 W
WMexico shares international borders with three nations:To the north the United States–Mexico border, which extends for a length of 3,141 kilometres (1,952 mi) through the states of Baja california, Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León and Tamaulipas. To the southeast, the Belize–Mexico border, 251 kilometres (156 mi) long, limiting the states of Quintana Roo and Campeche and almost exclusively following the course of the Río Hondo. Also to the southeast, the Guatemala–Mexico border, which measures 871 kilometres (541 mi) and touches the states of Campeche, Tabasco and Chiapas, and includes stretches of the Río Usumacinta, Río Salinas and Río Suchiate.
 W
WThe 28th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 28 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Africa, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America and the Atlantic Ocean.
 W
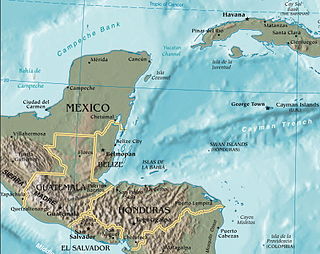
WThe Belize–Mexico border is an international border between Belize and Mexico. It is 250 km (160 mi) long and almost exclusively follows the course of the Hondo River. It separates Belize from the Mexican states of Quintana Roo and Campeche.
 W
WThe Guatemala–Mexico border is the international border between Guatemala and Mexico. The border measures 871 km (541 mi) and runs between north and west Guatemala and the Mexican states of Campeche, Tabasco and Chiapas. The border includes stretches of the Usumacinta River, the Salinas River, and the Suchiate River. There is no continuous wall on the border, although there are sections of fence near populated areas and official border crossings.
 W
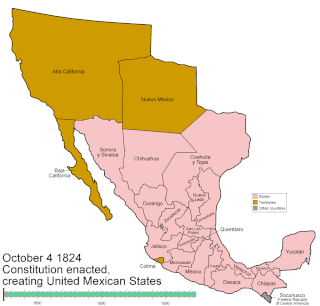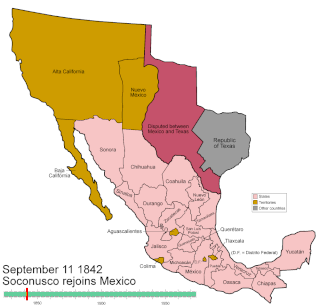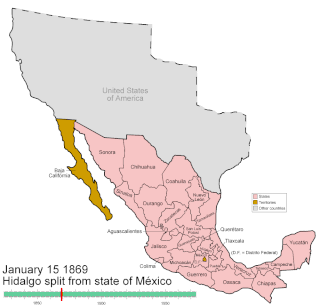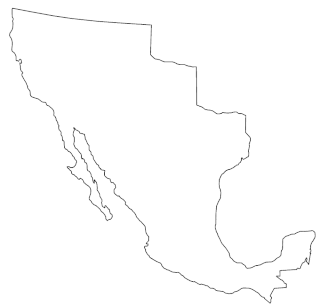
WMexico has experienced many changes in territorial organization during its history as an independent state. The territorial boundaries of Mexico were affected by presidential and imperial decrees. One such decree was the Law of Bases for the Convocation of the Constituent Congress to the Constitutive Act of the Mexican Federation, which determined the national land area as the result of integration of the jurisdictions that corresponded to New Spain, the Captaincy General of Yucatán, the Captaincy General of Guatemala and the autonomous Kingdoms of East and West. The decree resulted in the independence from Spain.
 W
WThe Mexico–United States border is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border traverses a variety of terrains, ranging from urban areas to deserts. The Mexico–United States border is the most frequently crossed border in the world, with approximately 350 million documented crossings annually. It is the tenth-longest border between two countries in the world.
 W
WThe Yucatán Channel or Straits of Yucatán is a strait between Mexico and Cuba. It connects the Yucatán Basin of the Caribbean Sea with the Gulf of Mexico. It is just over 200 kilometres (120 mi) wide and nearly 2,800 metres (9,200 ft) deep at its deepest point near the coast of Cuba.