of Reclamation to supply farmers with irrigation water and farmland in the Klamath Basin. The project also supplies water to the Tule Lake National Wildlife Refuge, and the Lower Klamath National Wildlife Refuge. The project was one of the first to be developed by the Reclamation Service, which later became the Bureau of Reclamation.
 W
WThe Kouhrang 1 Dam is a masonry gravity dam on the Kouhrang River about 4 km (2.5 mi) southwest of Chelgard in Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Province, Iran. The primary purpose of the dam is to divert up to 320,000,000 m3 (260,000 acre⋅ft) of water annually via the 2.8 km (1.7 mi) long Kouhrang 1 Tunnel to the Zayandeh River to the east where it would help supply cities like Isfahan with water. Since the era of Shah Abbas I, attempts had been made to diver the Kouhrang to the Zayandeh. Eventually, efforts by Alexander Gibb between 1948 and 1954 led to the completion of the Kouhrang 1 Dam and Tunnel.
 W
WThe Kouhrang 3 Dam is an arch dam currently under construction on the Kouhrang River in Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Province, Iran. It is located about 12 km (7.5 mi) northwest of Dashtak. The purpose of the dam is water supply and river regulation. Upstream of the dam will be the intake for the 23 km (14 mi) Kouhrang 3 Tunnel which will transfer water northeast to the Zayandeh River for use in major cities like Isfahan. Sabir Co. was awarded the contract for the dam's construction in February 2011 and construction began that same year. The diversion tunnels for the dam were completed in March 2013. The project was scheduled for completed in 2015.
 W
WThe Kouhrang 2 Hydroelectric Power Station is located just south of Chelgard and about 69 km (43 mi) northwest of Shahrekord in Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Province, Iran. The power station has an installed capacity of 33.3 MW and uses water diverted to the east from the Kouhrang River, via a small dam and the 2 km (1.2 mi) long Kouhrang 2 Tunnel, to produce power. Water from the Kouhrang is stored in a circular dam before being sent to the power station. The power station's three generators were commissioned between 2002 and 2004, the power plant were inaugurated in February 2005. Water discharged from the power station enters the Zayandeh River as part of a larger project to provide water to major cities like Isfahan. The intake for the power plant is located on the Kouhrang River just downstream of the Kouhrang 1 Dam which also diverts water, via the 2,800 m (9,200 ft) long Kouhrang 2 Tunnel, to near Chelgard and was completed in 1953. The Kouhrang 3 Dam is planned downstream to regulate river flows and divert more water to the Zayandeh via the Kouhrang 3 Tunnel.
 W
WThe Kulekhani Dam is a rock-fill dam on the Kulekhani River near Kulekhani in Makwanpur District of Narayani Zone, Nepal. The primary purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power generation and it supports the 60 MW Kulekhani I and 32 MW Kulekhani II Hydropower Stations. Construction began in 1977 and Kulekhani I was commissioned in 1982. Kulekhani II was commissioned in 1986 and a third power station, the 14 MW Kulekhani III was expected to be commissioned in May 2015 but is delayed due to issues with the builder. The project has not been completed until the year 2017 and is expected to generate electricity by the end of 2018. The US$117.84 million project received funding from the World Bank, Kuwait Fund, UNDP, Overseas Economic Cooperation Fund and OPEC Fund. It is owned by Nepal Electricity Authority.
 W
WThe Los Angeles Aqueduct system, comprising the Los Angeles Aqueduct and the Second Los Angeles Aqueduct, is a water conveyance system, built and operated by the Los Angeles Department of Water and Power. The Owens Valley aqueduct was designed and built by the city's water department, at the time named The Bureau of Los Angeles Aqueduct, under the supervision of the department's Chief Engineer William Mulholland. The system delivers water from the Owens River in the Eastern Sierra Nevada Mountains to Los Angeles, California.
 W
WMansi Wakal is a dam on the Mansi River in Udaipur district, Rajasthan, India.
 W
WThe Melones Dam, also known as the Mayarí Dam, is a concrete-face rock-fill dam on the Mayarí River about 7 km (4.3 mi) south of Mayarí in Holguín Province, Cuba. It is the tallest dam in the country and the center-piece of the East–West Transvase System.
 W
WThe Misicuni Multiplepurpose Project, better known as the Misicuni Dam, is a concrete-face rock-fill dam constructed on the Misicuni River about 35 km (22 mi) northwest of the city of Cochabamba, Bolivia. The dam will divert water from the Misicuni River to the Cochabamba Valley for several purposes to include providing water for irrigation and municipal water uses. In addition, the dam has an associated 120 MW hydroelectric power station, powered by 3 turbines 40 MW each. Construction on the dam began in June 2009 but was halted in November 2013 due to contract disputes. The company finished the construction and is started the operations in September 2017.
 W
WThe Mokelumne Aqueduct is a 95-mile (153 km) water conveyance system in central California, United States. The aqueduct is supplied by the Mokelumne River and provides water to 35 municipalities in the East Bay in the San Francisco Bay Area. The aqueduct and the associated dams, pipelines, treatment plants and hydroelectric system are owned and operated by the East Bay Municipal Utility District (EBMUD) and provide over 90 percent of the water used by the agency.
 W
WMontgomery Reservoir lies high in Colorado's Mosquito Range near Hoosier Pass a few miles north of Alma, Colorado. The reservoir sits at an altitude of 10,873 feet. It is owned by Colorado Springs Utilities and delivers water to Colorado Springs, Colorado for municipal use. Built in 1957, the reservoir stores water from the Middle Fork South Platte River and from a tunnel that brings water from the Blue River on the west side of the continental divide.
 W
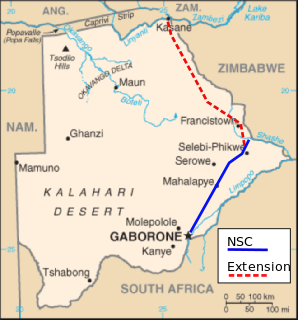
WMoralane is a key site on the North-South Carrier (NSC), in Botswana, the main pipeline delivering raw water from the northeast to the Mmamashia water treatment plant just north of Gaborone.
 W
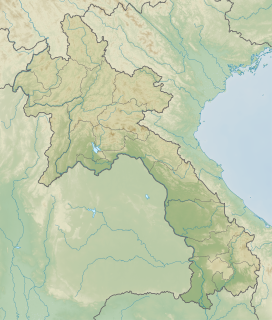
WThe Nam Theun 2 Hydropower Project, or simply NT2, is a hydroelectric dam on the Nam Theun River in Laos. Commercial operation of the plant began in April 2010. The scheme diverts water from the Nam Theun, a tributary of the Mekong River, to the Xe Bang Fai River, enabling a generation capacity of 1,075 MW, from a 350 m (1,148 ft) difference in elevation between the reservoir and the power station.
 W
WThe National Water Carrier of Israel is the largest water project in Israel. Its main purpose is to transfer water from the Sea of Galilee in the north of the country to the highly populated center and arid south and to enable efficient use of water and regulation of the water supply in the country. Up to 72,000 cubic meters of water can flow through the carrier each hour, totalling 1.7 million cubic meters in a day.
 W
WThe New Croton Aqueduct is an aqueduct in the New York City water supply system in Westchester County, New York carrying the water of the Croton Watershed. Built roughly parallel to the Old Croton Aqueduct it originally augmented, it opened in 1910. The old aqueduct remained in service until 1955, when supply from the Delaware and Catskill Aqueducts was sufficient to take it off line.
 W
WThe New Valley Project or Toshka Project consists of building a system of canals to carry water from Lake Nasser to irrigate part of the sandy wastes of the Western Desert of Egypt, which is part of the Sahara Desert. In 1997 the Egyptian government decided to develop a new valley where agricultural and industrial communities would develop. It has been an ambitious project which was meant to help Egypt cope with its rapidly growing population.
 W
WThe North Crimean Canal is a land improvement canal for irrigation and watering of Kherson Oblast in southern Ukraine, and the Crimean Peninsula. The canal also has multiple branches throughout Kherson Oblast and the Crimean Peninsula.
 W
WThe North-South Carrier (NSC) is a pipeline in Botswana that carries raw water south for a distance of 360 kilometres (220 mi) to the capital city of Gaborone. Phase 1 was completed in 2000. Phase 2 of the NSC, under construction, will duplicate the pipeline to carry water from the Dikgatlhong Dam, which was completed in 2012. A proposed extension to deliver water from the Zambezi would add another 500 to 520 kilometres to the total pipeline length. The NSC is the largest engineering project ever undertaken in Botswana.
 W
WThe North–South Pipeline, also known as the Sugarloaf Pipeline, is a water pipeline in Central Victoria, Australia, northeast of Melbourne that is part of Victoria's water system, acting as a link between Melbourne's water grid and the Murray-Goulburn water grid, supplying water via a series of existing and proposed pipelines. The 70-kilometre pipeline was connected to Melbourne in February 2010 to carry water from the Goulburn River to Melbourne’s Sugarloaf Reservoir. It is the government's policy that it only be used in times of critical human need: when Melbourne’s total water storages are less than 30% full on 30 November of any year. The pipeline can transfer a portion of Lake Eildon’s water that is set aside for Melbourne, called the critical water reserve. This was 38,400 megalitres at 2 June 2014, and any changes are based on Goulburn-Murray Water’s advice.
 W
WThe Orange–Fish Tunnel is a 82.8 kilometres long irrigation tunnel in central South Africa, built to divert water from the Orange River to the Fish River valley. It is the longest continuous enclosed aqueduct in the southern hemisphere.
 W
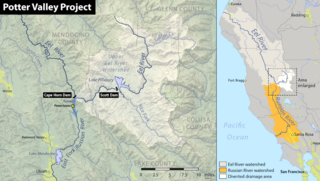
WThe Potter Valley Project is an interbasin water transfer project in Northern California in the United States, delivering water from the Eel River basin to the headwaters of the Russian River. The project is owned and operated by Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E). The main facilities are two dams on the Eel River, a diversion tunnel and hydroelectric plant. Average annual throughput is 159,000 acre⋅ft (196,000,000 m3), although this figure varies significantly with both the amount of precipitation in the Eel River basin and the demand on the Russian River.
 W
WThe San Juan–Chama Project is a U.S. Bureau of Reclamation interbasin water transfer project located in the states of New Mexico and Colorado in the United States. The project consists of a series of tunnels and diversions that take water from the drainage basin of the San Juan River – a tributary of the Colorado River – to supplement water resources in the Rio Grande watershed. The project furnishes water for irrigation and municipal water supply to cities along the Rio Grande including Albuquerque and Santa Fe.
 W
WSharq El Owainat is located in the New Valley Governorate of Egypt. It is in the south-west of the country, between the Nile and Libya.
 W
WThe Silveh Dam is an earth-fill embankment dam on the Lavin River just downstream of the village of Silveh in Piranshahr County, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran. The primary purpose of the dam is interbasin transfer for irrigation. Since completion, a tunnel and canals shift water from the reservoir north to the Chaparabad area. The project essentially transfers water from the Little Zab River basin to the Lake Urmia basin in an effort to help replenish the lake and irrigate about 9,400 ha of farmland. Construction on the dam began in 2004 and it was expected to be complete by the end of 2015. The dam was effectively completed as of 2018. The village of Silveh will be flooded when the reservoir is impounded.
 W
WThe Snowy Mountains scheme or Snowy scheme is a hydroelectricity and irrigation complex in south-east Australia. The Scheme consists of sixteen major dams; nine power stations; two pumping stations; and 225 kilometres (140 mi) of tunnels, pipelines and aqueducts that were constructed between 1949 and 1974. The Scheme was completed under the supervision of Chief Engineer, Sir William Hudson. It is the largest engineering project undertaken in Australia.
 W
WThe South–North Water Transfer Project, also translated as the South-to-North Water Diversion Project is a multi-decade infrastructure mega-project in China. Ultimately it aims to channel 44.8 billion cubic meters of fresh water annually from the Yangtze River in southern China to the more arid and industrialized north through three canal systems:The Eastern Route through the course of the Grand Canal; The Central Route from the upper reaches of Han River via the Grand Aqueduct to Beijing and Tianjin; The Western Route which goes from three tributaries of Yangtze River near the Bayankala Mountain to provinces like Qinghai, Gansu, Shaanxi, Shanxi, Inner Mongolia and Ningxia.
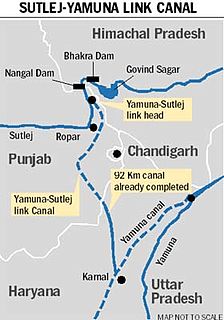 W
WSatluj Yamuna Link Canal or SYL as it is popularly known, is an under-construction 214-kilometer (133 mi) long canal in India to connect the Sutlej and Yamuna rivers. However, the proposal met obstacles and was referred to the Supreme Court of India. It defines river water sharing between the states of Punjab and Haryana. Captain Abhimanyu, Finance Minister of Haryana, while presenting the Government of Haryana 2018-19 budget in March 2018 announced that INR 100 crore funds had been allocated for completion of the construction of SYL.
 W
WThe Sykia Dam is a mostly constructed but unused earth-filled embankment dam on the Acheloos River along the border of Karditsa and Arta, Greece. The 170 m (560 ft) tall dam is part of the Acheloos River Diversion which is intended to divert a portion of the Acheloos west to irrigate 240,000–380,000 ha in the Thessaly plains. The project includes the Sykia, Messochora, Mouzaki and Pyli Dams along with a 17.4 km (10.8 mi) long channel.
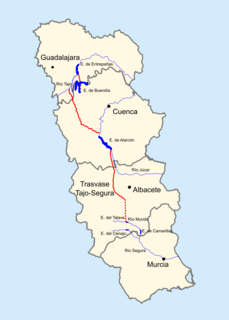 W
WThe Tagus-Segura Water Transfer is one of the largest works of hydraulic engineering ever produced in Spain. Water from the Tagus River is channeled through this transfer system from the reservoirs of Entrepeñas and Buendía into the Talave Reservoir on the Mundo River, a tributary of the Segura River.
 W
WThe Tana-Beles interbasin water transfer takes water from Lake Tana in Ethiopia and delivers it to the Beles River via the Tana Beles hydroelectric power plant. The water downstream is also used for irrigation..
 W
WThe Telugu Ganga project is a joint water supply scheme implemented in 1980s by the then Andhra Pradesh chief minister N.T.Ramarao and Tamilnadu Chief minister M. G. Ramachandran to provide drinking water to Chennai city in Tamil Nadu. It is also known as the Krishna Water Supply Project, since the source of the water is the Krishna river in erstwhile Andhra Pradesh. Water is drawn from the Srisailam reservoir and diverted towards Chennai through a series of inter-linked canals, over a distance of about 406 kilometres (252 mi), before it reaches the destination at the Poondi reservoir near Chennai. The main checkpoints en route include the Somasila reservoir in Penna River valley, the Kandaleru reservoir, the 'Zero Point' near Uthukkottai where the water enters Tamil Nadu territory and finally, the Poondi reservoir, also known as Satyamurthy Sagar. From Poondi, water is distributed through a system of link-canals to other storage reservoirs located at Red Hills, Sholavaram and Chembarambakkam.
 W
WToorourrong Reservoir is a small water supply reservoir located on the southern slopes of the Great Dividing Range approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. The reservoir is formed by the Toorourrong Dam across the Plenty River, and an interbasin transfer. The dam is operated by Melbourne Water and the reservoir forms part of the Melbourne water supply system. Water from the Toorourrong Reservoir flows by aqueduct to the Yan Yean Reservoir.
 W
WThe Transfer of the São Francisco River is a large-scale interbasin transfer to the dry sertão in the four northeastern states of Ceara, Rio Grande do Norte, Paraiba and Pernambuco in Brazil. The project, which was given the green light to go ahead by Brazil's government in 2005, is estimated to cost US$2 billion and is expected to improve the lives of 12m people. After legal challenges were brought against the project, the Supreme Court allowed it to go ahead in December 2007.
 W
WThe Yuba–Bear Hydroelectric Project is a complex hydroelectric scheme in the northern Sierra Nevada in California, tapping the upper Yuba River and Bear River drainage basins. The project area encompasses approximately 400 square miles (1,000 km2) in Nevada, Placer, and Sierra Counties. Owned by the Nevada Irrigation District, it consists of 16 storage dams plus numerous diversion and regulating dams, and four generating stations producing 425 million kilowatt hours of electricity each year. The Yuba–Bear Hydroelectric Project consists of the Bowman development, Dutch Flat No. 2 development, Chicago Park development, and Rollins development.